The ChatGPT Traffic Playbook: How to Track, Measure, and Grow
In this guide, you’ll learn what makes ChatGPT traffic unique, how to track it in your analytics, and strategies to increase both direct and indirect visits from this AI assistant. ChatGPT traffic works differently from regular search engine traffic....

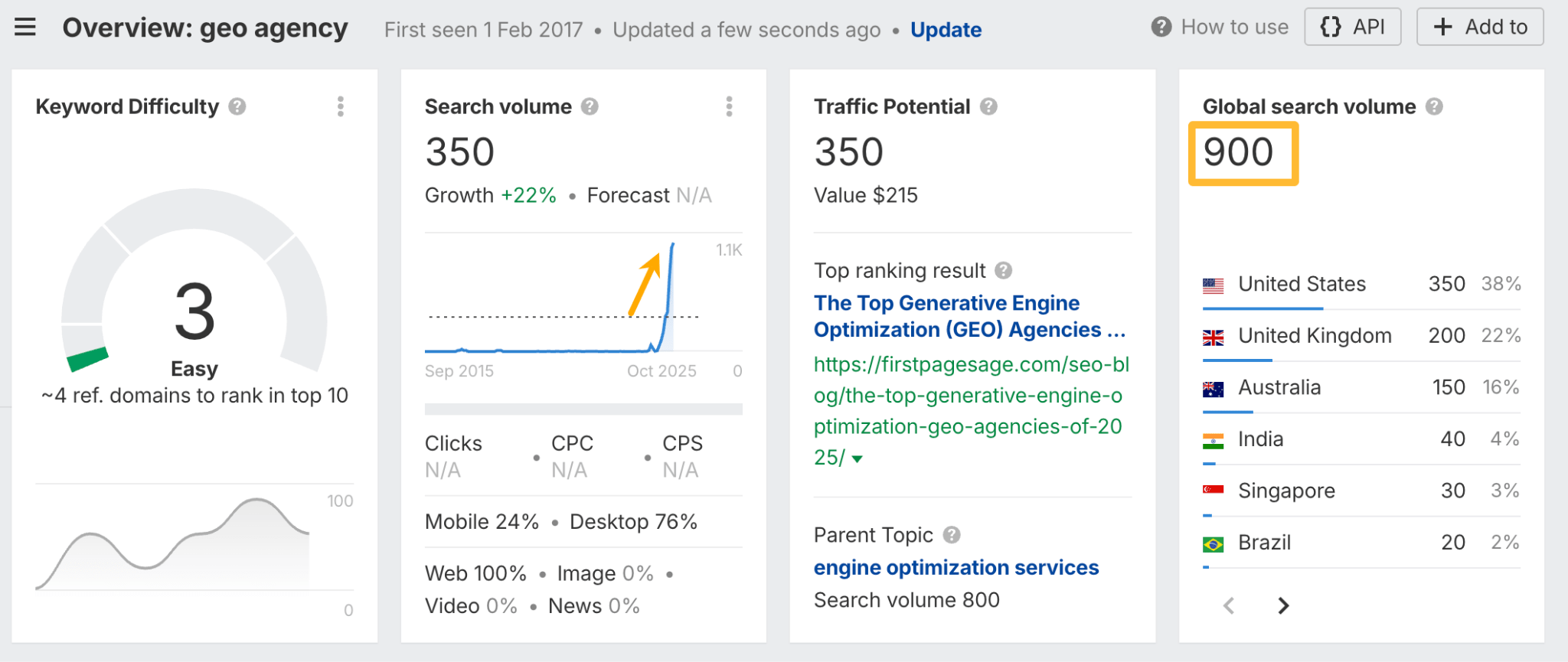
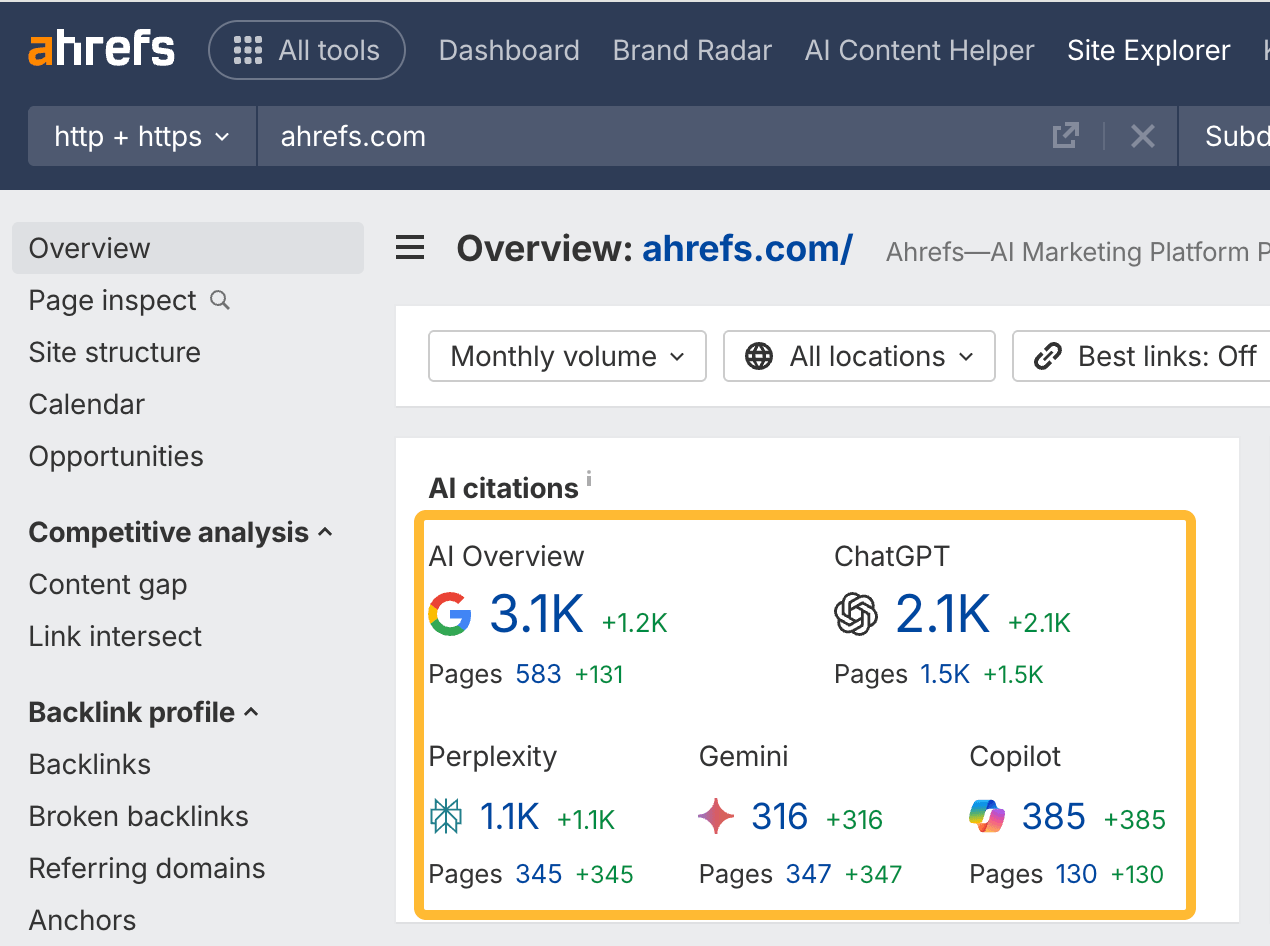
