A.I. takes center stage at HIMSS health conference
Experts say AI technology has "tremendous" potential solving big problems in health care
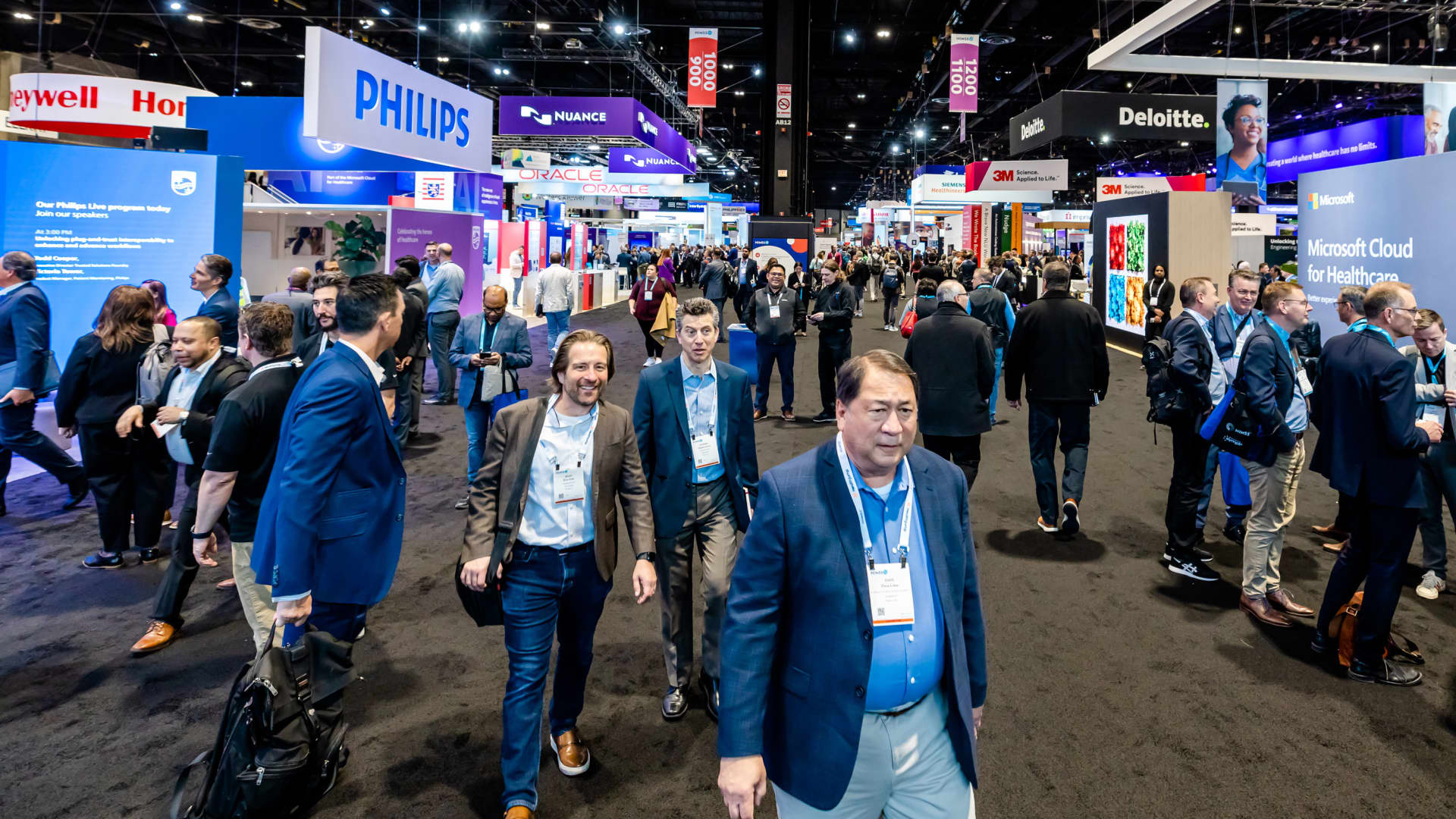

HIMSS conference attendees walk the exhibition floor
Source: HIMSS
Debates over artificial intelligence and its role in health care took center stage at the HIMSS Global Health Conference in Chicago this week, where more than 35,000 physicians, executives, engineers and health-care workers convened to discuss the latest advancements in health and technology.
Companies like Microsoft, Google and Amazon prominently advertised new health applications for AI on booths across a sprawling exhibition floor, and panels of experts answered questions about how the technology can be used to address industry-wide challenges like staffing shortages and physician burnout.
Many health-care organizations and companies have been using AI in various capacities for years, but a subset known as generative AI exploded into public consciousness late last year when Microsoft-backed OpenAI launched its viral new chatbot called ChatGPT. Generative AI refers to programs that can use fairly complicated prompts from end users to generate text or images.
Just as generative AI has captured the attention of the general public, it has also captivated the medical community.
AI was the focus of the HIMSS conference's opening keynote, and HIMSS CEO Hal Wolf prefaced the discussion by revealing that he had asked ChatGPT how to solve global healthcare challenges. The member-based organization called the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society, or HIMSS, puts on the conference each year.
Wolf posed the question to ChatGPT in jest, but David Rhew, Global Chief Medical Officer at Microsoft, told CNBC in an interview that generative AI could really be "transformative" for solving big problems in the health-care industry.
