Google Link Building Ethics Every Website Owner Should Know
Key Takeaways Modern link building has shifted from engineering links to *earning* them — Google now rewards genuine authority signals over manufactured tactics. Relevance and trust matter far more than raw link quantity; a few contextually aligned links from...

Key Takeaways
Modern link building has shifted from engineering links to *earning* them — Google now rewards genuine authority signals over manufactured tactics. Relevance and trust matter far more than raw link quantity; a few contextually aligned links from authoritative sites can outperform hundreds of low-quality backlinks. Google’s AI systems, including SpamBrain, are highly effective at ignoring or penalizing manipulative tactics such as PBNs, link farms, over-optimized anchors, and scaled content abuse. Ethical link building relies on two pillars: creating link-worthy assets (research, tools, guides) and running highly personalized outreach that delivers real value. Ongoing profile management — monitoring lost links, auditing toxic links, and avoiding excessive exchanges or untagged paid placements — is essential for long-term rankings and risk reduction.Too Busy to Read? Listen to the Deep Dive
At Stan Ventures, we’ve recovered dozens of sites from devastating penalties and built authoritative backlink profiles from the ground up. The common thread isn’t a secret tactic; it’s a fundamental shift in mindset.
For years, backlinks have been a foundational pillar of search engine visibility especially on Google. However, the link building landscape has fundamentally shifted from a game of volume to a discipline of earning trust.
Google’s algorithms have evolved, becoming incredibly adept at distinguishing between authentic endorsements and manipulative link schemes.
This guide provides the clear, authoritative framework we use for building a high-quality backlink profile that aligns with Google’s policies, focusing on sustainable, long-term success.
Free SEO Audit: Uncover Hidden SEO Opportunities Before Your Competitors Do
Gain early access to a tailored SEO audit that reveals untapped SEO opportunities and gaps in your website.

The core philosophy of this guide is simple: modern link building is a byproduct of creating genuine value and fostering real relationships.
The following sections will deconstruct what makes a link valuable in 2026, identify the dangerous shortcuts that can lead to penalties, and provide an actionable playbook for earning the kinds of links that build lasting authority and drive meaningful growth.
The Foundational Mindset: Earning Links, Not Engineering Them
Adopting a “user-first” mentality is the most critical strategic decision you can make in modern SEO. This isn’t a limitation; it is the most durable competitive advantage.
By aligning your goals directly with Google’s mission to reward helpful, reliable content, you build a foundation that is resilient to algorithm updates and focused on what truly matters: serving your audience.
This mindset shifts the focus from chasing metrics to creating assets that deserve to be cited.
The “Quality Over Quantity” Mandate
The era of amassing backlinks for the sake of high counts is definitively over. Today, a handful of backlinks from authoritative, topically relevant websites are exponentially more valuable than hundreds or even thousands of low-quality links. Quality always trumps quantity.
Consider this real-world example: our CBD SEO service page secured a top-three ranking for its target keyword with just 6 backlinks. The secret to its success was not volume, but the authority of the sources.

