What Is LLMs.txt? & Do You Need One?
Most site owners don’t realize how much of their content large language models (LLMs) already gather. ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini pull from publicly available pages unless you tell them otherwise. That’s where LLMs.txt for SEO comes into the picture....
Most site owners don’t realize how much of their content large language models (LLMs) already gather. ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini pull from publicly available pages unless you tell them otherwise. That’s where LLMs.txt for SEO comes into the picture.
LLMs.txt gives you a straightforward way to tell AI crawlers how your content can be used. It doesn’t change rankings, but it adds a layer of control over model training, something that wasn’t available before.
This matters as AI-generated answers take up more real estate in search results nowadays. Your content may feed those answers unless you explicitly opt out. LLMs.txt provides clear rules for what’s allowed and what isn’t, giving you leverage in a space that has grown quickly without much input from site owners.
Whether you allow or restrict access, having LLMs.txt in place sets a baseline for managing how your content appears in AI-driven experiences.
Key Takeaways
LLMs.txt lets you control how AI crawlers such as GPTBot, ClaudeBot, and Google-Extended use your content for model training. It functions similarly to robots.txt but focuses on AI data usage rather than traditional crawling and indexing. Major LLM providers are rapidly adopting LLMs.txt, creating a clearer standard for consent. Allowing access may strengthen your presence in AI-generated answers; blocking access protects proprietary material. LLMs.txt doesn’t impact rankings now, but it helps define your position in emerging AI search ecosystems.What is LLMs.txt?
LLMs.txt is a simple text file you place at the root of your domain to signal how AI crawlers can interact with your content. If robots.txt guides search engine crawlers, LLMs.txt guides LLM crawlers. Its goal is to define whether your public content becomes part of training datasets used by models such as GPT-4, Claude, or Gemini.

Here’s what the file controls:
Access permissions for each AI crawler Whether specific content can be used for training How your site participates in AI-generated answers Transparent documentation of your data-sharing rulesThis protocol exists because AI companies gather training data at scale. Your content may already appear in datasets unless you explicitly opt out. LLMs.txt adds a consent layer that didn’t previously exist, giving you a direct way to express boundaries.
OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google introduced support for LLMs.txt in response to rising concerns around ownership and unauthorized data use. Adoption isn’t universal yet, but momentum is growing quickly as more organizations ask for clarity around AI access.
LLMs.txt isn’t replacing robots.txt because the two files handle different responsibilities. Robots.txt manages crawling for search engines, while LLMs.txt manages training permissions for AI models. Together, they help you protect your content, define visibility rules, and prepare for a future where AI-driven search continues to expand.
Why is LLMs.txt a Priority Now?
Model developers gather massive datasets, and most of that comes from publicly accessible content. When OpenAI introduced GPTBot in 2023, it also introduced a pathway for websites to opt out. Google followed with Google-Extended, allowing publishers to restrict their content from AI training. Anthropic and others soon implemented similar mechanisms.
This shift matters for one reason: your content may already be part of the AI ecosystem unless you explicitly say otherwise.
LLMs.txt is becoming a standard because site owners want clarity. Until recently, there was no formal way to express whether your content could be repurposed inside model training pipelines. Now you can define that choice with a single file.
There’s another angle to this. Generative search tools increasingly rely on trained data to produce answers. If you block AI crawlers, your content may not appear in those outputs. If you allow access, your content becomes eligible for reference in conversational responses, something closely tied to how brands approach LLM SEO strategies.
Neither approach is right for everyone. Some companies want tighter content control. Others want stronger visibility in AI-driven areas. LLMs.txt helps you set a position instead of defaulting into one.
As AI-generated search becomes more prominent, the importance of LLMS.txt grows. You can adjust your directives over time, but having the file in place keeps you in control of how your content is used today.
How LLMs.txt Works
LLMs.txt is a plain text file located at the root of your domain. AI crawlers that support the protocol read it to understand which parts of your content they can use. You set the rules, upload the file once, and update it anytime your strategy evolves.