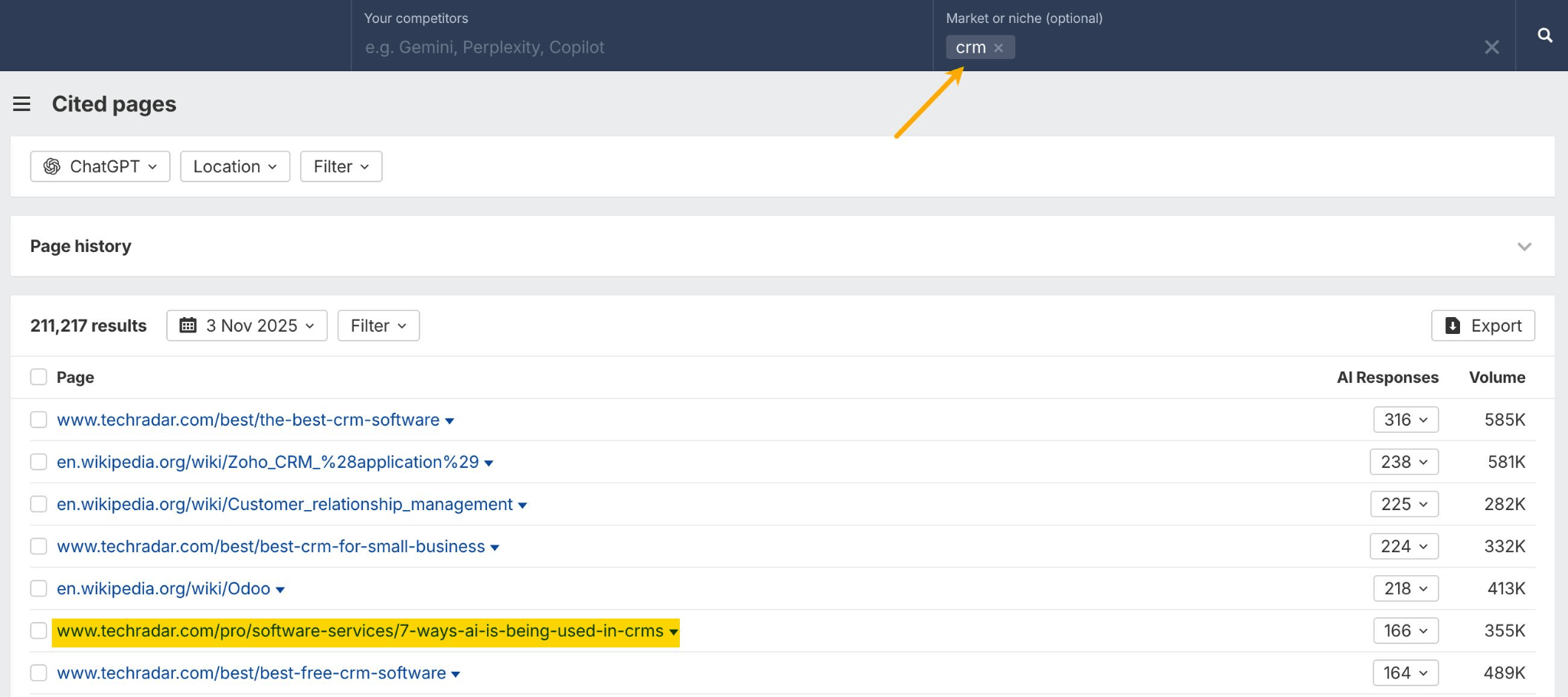
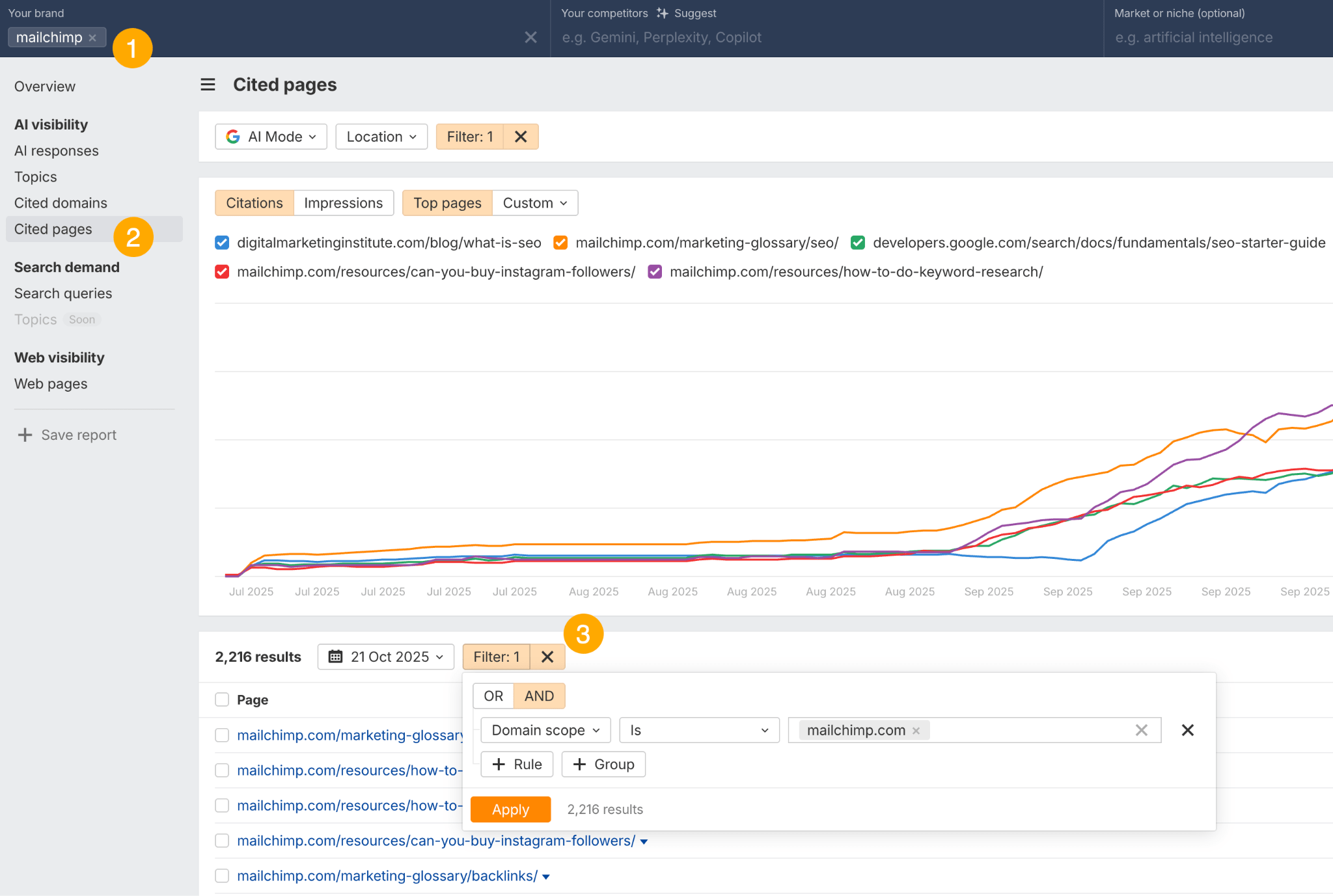
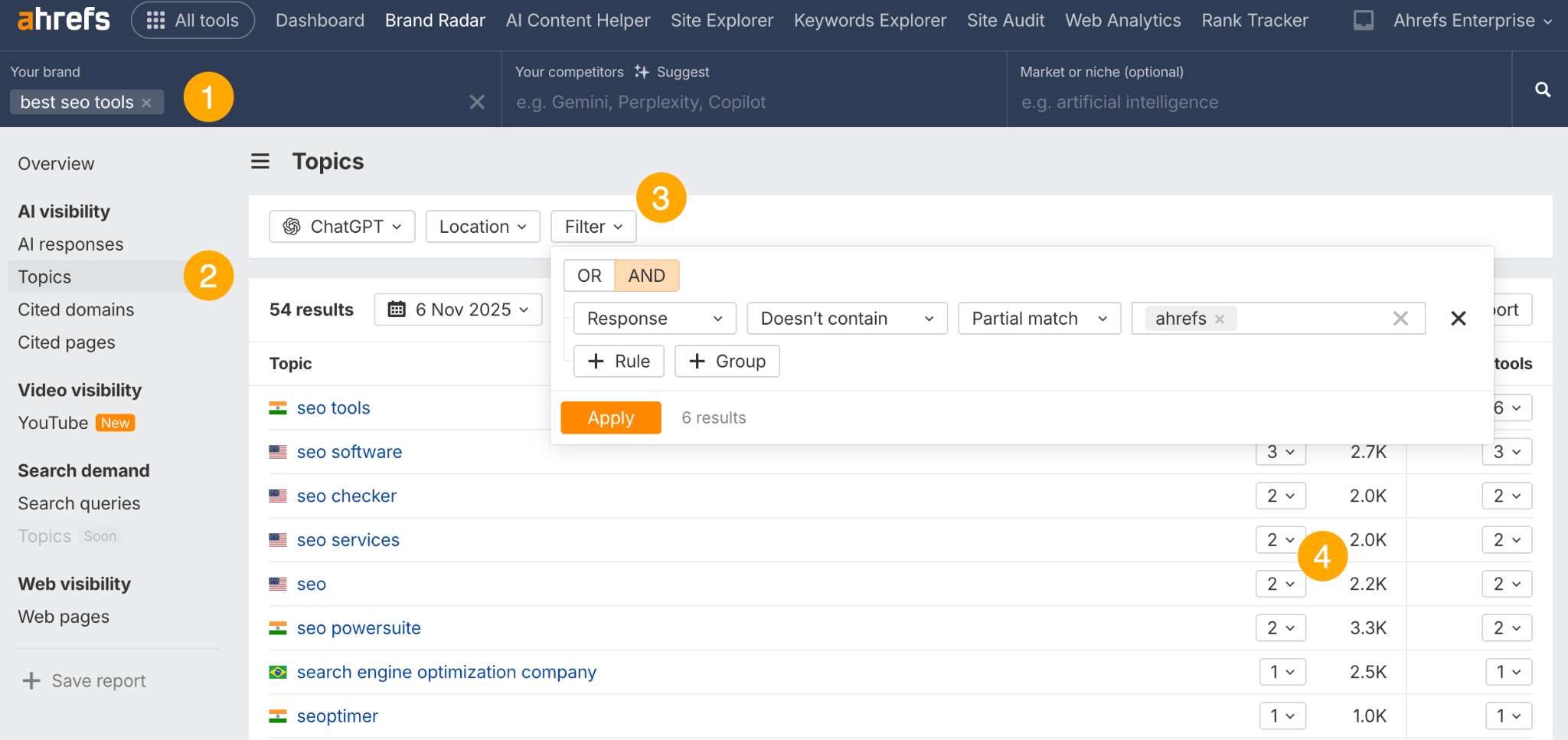