Three of those links came from highly reputable sites with a Domain Rating (DR) of 30+ or higher.
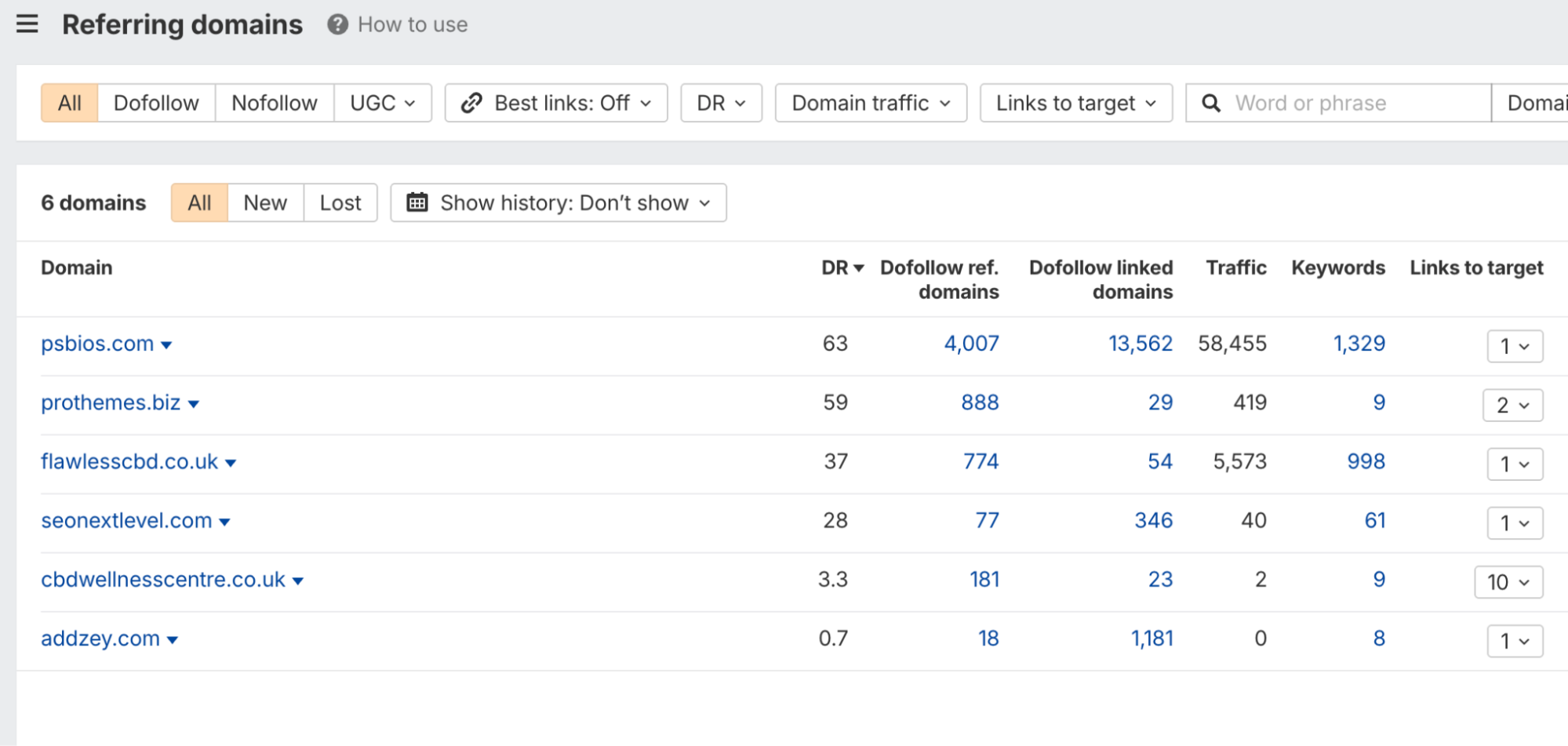
This demonstrates that Google prioritizes the trust and relevance of the linking domain far more than the total number of links pointing to a page.
The Litmus Test: The “User-First” Principle
Before pursuing any link-building opportunity, apply this critical litmus test: “Would this link exist if search engines didn’t?”
If a link’s sole purpose is to manipulate rankings rather than to genuinely help a human reader by citing a source, providing additional context, or pointing to a useful resource, it is an unnatural link.
These are precisely the types of links that Google’s systems are designed to identify and devalue. An authentic link serves the user first and the search engine second.
Understanding Google’s AI-Driven Detection
Google’s AI-powered systems, most notably SpamBrain, have become remarkably effective at identifying and neutralizing unnatural linking patterns.
These systems can analyze links at a massive scale, rendering outdated, black-hat shortcuts like automated link blasts and Private Blog Networks (PBNs) not only risky but largely a waste of time and resources.
Disavowing links can clean up the damage from these now-obsolete tactics. However, Google’s algorithm is now sophisticated enough to simply ignore these links, meaning you get all of the risk with none of the reward.
In fact, we have been noticing in Stan Ventures that hundreds of low quality links were being built to almost all of our service, blogs and news pages. Though disavowing them was considered as the option in the first place, we decided not to.

And when we checked the external link profile in our Google Search console these links didn’t even exist. That proves how smart Google’s algorithms are in detecting such links which are totally out of the control of the webmaster.
This foundational philosophy is the key to building a backlink profile that stands the test of time. Now, let’s deconstruct the specific attributes that make a link valuable in this new environment.
Deconstructing a High-Value Backlink: The Anatomy of Authority
The single biggest mistake we see new clients make is chasing high DR scores. It’s a vanity metric that can lead you to acquire worthless, or even harmful, links.
While scores like Domain Authority (DA) or Domain Rating (DR) offer a quick snapshot, they don’t tell the whole story and can be easily manipulated.
A sophisticated understanding of a link’s qualitative attributes is essential for assessing its true impact on your rankings and brand authority.
Topical Relevance: The Cornerstone of Value
Topical relevance is the single most crucial factor in determining a backlink’s value. A link from a thematically aligned website acts as a strong signal to Google that your content is a credible resource on that subject.
Google assesses relevance by analyzing the context of the linking page, the text immediately surrounding the link, and the anchor text itself.
For a link to be considered relevant, the linking site doesn’t need to be in the exact same niche, but their audiences should overlap.
For example, a link from a content marketer’s blog to a website designer’s portfolio is a perfectly relevant exchange, as both share a target audience of business owners.
In the screenshot below, you can see Hubspot linking naturally to one of my blogs. Stan Ventures is not in the business of CRMs but still there is an audience overlap as both industries serve businesses with a website. This makes it an ideal backlink in the eyes of Google.