Where it Lives
LLMs.txt must be placed at:
yoursite.com/llms.txt
This mirrors the structure of robots.txt and keeps things predictable for crawlers. Every supported AI bot checks this exact location to find your rules. It must be in the root directory to work correctly, subfolders won’t register.
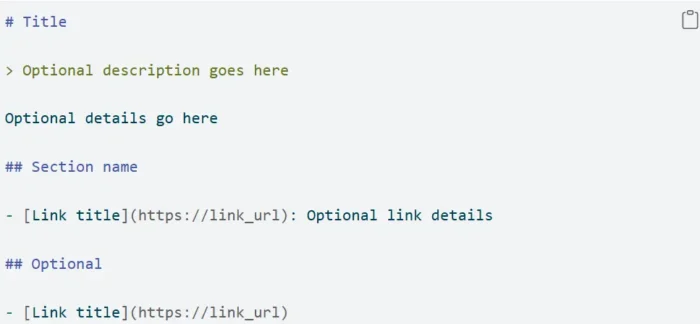
The file is intentionally public. Anyone can view it by navigating directly to the URL. This transparency allows AI companies, researchers, and compliance teams to see your stated preferences.
What You Can Control
Inside LLMs.txt, you specify allow or disallow directives for individual AI crawlers. Example:
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: Google-Extended
Allow: /
You can grant universal permissions or block everything. The file gives you fine-grained control over how your public content flows into AI training datasets.
Current LLMs That Respect It
Several major AI crawlers already check LLMs.txt automatically:
GPTBot (OpenAI) — supports opt-in and opt-out training rules Google-Extended — used for Google’s generative AI systems ClaudeBot (Anthropic) — honors site-level directives CCBot (Common Crawl) — contributes to datasets used by many models PerplexityBot — early adopter in 2024Support varies across the industry, but the direction is clear: more crawlers are aligning around LLMs.txt as a standardized method for training consent.
LLMs.txt vs Robots.txt: What’s the Difference?
Robots.txt and LLMs.txt serve complementary but distinct purposes.
Robots.txt controls how traditional search engine crawlers access and index your content. Its focus is SEO: discoverability, crawl budgets, and how pages appear in search results.

LLMs.txt, in contrast, governs how AI models may use your content for training. These directives tell model crawlers whether they can read, store, and learn from your pages.
Here’s how they differ:
Different crawlers: Googlebot and Bingbot follow robots.txt; GPTBot, ClaudeBot, and Google-Extended read LLMs.txt. Different outcomes: Robots.txt influences rankings and indexing. LLMs.txt influences how your content appears in generative AI systems. Different risks and rewards: Robots.txt affects search visibility. LLMs.txt affects brand exposure inside AI-generated answers — and your control over proprietary content.Both files are becoming foundational as search shifts toward blended AI and traditional results. You’ll likely need each one working together as AI-driven discovery expands.
Should You Use LLMs.txt for SEO?
LLMs.txt doesn’t provide a direct ranking benefit today. Search engines don’t interpret it for SEO purposes. Still, it influences how your content participates in generative results, and that matters.
Allowing AI crawlers gives models more context to work with, improving the odds that your content appears in synthesized answers. Blocking crawlers protects proprietary or sensitive content but removes you from those AI-based touchpoints.
Your approach depends on your goals. Brands focused on reach often allow access. Brands focused on exclusivity or IP protection typically restrict it.
LLMs.txt also pairs well with thoughtful LLM optimization work. Content structured for clarity, strong signals, and contextual relevance helps models interpret your material more accurately. LLMs.txt simply defines whether they’re allowed to learn from it.
“LLMs.txt doesn’t shift rankings today, but it sets early rules for how your content interacts with AI systems. Think of it like robots.txt in its early years: small now, foundational later.” explains Anna Holmquist, Senior SEO Manager at NP Digital.
Who Actually Needs LLMs.txt?
Some websites benefit more than others from adopting LLMs.txt early.