"The opportunity to apply these large language models and the artificial intelligence in clinical workflows is tremendous, and we have to do it responsibly," he said.
For Rhew, that means starting with "high-impact, low-risk" uses for the technology, like streamlining administrative tasks.
Developing diagnostic or directly patient-facing generative AI applications are higher risk since they pose significant regulatory questions for companies, academics and federal agencies like the Food and Drug Administration to work through. Rhew said to think of AI as if the health-care industry has just been introduced to a car, while none of the stop signs, traffic lights or roads have been created yet.
"We still have to figure out how to do this together," he said.
HIMSS CEO Hal Wolf speaks at the HIMSS conference
Source: HIMSS
But in the meantime, administrative or "back office" tasks require less regulatory oversight, and there is a real need for efficient solutions since clerical work is often burdensome for clinicians.
A study funded by the American Medical Association in 2016 found that for every hour a physician spent with a patient, they spent an additional two hours on administrative work. The study said that physicians also tend to spend another one to two hours doing clerical work outside of working hours.
Similarly, in 2017, the Journal of the Association of American Medical Colleges published a survey where respondents said around 24% of their working hours are spent on administrative tasks. More than two-thirds of the physicians surveyed reported that administrative responsibilities "negatively affect their ability to deliver high-quality care."
HIMSS attendees told CNBC they believe generative AI can help with these tasks.
Letting AI do the clerical work
On Monday, Microsoft announced an expanded partnership with Epic Systems, a health care software company that helps hospitals and other health systems store, share and access electronic health records. More than 160 million people use Epic's MyChart software, which provides patients with direct access to their health information and care team.
Epic's first application of the AI technology automatically generates draft responses to the messages that physicians receive from patients through MyChart. The physicians don't have to use the suggested draft at all, but it saves them time if they choose to edit or send it.
Seth Hain, senior vice president of R&D at Epic, told CNBC in an interview that AI could serve as an impactful hypothesis generation tool for physicians in the future. He said they will be able to ask patient-specific questions like "what do you think I should look at next in regard to this problem?"
Peter Lee, corporate vice president of research and incubations at Microsoft, told CNBC that an early look at Epic's AI developments brought tears to his eyes.
"It just blew me away," he said.
Microsoft's speech recognition subsidiary Nuance Communications also announced a clinical notes application called DAX Express ahead of HIMSS in March. DAX Express aims to help reduce clinician's administrative burdens by automatically drafting a clinical note within seconds after a patient visit.
In a live demo at HIMSS, Nuance previewed future projects and showcased DAX Express' capabilities, which were met with gasps and joyful exclamations from some of the physicians, nurses and health-care workers in the room.
More than 35,000 people attended the HIMSS conference in 2023
Source: HIMSS
Other companies are also working to use generative AI to reduce administrative burdens.
Amazon Web Services on Monday announced an expanded partnership with Philips, a Netherlands-based health technology company. AWS has already been supporting many of Philips' existing cloud-based and AI initiatives, like those that help radiologists analyze scans and medical images more quickly – even from their homes.
But Monday's announcement means Philips will also use AWS' generative AI technology to simplify its clinical workflows and advance its imaging capabilities even further.
"What's most exciting is the fact that we are approaching a precipice where we have this tipping point, where we make the right thing, the easy thing," Shez Partovi, Philips' chief innovation and strategy officer, told CNBC in an interview. "And right now, in most technology, the right thing is a lot of clicks away."
Partovi said all the small tasks that physicians have to complete are like "death by 1,000 cuts," so using AI to tease out administrative challenges can make a real impact on the quality of physicians' lives.
On Tuesday, 3M Health Information Systems also announced that it is also working with Amazon Web Services' machine learning and generative AI to help reduce physicians' administrative workload. 3M HIS supports a conversational AI platform used by more than 300,000 physicians, and the company said in a release that the AWS technology will make it easier for doctors to automate and complete accurate clinical notes in the electronic health record.
Similarly, Google Cloud announced a Claims Acceleration Suite last week that uses AI to streamline health insurance claims processing and prior authorization.
According to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, the current prior authorization process takes an average of 10 days. Google's AI will help alleviate some of that administrative burden for providers by converting the unstructured data that appears in images, PDFs or other health records into a more easily digestible, structured format.
"They actually require a human being to go in there and to take that data and rekey it into the system for review," Amy Waldron, director of global health plans strategy and solutions at Google Cloud said during a media briefing with reporters at HIMSS. "Which, to me, makes absolutely no sense given that someone has to take time to put all that rich data there, and we have AI that can unlock that value."
Generative AI has "tremendous" potential to improve administrative efficiency in healthcare, said Microsoft's David Rhew. But as healthcare and technology companies continue to make more sophisticated advancements, industry leaders, regulators and academics in the community will have to ensure that generative AI is equitable and does not cause harm to communities.
The technology is vulnerable to bias and discrimination if it is trained on health-care data that does not properly represent a patient population, which could ultimately lead to inadequate decision making or treatment plans.
As a result, Rhew said there is a collective responsibility to figure out how to deploy AI with care.
"It is a transformative technology," he said, "but we have to figure out how to do it responsibly."

 JaneWalter
JaneWalter