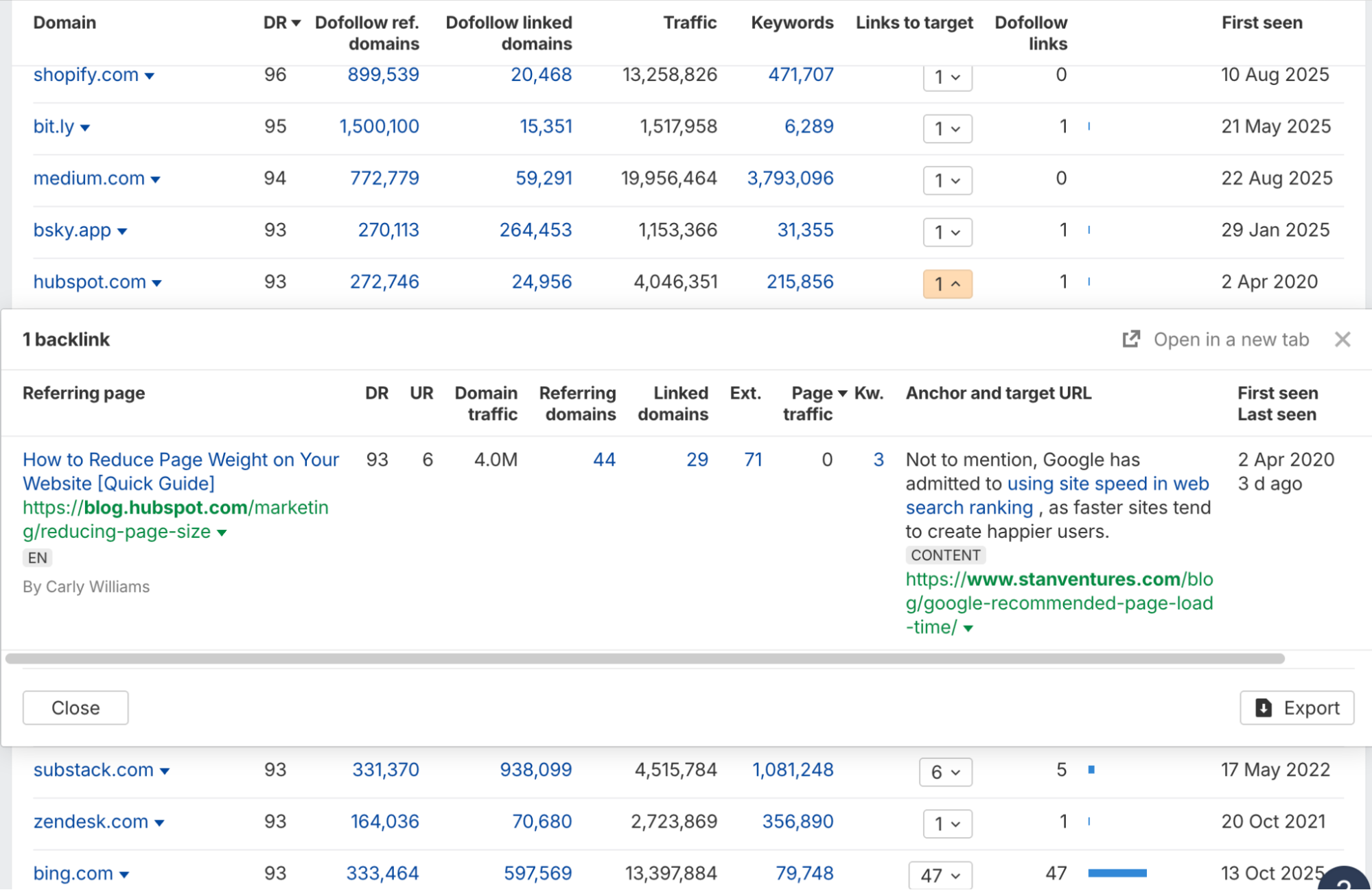
Conversely, a link from a pet grooming blog to a financial services firm would be contextually irrelevant and likely carry little to no weight.
Authority and Trust Beyond Simple Metrics
Once relevance is established, you must assess a site’s true authority. Move beyond third-party metrics and look for tangible signs of a healthy, trustworthy website.
Real Organic Traffic
A high DR/DA score is meaningless if the site has no actual visitors. A lack of organic traffic is a major red flag and often indicates that the site’s authority metrics have been artificially inflated.

For instance, the above site was found to have a DR of 84 but an estimated monthly traffic of 0 visitors. This disparity suggests the site is not a genuine authority and a link from it would be worthless.
Inbound/Outbound Link Ratio
The more external sites a page links out to, the less authority or “link juice” any single one of those links passes.
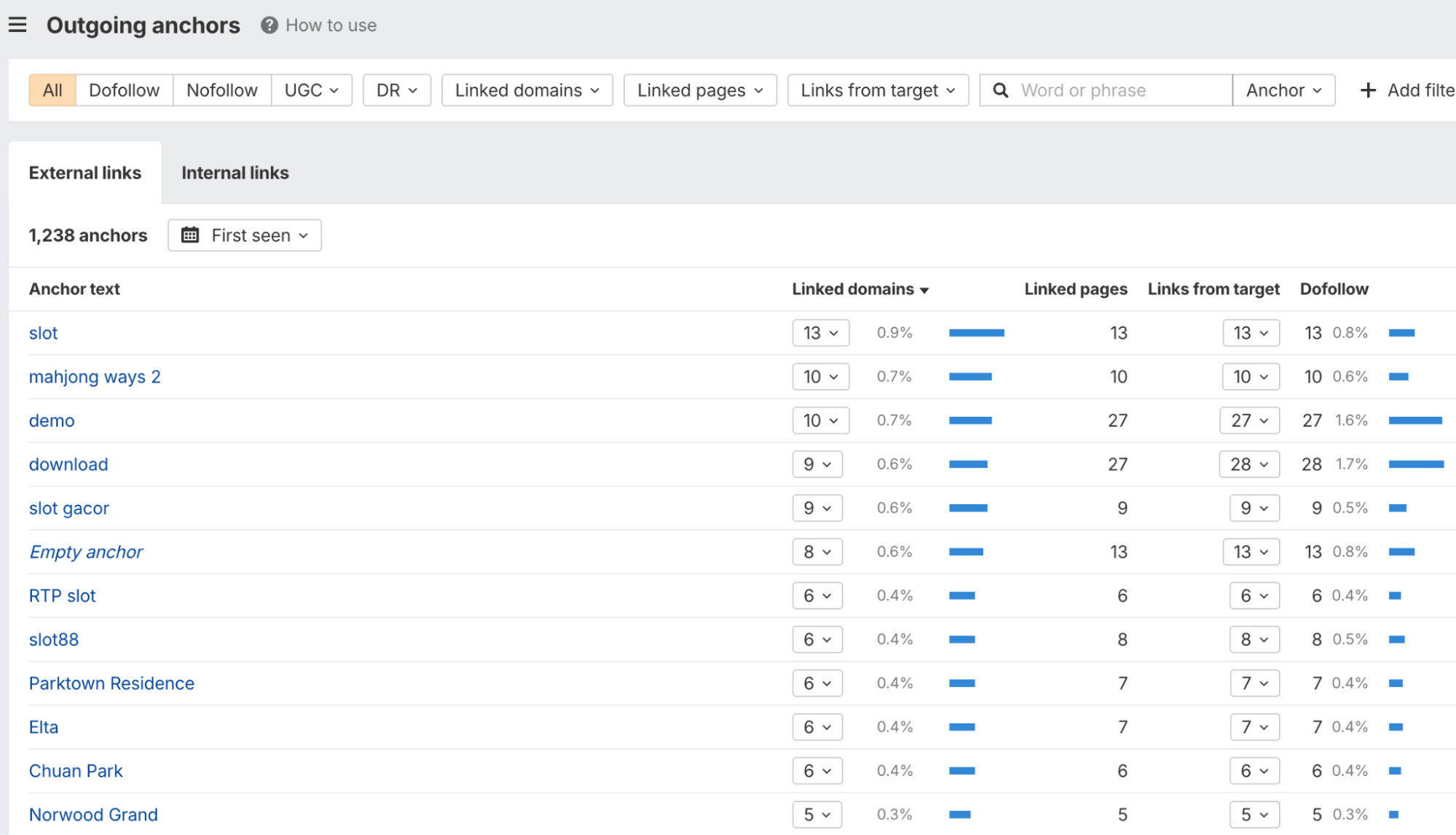
A page that links sparingly is vouching for those resources, whereas a page with hundreds of outbound links with spammy anchors is likely a low-quality directory or link farm.
Editorial Standards
Links from websites with clear editorial vetting processes—such as established news publications, industry journals, or well-curated blogs—are inherently more valuable. These sites don’t link out lightly; an editor or writer has made a conscious decision that your content adds value for their readers.
The Power of Placement and Context
Where a link is placed on a page and how it’s framed are powerful indicators of its quality. An editorially placed, contextual link is the gold standard. Use this checklist to evaluate any potential link placement:
In-Body and Contextual: Is the link placed within the main body of the content, not in a footer or sidebar? Explanatory Surroundings: Does the surrounding text explain why the linked resource is relevant and what a user will find if they click? Pass the ‘Removal Test’: If you remove the link, does the sentence still make perfect sense?Natural links are citations, not the structural foundation of the sentence itself.