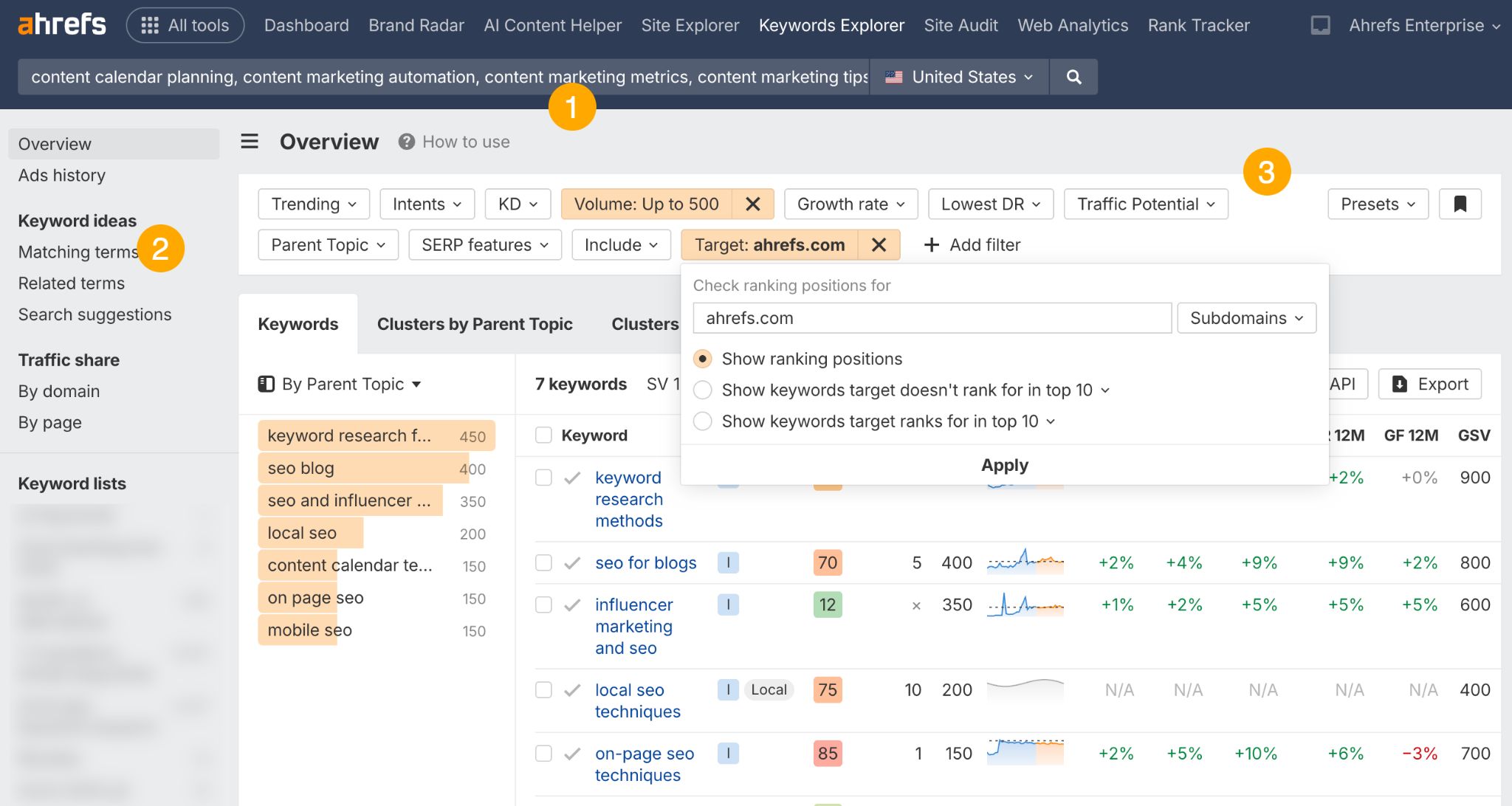
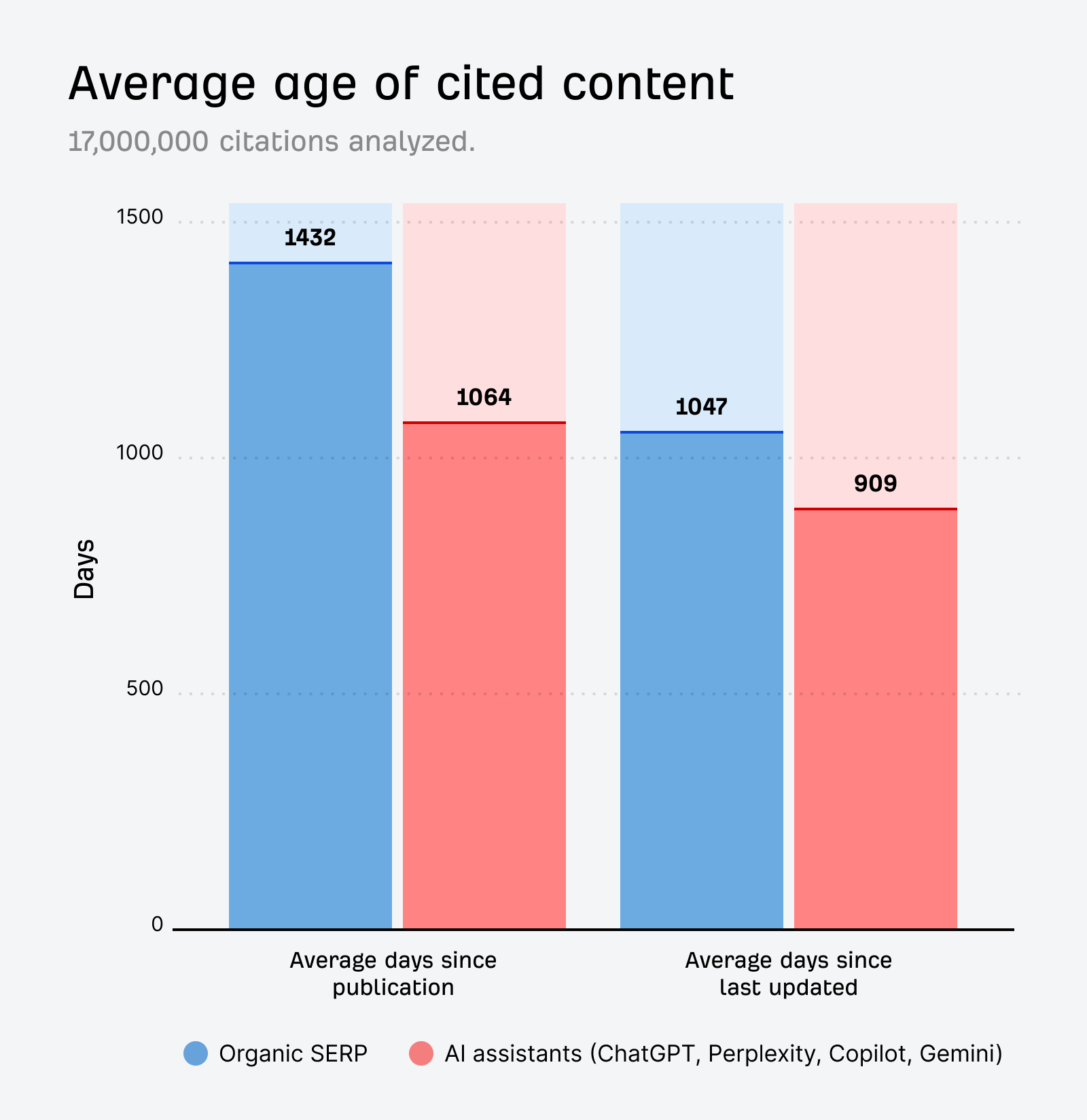
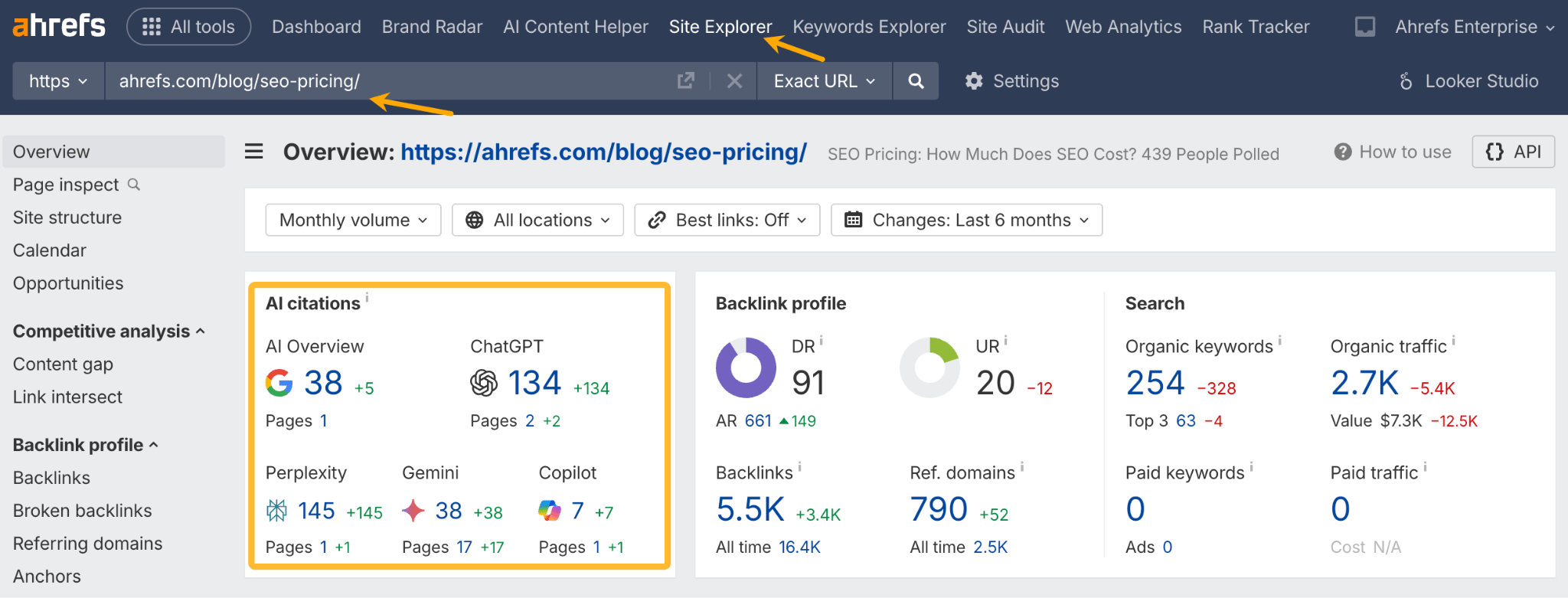