Content-heavy sitesPublishers, educators, and documentation libraries often prefer structure around how their content is reused by AI systems. Brands with proprietary material
If your revenue depends on premium reports, gated content, or specialized datasets, LLMs.txt offers a necessary layer of protection. SEOs planning for AI search
As generative results become more common, brands want control over how content feeds into those answer engines. LLMs.txt helps set boundaries while still supporting visibility. Industries with compliance requirements
Healthcare, finance, and legal organizations often need strict data-handling rules. Blocking AI crawlers becomes part of their governance approach.
LLMs.txt doesn’t lock you into a long-term decision. You can update it as AI search evolves.
How To Set Up an LLMs.txt File
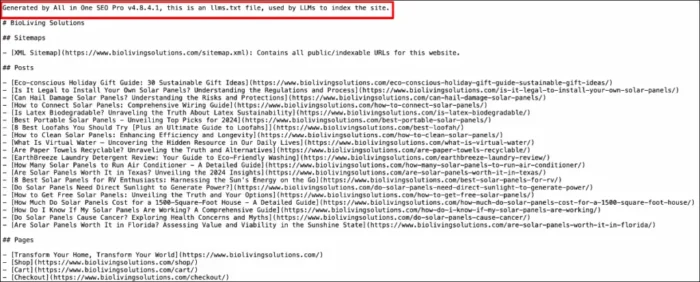
Setting up an LLMs.txt file is simple. Here’s the process. If you want assistance doing this, there are tools and generators that can assist.
1. Create the File
Open a plain text editor and create a new file called llms.txt.
Add a comment at the top for clarity:
# LLMS.txt — AI crawler access rules
2. Add Bot Directives
Define which crawlers can read and train on your content. For example:
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: Google-Extended
Allow: /
You can open or close access globally:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
or:
User-agent: *
Allow: /
3. Upload to Your Root Directory
Place the file at:
yoursite.com/llms.txt
This location is required for crawlers to detect it. Subfolders won’t work.
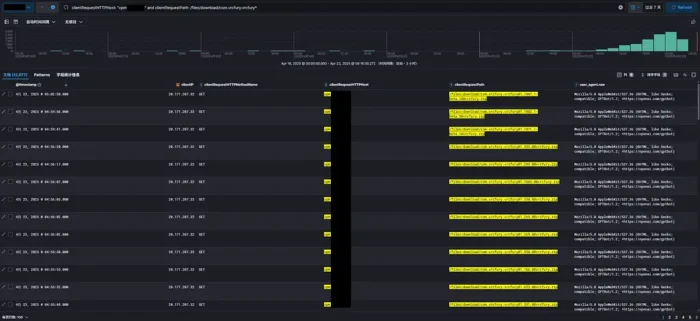
4. Monitor AI Crawler Activity
Check your server logs to confirm activity from:
GPTBot ClaudeBot Google-Extended PerplexityBot CCBotThis helps you verify whether your directives are working as expected.
FAQs
What is LLMs.txt?
It’s a file that tells AI crawlers whether they can train on your content. It’s similar to robots.txt but designed specifically for LLMs.
Does ChatGPT use LLMs.txt?
Yes. OpenAI’s GPTBot checks LLMs.txt and follows the rules you specify.
How do I create an LLMs.txt file?
Create a plain text file, add crawler rules, and upload it to your site’s root directory. Use the examples above to set your directives.
Conclusion
LLMs.txt gives publishers a way to define how their content interacts with AI training systems. As AI-generated search expands, having explicit rules helps protect your work while giving you control over how your brand appears inside model-generated answers.
This file pairs naturally with stronger LLM SEO strategies as you shape how your content is discovered in AI-driven environments. And if you’re already improving your content structure for model comprehension, LLMs.txt fits neatly beside ongoing LLM optimization efforts.
If you need help setting up LLMs.txt or planning for AI search visibility, my team at NP Digital can guide you.

 AbJimroe
AbJimroe 





