Just as there are clear signals of a high-value link, there are explicit violations that can actively damage your site’s performance and reputation.
The Red Flags: Link Building Practices That Violate Google’s Spam Policies
This section serves as an essential guide to risk mitigation. Understanding and strictly avoiding practices that Google defines as “link spam” is non-negotiable for anyone serious about sustainable SEO success. Let me be blunt: these shortcuts are a direct path to an algorithmic penalty. We’ve seen it happen time and again.
Prohibited Link Schemes
Google’s spam policies are unambiguous about what constitutes a manipulative link scheme. The following practices are explicitly forbidden and should be avoided at all costs.
Buying or Selling Links for Ranking: This is the direct exchange of money, goods, or services for a backlink that passes ranking credit (i.e., a “dofollow” link). This is a core violation of Google’s guidelines. Private Blog Networks (PBNs): These are networks of interconnected websites created for the sole purpose of building links to a primary site and manipulating search rankings. Google is highly effective at identifying the footprints of PBNs and devaluing them entirely. Link Farms and Low-Quality Directories: These are websites that exist only to sell or list links. They typically lack quality content, have an abnormally high number of external links, and often link out to diverse and “dodgy” niches like gambling or adult content. Excessive Link Exchanges: This refers to large-scale “Link to me and I’ll link to you” schemes or the creation of dedicated partner pages exclusively for the purpose of cross-linking. This is different from natural, small-scale reciprocal linking between relevant businesses.Deceptive and Low-Value Tactics
Beyond overt schemes, several other common tactics are considered manipulative or low-value and can harm your backlink profile.