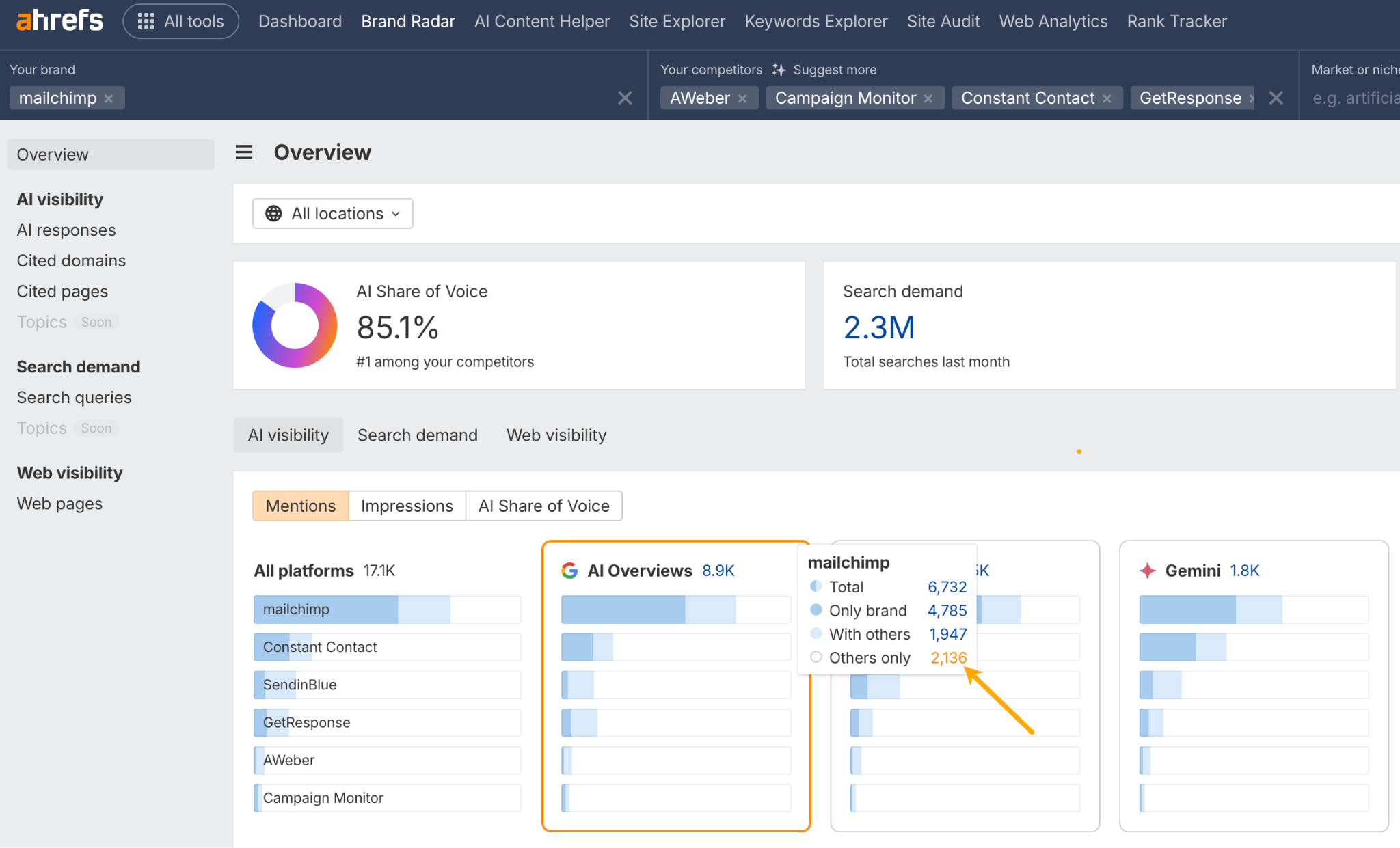
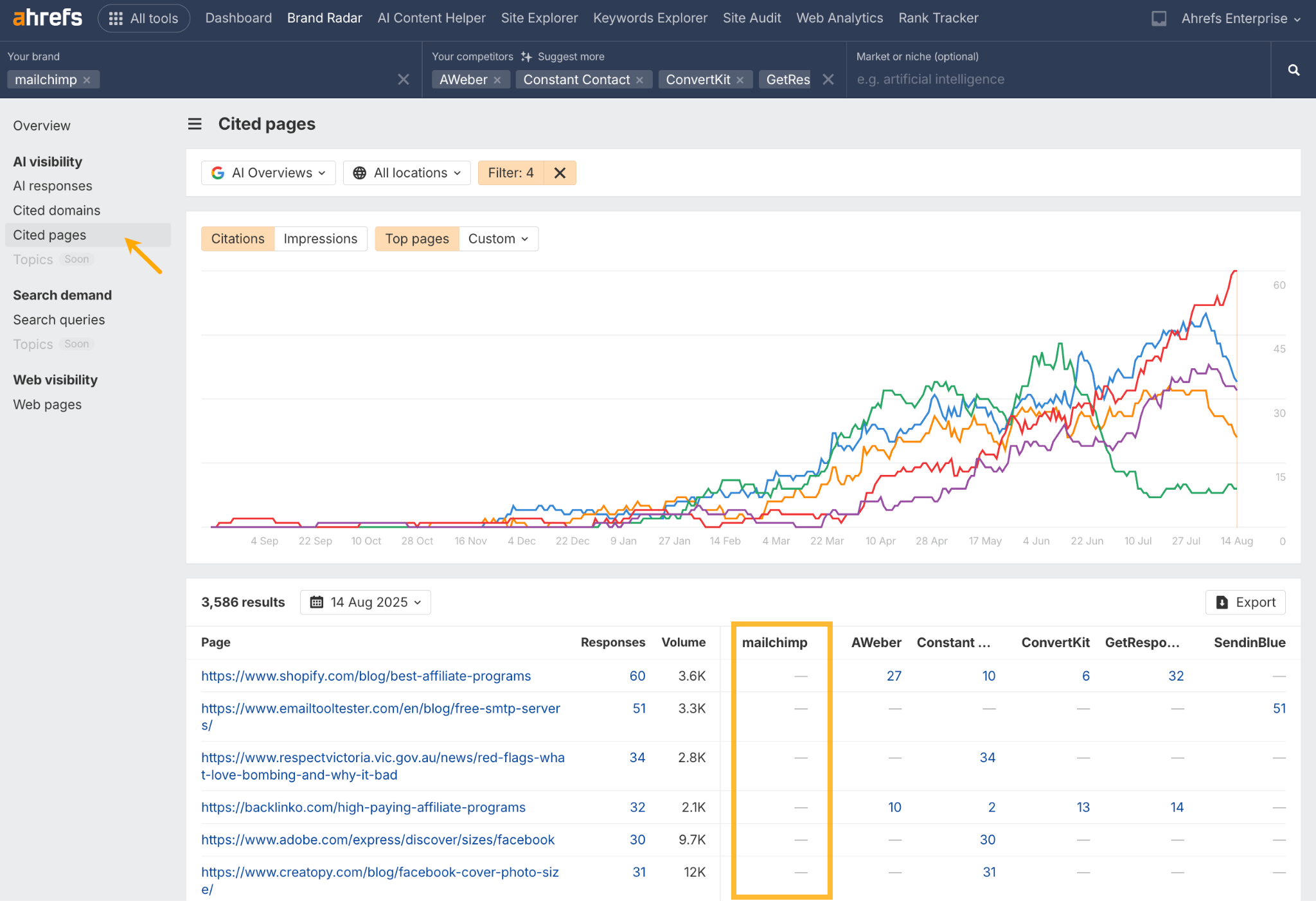
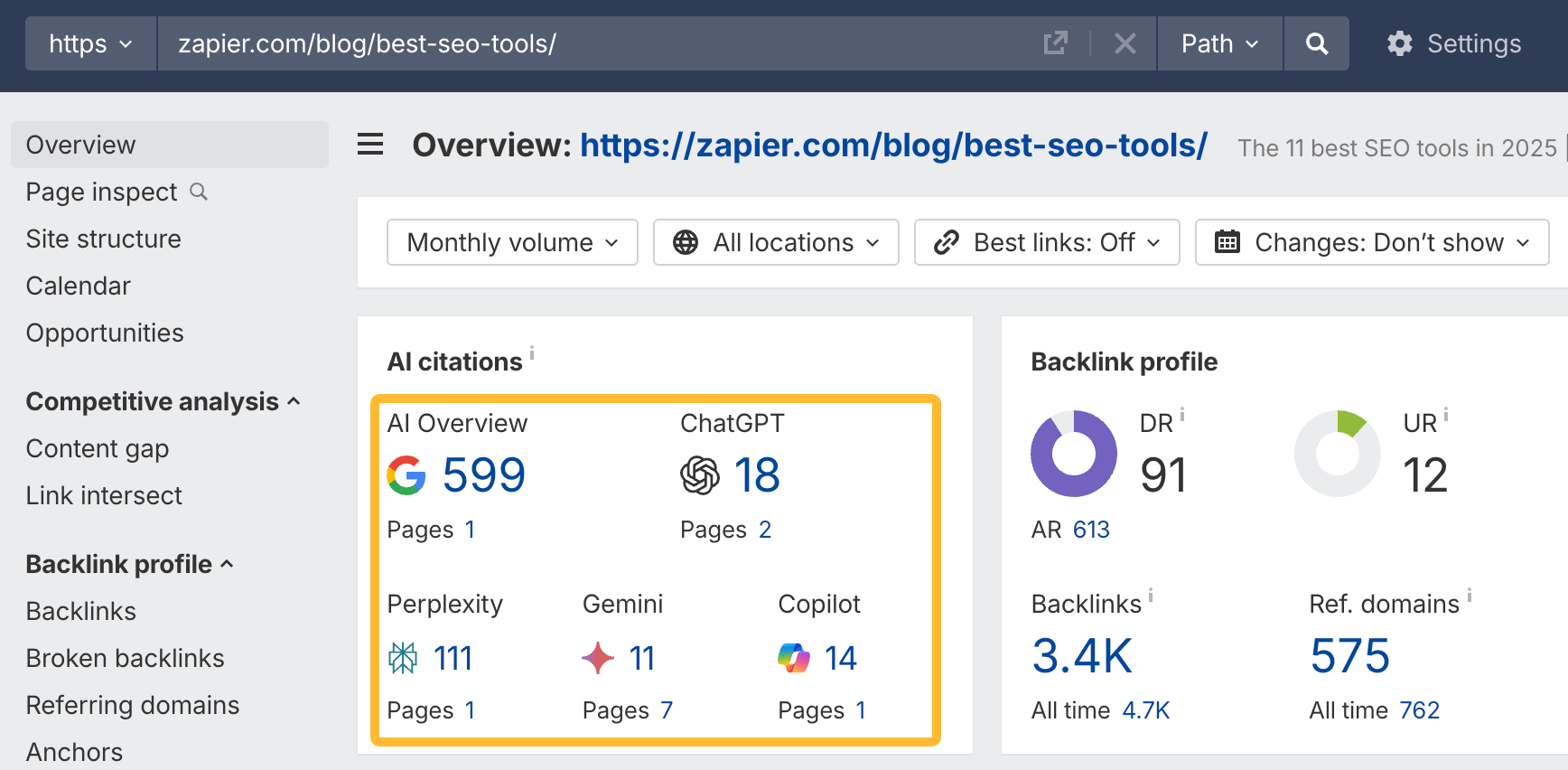
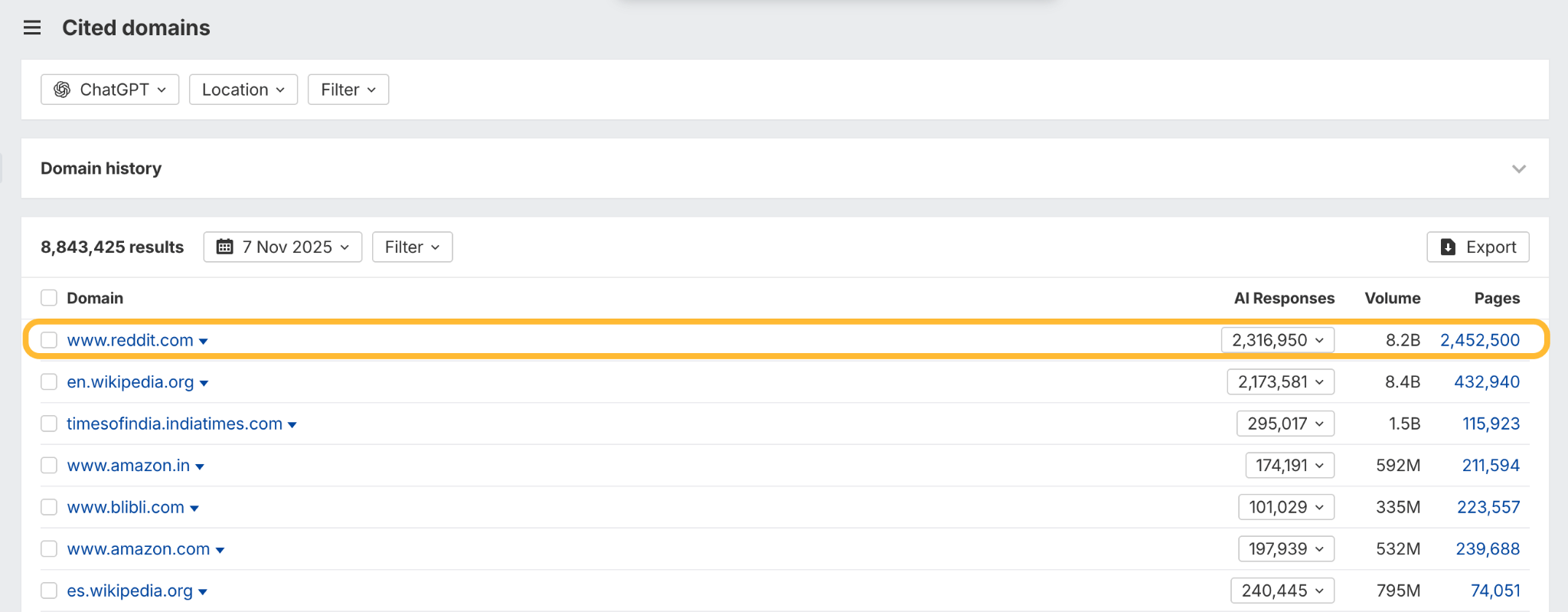