Over-Optimized Anchor
Text Stuffing your anchor text with exact-match keywords is a clear signal of an attempt to manipulate rankings. A natural backlink profile features a diverse range of anchor text types:
Branded: “Stan Ventures” Generic/Naked URL: “click here,” “www.stanventures.com” Partial-Match/Topic: “ethical link building guide”Here is an example:
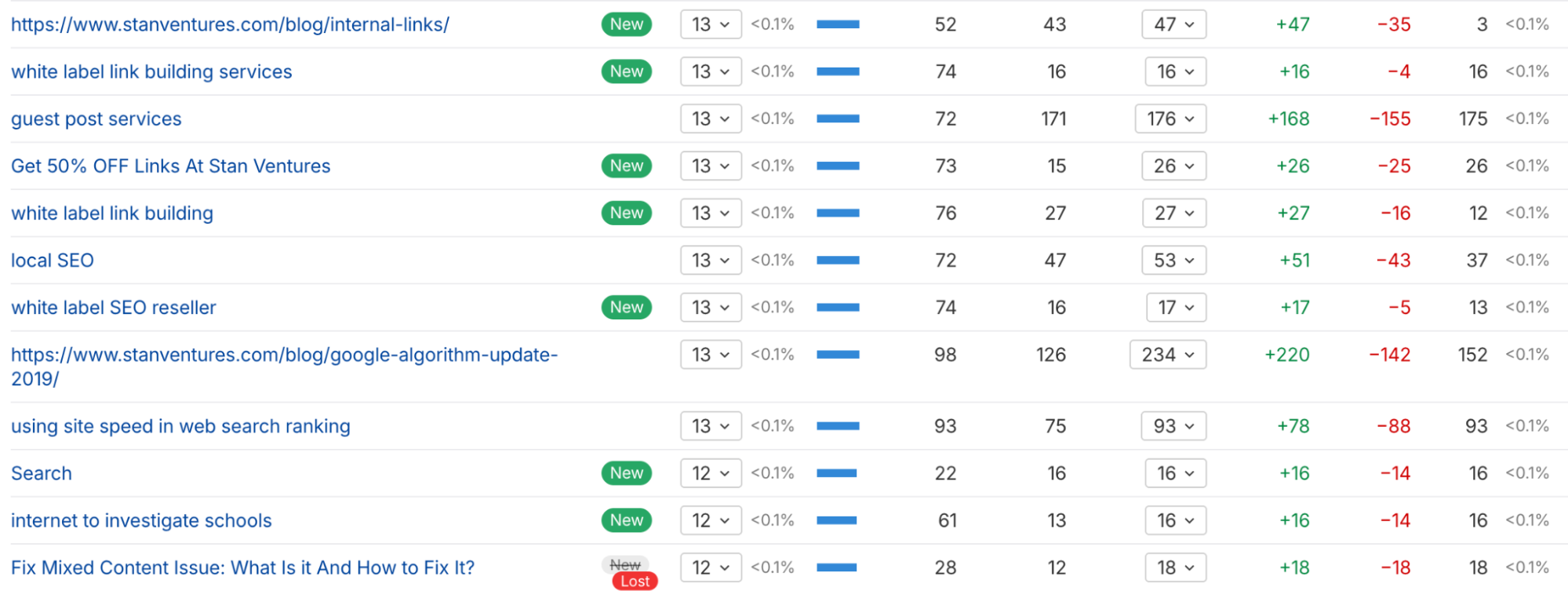
Spamming forums and blog comments: While participating in relevant online communities can be valuable, dropping spammy links in forum signatures or blog comments is ineffective.
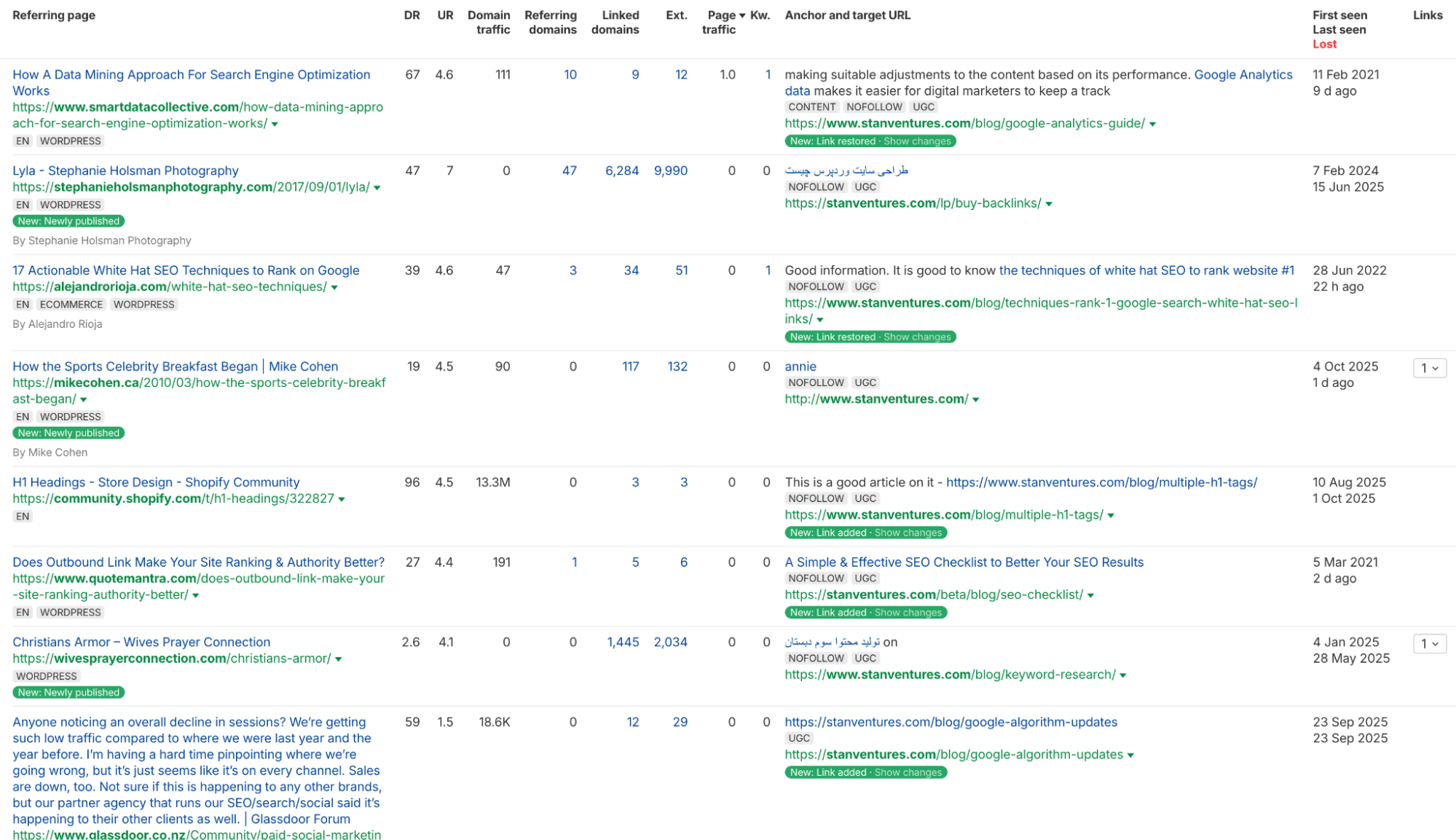
These links are almost always tagged with a rel=”UGC” (User-Generated Content) attribute, which signals to Google that they are not editorial endorsements and should carry limited, if any, SEO weight.
Scaled Content Abuse: This involves generating large volumes of unoriginal content, whether through AI tools, scraping content from other sites, or stitching together different sources for the primary purpose of creating pages to place links on. This practice provides no value to users and is a direct violation of Google’s spam policies.
Site Reputation Abuse: A more recent tactic, this involves publishing low-quality, third-party content on a reputable host site to exploit its strong ranking signals.
For example, a trusted educational institution might host a third-party page about payday loan reviews. Google is actively cracking down on this practice, which it considers deceptive.
Both of these last two tactics betray the “user-first” principle. They are attempts to exploit authority signals without creating genuine value, a shortcut Google’s systems are now explicitly designed to penalize.
Avoiding these red flags isn’t just about dodging penalties; it’s about reallocating your resources away from dead-end tactics and toward the sustainable, value-driven strategies we’ll cover next.
Every dollar spent on a PBN is a dollar you didn’t invest in a linkable asset that could earn links for years.
The White-Hat Playbook: Actionable Strategies for Earning Quality Links
Our approach to ethical link building is a two-part engine:
We first create high-value ‘linkable assets’ (Pillar 1) that act as link magnets.
Then, we amplify their discovery through professional outreach (Pillar 2), which in turn informs what assets to build next.
Pillar 1: Creating Link-Worthy Content Assets
You cannot earn links without having something worth linking to. Linkable assets are pieces of content that provide unique value, answer difficult questions, or offer utility that makes them a go-to resource in your industry.
Original Research and DataExamples: Industry benchmark reports, consumer surveys, proprietary data analyses, in-depth case studies.
Why it works: Journalists, bloggers, and writers need credible data to support their arguments and add authority to their work. When you publish unique statistics or findings, your content becomes a primary source that others will cite and link back to.
Free Tools and Interactive ResourcesExamples: Calculators, diagnostic tools, interactive checklists, templates.
Why it works: These assets provide ongoing, tangible utility. A user might return to a helpful calculator again and again, and other websites will link to it as a valuable resource for their own audience, driving both links and referral traffic.
Comprehensive “Skyscraper” GuidesThe process: Identify a relevant keyword, analyze the top-ranking content for that term, and then create a resource that is demonstrably better—more thorough, more up-to-date, better designed, and with more expert insights.
Why it works: This strategy is effective because you are creating the definitive resource on a topic, making it the most logical and compelling page for others to link to when discussing that subject.
High-Quality Visual ContentExamples: Infographics, data visualizations, charts, diagrams.
Why it works: Visual assets are highly shareable and easily embeddable. When another site uses your infographic to illustrate a point, they will almost always include a link back to your site as the original source, making it a powerful way to earn attribution links.
Pillar 2: Mastering Professional and Personalized Outreach
Even the best content won’t earn links if no one knows it exists. Professional outreach is the art of connecting your valuable asset with a relevant audience.
Research and Personalization: Generic, mass-emailed templates no longer work. Before reaching out, research the recipient and their website. Understand their content, their audience, and their recent posts. Mention something specific you liked to demonstrate genuine interest. Offer Value Upfront: Frame your outreach around providing value, not just asking for a link. You might suggest a collaboration, offer them exclusive access to your data before it’s published, or point out a broken link on their site that your resource could replace. Lead with how you can help them. Clarity and Brevity: Respect the recipient’s time. Get straight to the point, clearly explain why you’re reaching out, and make your request easy to understand and act upon.Proven Outreach Tactics and Email Templates
Certain outreach tactics have proven to be consistently effective because they are based on a mutually beneficial exchange of value.
| Tactic | Strategic Purpose & Application |
| Broken Link Building | Identify a broken link on a relevant site and offer your high-quality content as a replacement. This is a win-win, as it helps the site owner fix an error while earning you a link. |
| Unlinked Brand Mentions | Use tools to find where your brand is mentioned online without a link. Reaching out to request a link is often successful as they are already familiar with your brand. |
| Guest Blogging | Author a high-quality, relevant article for another site in your niche. This builds authority and provides a natural, contextual backlink opportunity. |
While these core strategies form the foundation of an ethical link-building program, success also requires navigating specific situations that come with their own set of rules.