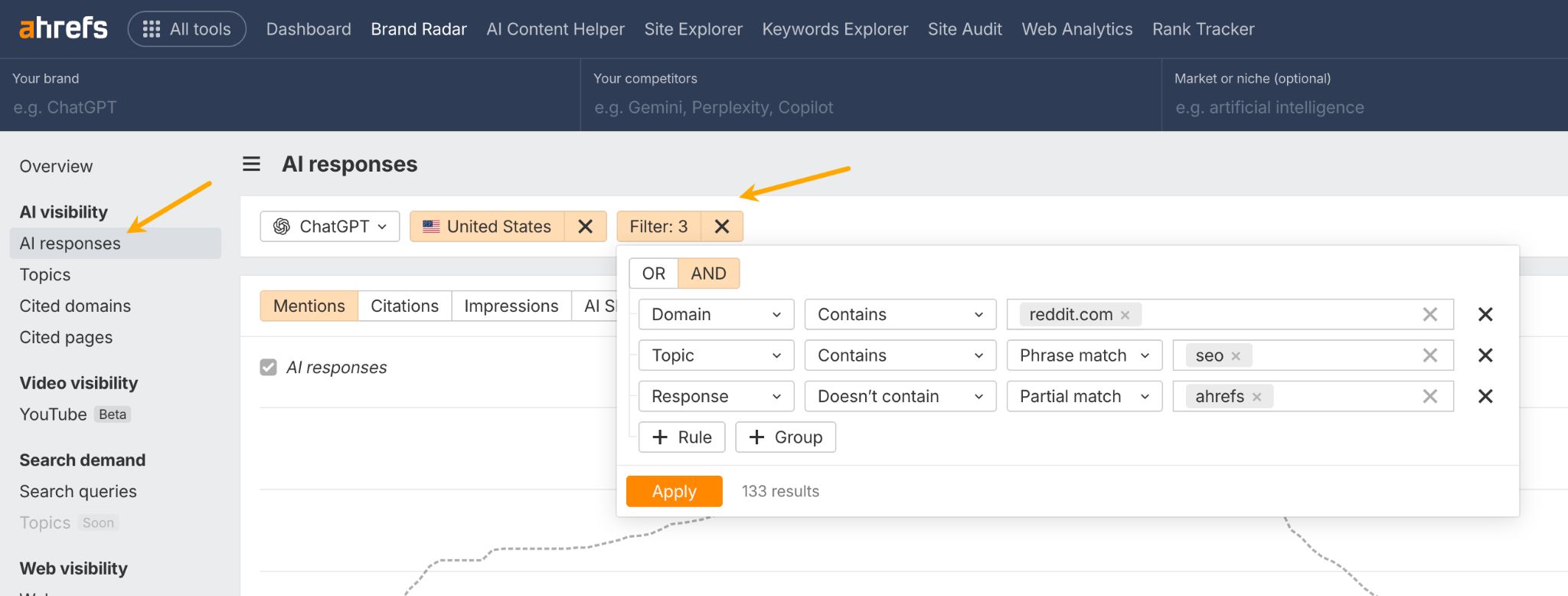
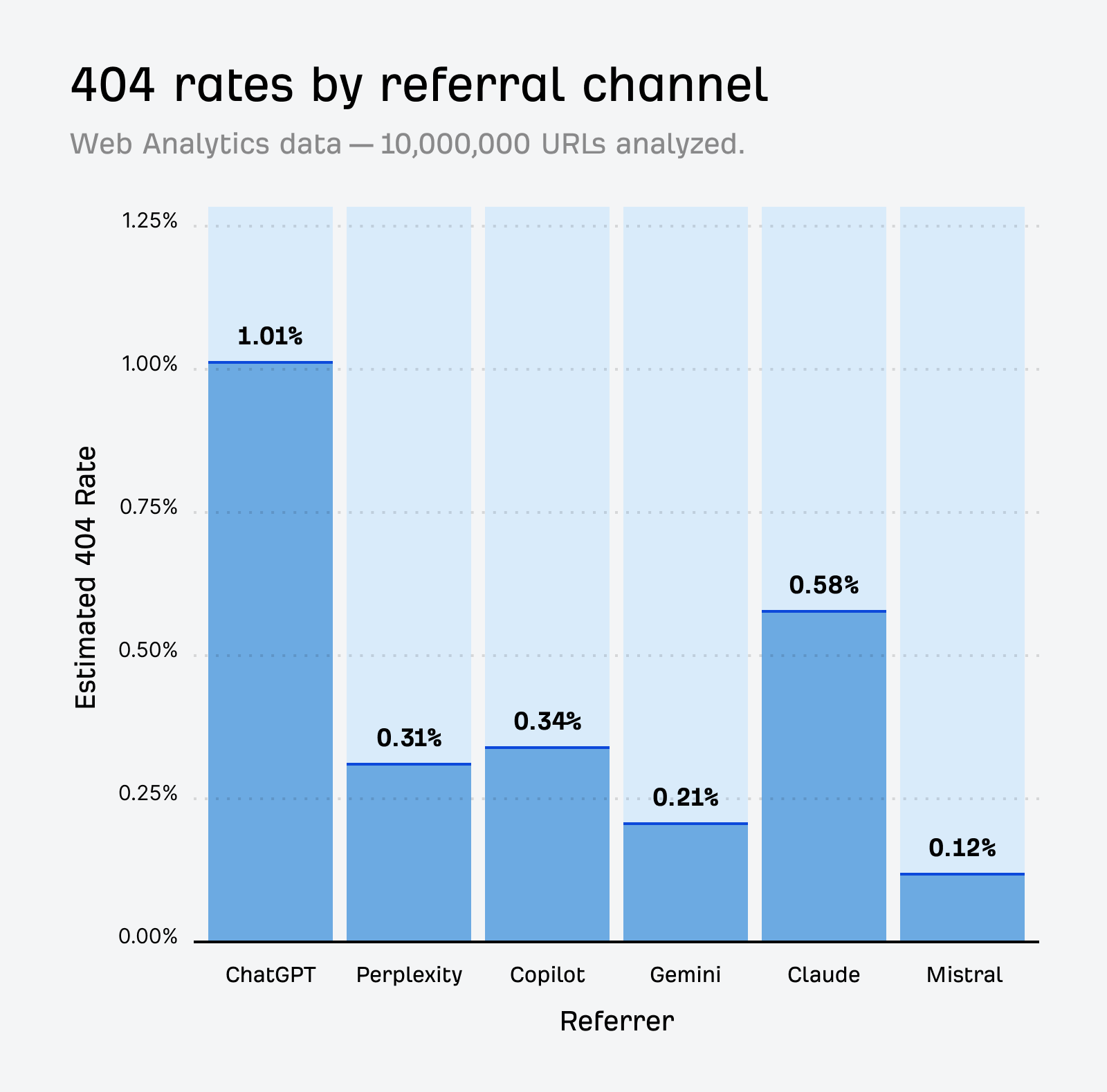
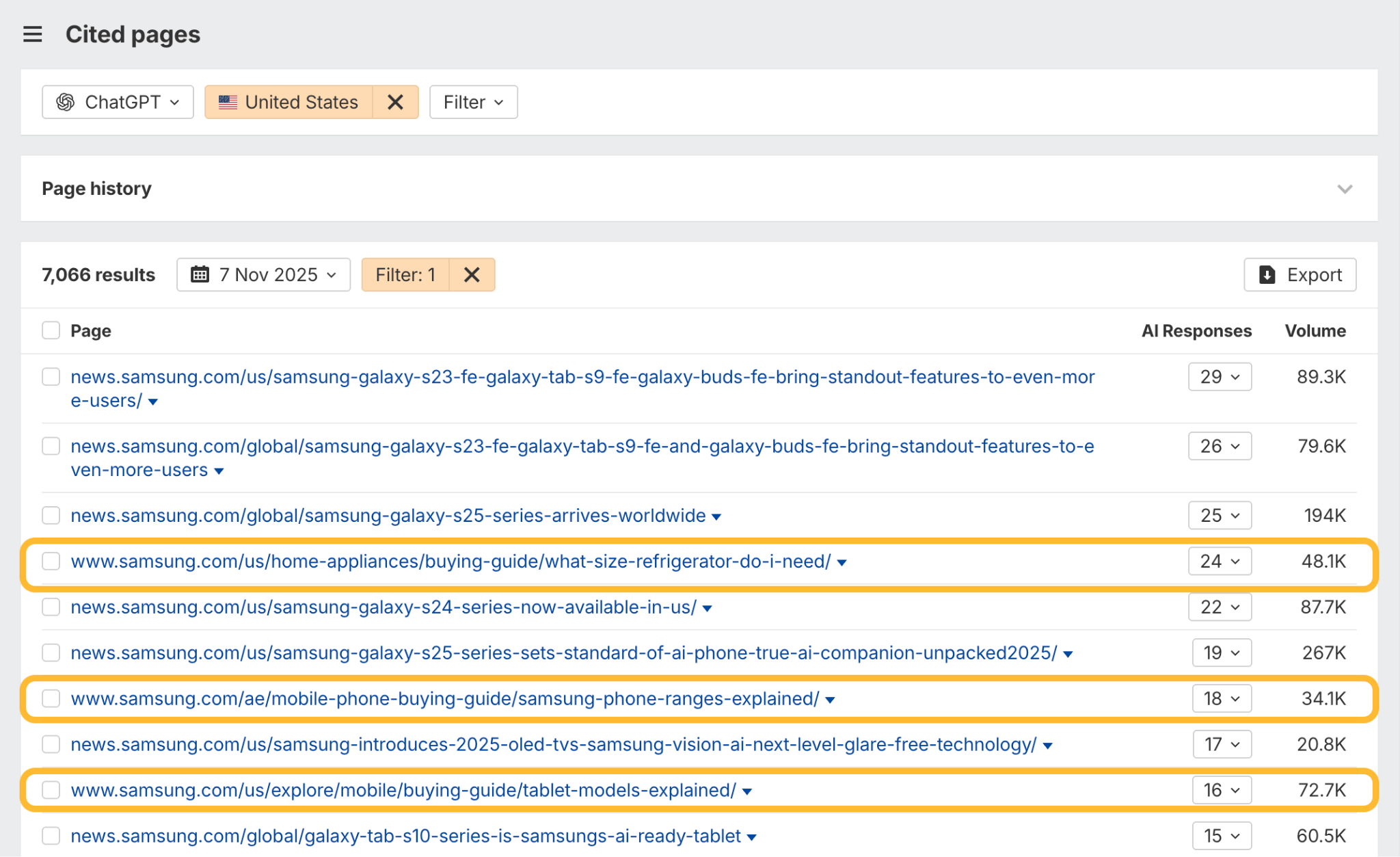