Navigating the Nuances: Special Cases in Modern Link Building
Beyond the core strategies of asset creation and outreach, effective link building requires a nuanced understanding of the fine lines and specific rules Google applies to more complex situations. Misinterpreting the guidelines around reciprocal and paid links can inadvertently lead to policy violations.
Reciprocal Links: The Line Between Natural and Manipulative
The idea that all reciprocal linking is inherently bad is a common misconception. As clarified by Google’s John Mueller, some reciprocal links are perfectly natural and expected.
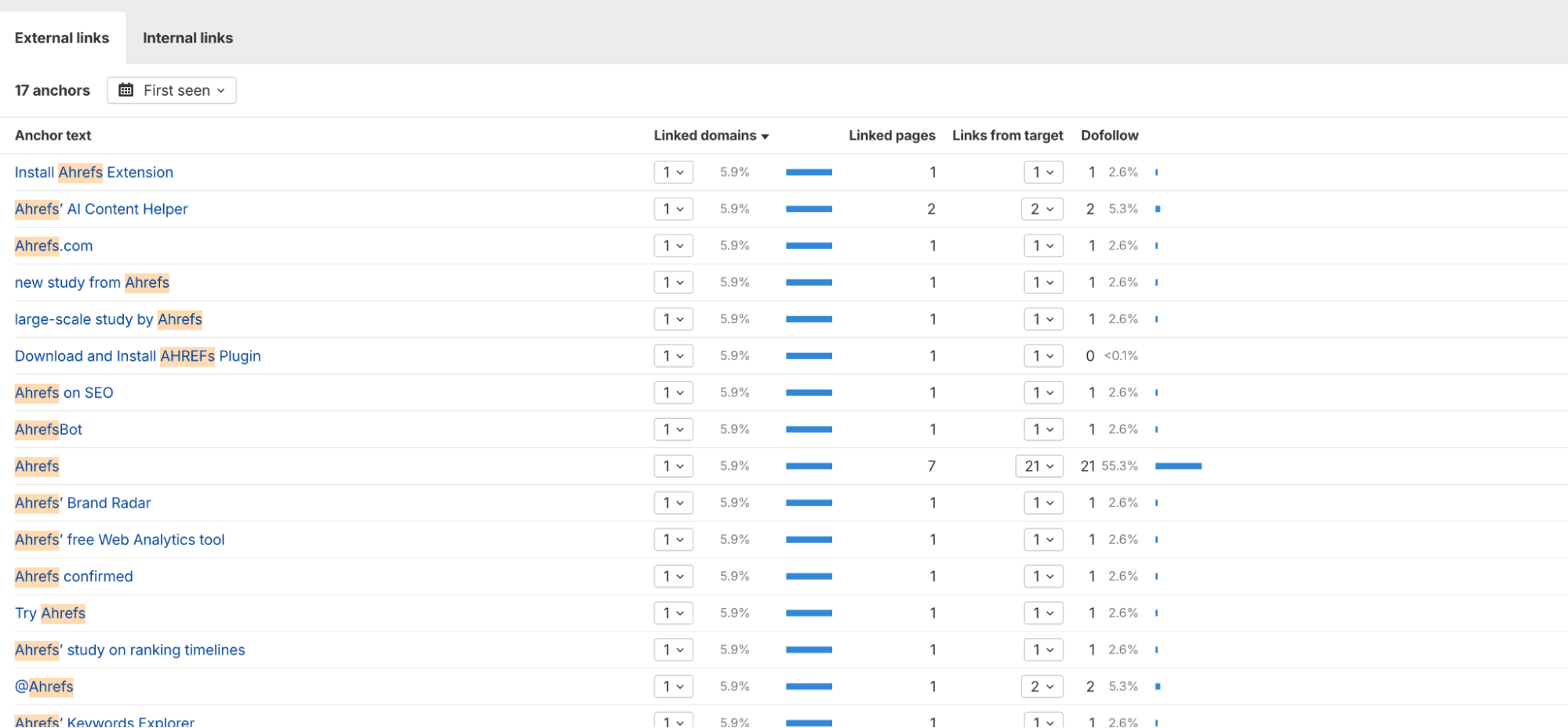
For example, it makes sense for a SEO agency like ours to link to a SEO tools provider like SEMRush or Ahrefs, or for a company to link to a news article that featured them. These links provide value and context for the user.
However, this differs significantly from “excessive” link exchanges. This manipulative tactic involves creating agreements or dedicated partner pages with the sole purpose of cross-linking to boost rankings. The key distinction is intent: a natural reciprocal link serves the user, whereas a manipulative one exists only to try and game search algorithms.
Paid Placements & Sponsored Content: The Rules of Transparency
Google’s official stance on paid links is clear and strict: buying or selling links that pass PageRank for the purpose of manipulating search rankings is a direct violation of its spam policies.
However, this does not mean all forms of paid promotion are forbidden. Using links for advertising, sponsorship, or public relations is a legitimate part of the digital economy. The crucial requirement is transparency.
Any link that has been paid for in any way—whether through money, free products, or services—must be qualified with a rel=”sponsored” or rel=”nofollow” attribute.
This tag tells Google not to pass any ranking credit through the link, effectively neutralizing its ability to influence search rankings while still allowing it to drive referral traffic and brand awareness.
Once a strong, ethical backlink profile is under construction, the work shifts from acquisition to ongoing maintenance and protection.
Proactive Profile Management: Monitoring, Reclamation, and Recovery
Link building is not a “set it and forget it” activity; it is an ongoing process of asset management. A healthy backlink profile requires constant vigilance. This includes proactively monitoring for valuable links that have been lost and auditing your profile for toxic links—often acquired by previous agencies or through negative SEO—that could be harming your site’s reputation and performance.
Combating Link Rot: Monitoring and Reclaiming Lost Links
“Link rot” is the natural decay of the web, where links disappear over time because pages are removed or sites are restructured. Data from Ahrefs reveals a startling reality: at least 66.5% of all backlinks are lost over a nine-year period.
That averages out to a decay rate of 7% per year.
Not tracking these lost links is a costly mistake. It’s essential to use a link monitoring tool to receive alerts when a backlink is removed. Once a lost link is detected, you can contact the website owner, politely inquire about the removal, and see if they would be willing to reinstate it. Reclaiming a lost link is often much easier than earning a new one.
Auditing and Disavowing Links
Sometimes, a backlink profile contains harmful links that actively suppress rankings. In these cases, a thorough audit and disavow process is necessary.
Google has been claiming that unless the links are found to be truly spammy and causing great damage to the reputation of the website, they don’t have to be disavowed as their systems are as efficient at ignoring low quality and irrelevant links.
The future of link building belongs to those who prioritize quality, relevance, and user value above all else. Based on our experience recovering and growing sites, we know that ethical, white-hat link building is not a series of shortcuts but a long-term strategy centered on creating exceptional content, building genuine relationships, and earning the trust of both users and search engines.
This approach is not just about adhering to guidelines; it’s about building a durable competitive advantage. By focusing on earning links rather than engineering them, you create a powerful SEO moat that can withstand algorithm updates, drive sustainable organic growth, and cement your website’s authority for years to come.
FAQs
1. What is the foundational mindset for effective and ethical link building in the modern SEO landscape?
The core philosophy for modern, ethical link building requires shifting the mindset from focusing on link volume to becoming a discipline of earning trust. A “user-first” mentality is the most critical strategic decision, as it aligns goals with Google’s mission to reward helpful, reliable content and focuses on creating assets that deserve to be cited. Google’s algorithms emphasize the importance of quality and relevance over quantity in link acquisition. Consequently, a few backlinks from authoritative, topically relevant websites are exponentially more valuable than thousands of low-quality or irrelevant links.
2. What is an editorial link, and why do they outperform other link types like guest posts?
An editorial link is a naturally earned link that is added by an editor or writer because the content enhances their piece, meaning it is not paid for, requested, or part of a link exchange. This type of link is highly favored because it is inherently reader-first and context-rich. Editorial links are structurally safer than scaled placements and align with Google’s spam policies, meaning they tend to survive algorithm updates and continue passing value long after campaign cycles end.
3. Which link-building practices are explicitly prohibited by Google and considered manipulative link schemes?
Google explicitly prohibits several manipulative practices that violate its spam policies, as they are intended to deceive users or manipulate search rankings. Prohibited link schemes include buying or selling links for ranking purposes (exchanging money, goods, or services for links that pass ranking credit). Other forbidden tactics are using Private Blog Networks (PBNs), excessive “Link to me and I’ll link to you” exchanges, using automated programs to create links, and building links from low-quality directories or link farms.
4. Are reciprocal links (link exchanges) always penalized by Google?
No, Google does not consider all reciprocal linking unnatural. It is often natural for two relevant sites to link to each other, such as local businesses linking to their neighbors or a site linking back to a news feature in which they were mentioned. However, excessive link exchanges or those done purely to manipulate search rankings are strictly prohibited and are considered link spam. The key distinction is intent: a natural reciprocal link serves the user, whereas a manipulative one exists only to try and game search algorithms.
5. What are the recommended practices for using anchor text to ensure a natural backlink profile?
Anchor text, the clickable text of a link, should be natural, descriptive, and relevant to the linked content, giving both users and Google a clear idea of the destination page’s topic. Best practices involve varying the anchors and prioritizing branded terms and partial/semantic match keywords. It is important to avoid over-optimizing with exact-match keywords, especially in an unnatural or repetitive way, as this is a red flag that search engines may view as an attempt to manipulate rankings. A natural backlink profile typically features a diverse mix, such as 40–60% branded/URL anchors and 20–40% partial/semantic anchors.
Dileep Thekkethil is the Director of Marketing at Stan Ventures and an SEMRush certified SEO expert. With over a decade of experience in digital marketing, Dileep has played a pivotal role in helping global brands and agencies enhance their online visibility. His work has been featured in leading industry platforms such as MarketingProfs, Search Engine Roundtable, and CMSWire, and his expert insights have been cited in Google Videos. Known for turning complex SEO strategies into actionable solutions, Dileep continues to be a trusted authority in the SEO community, sharing knowledge that drives meaningful results.

 ShanonG
ShanonG