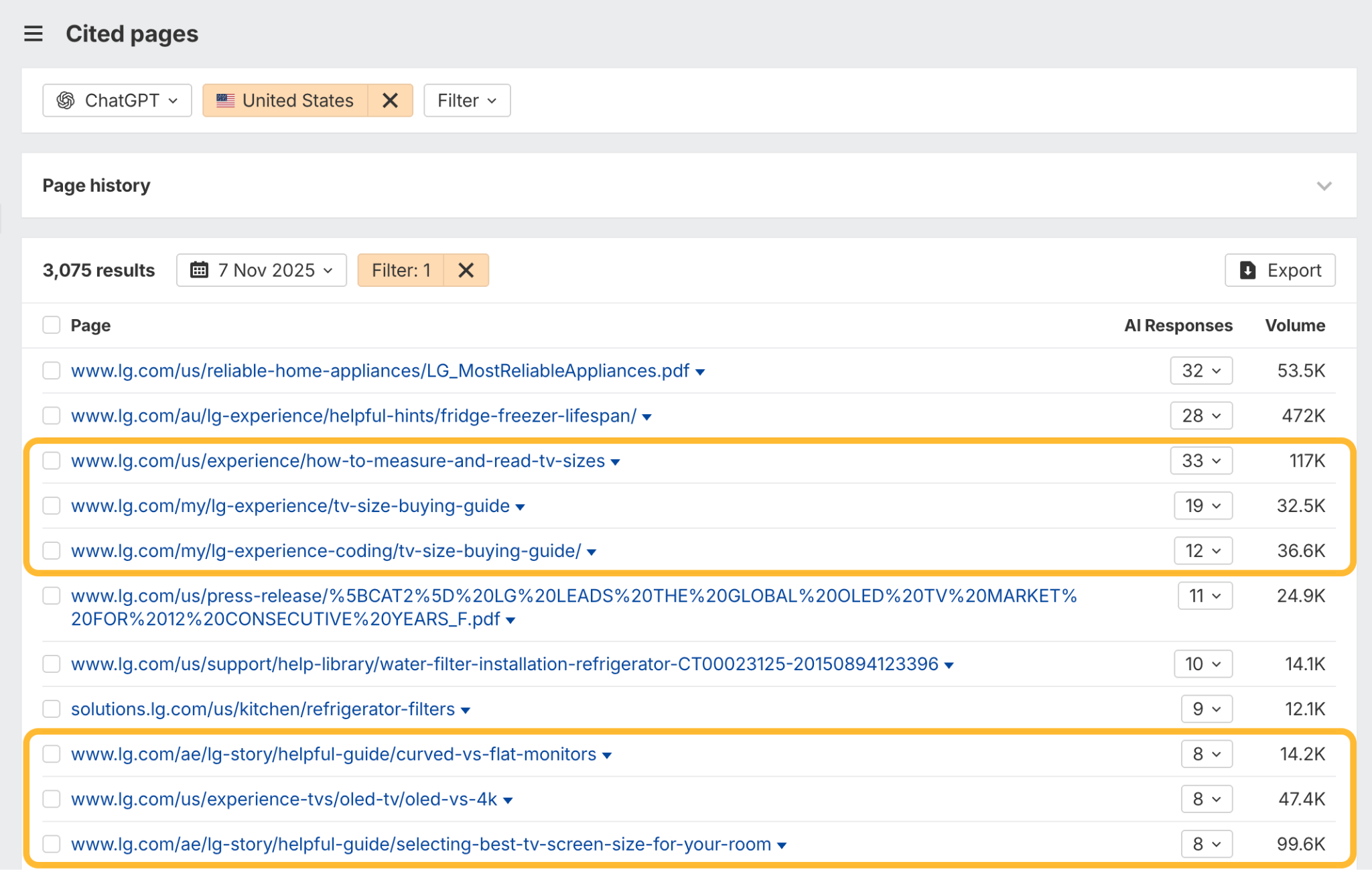
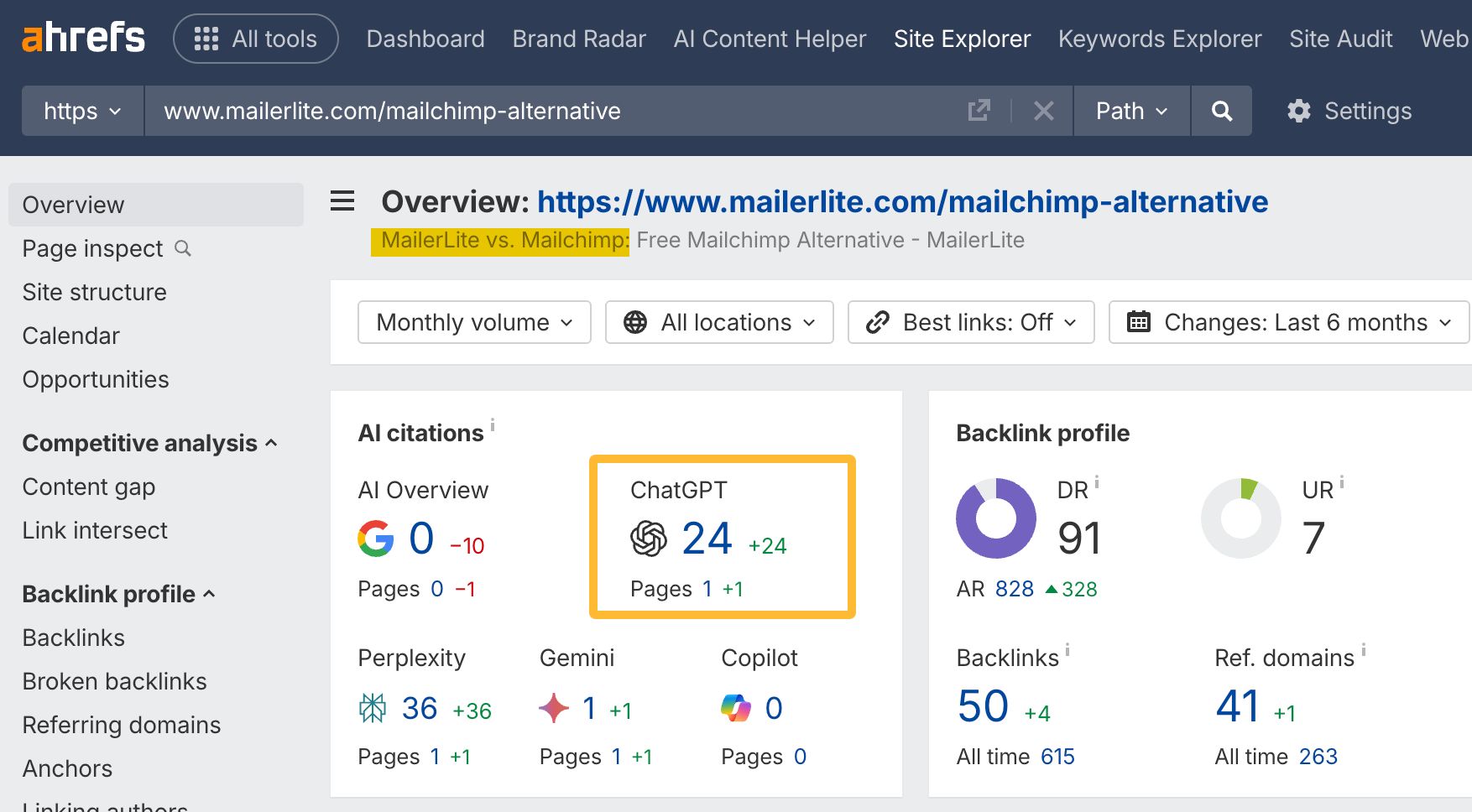
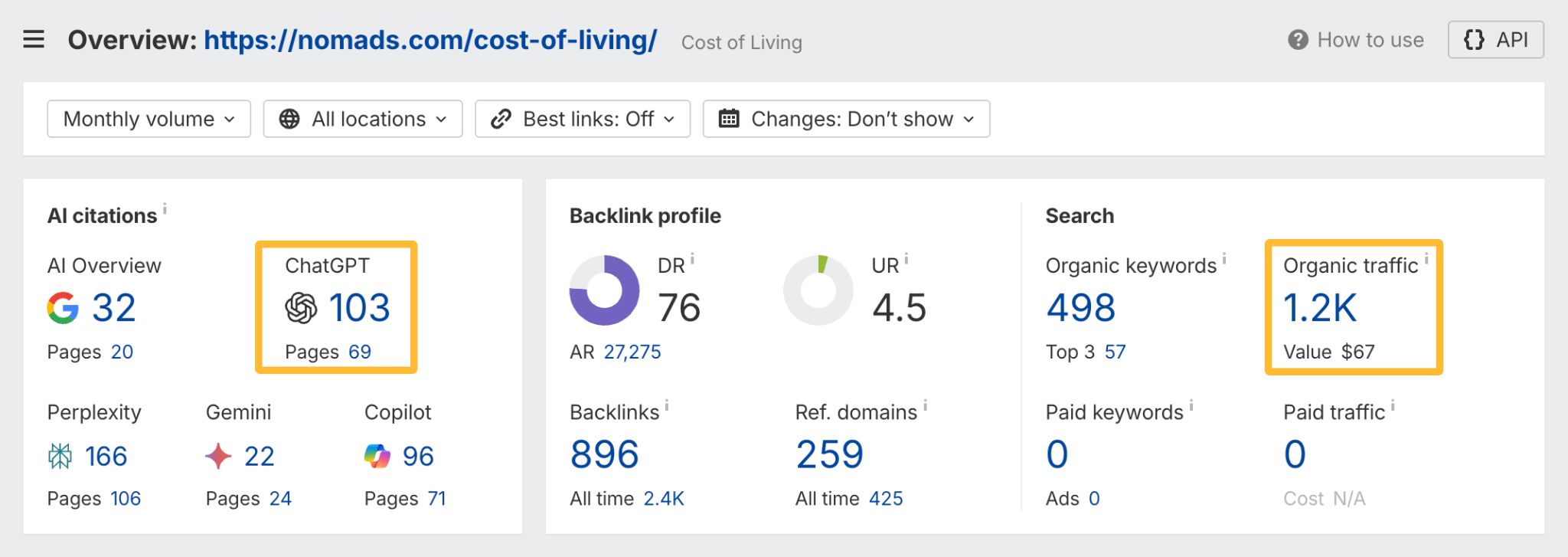
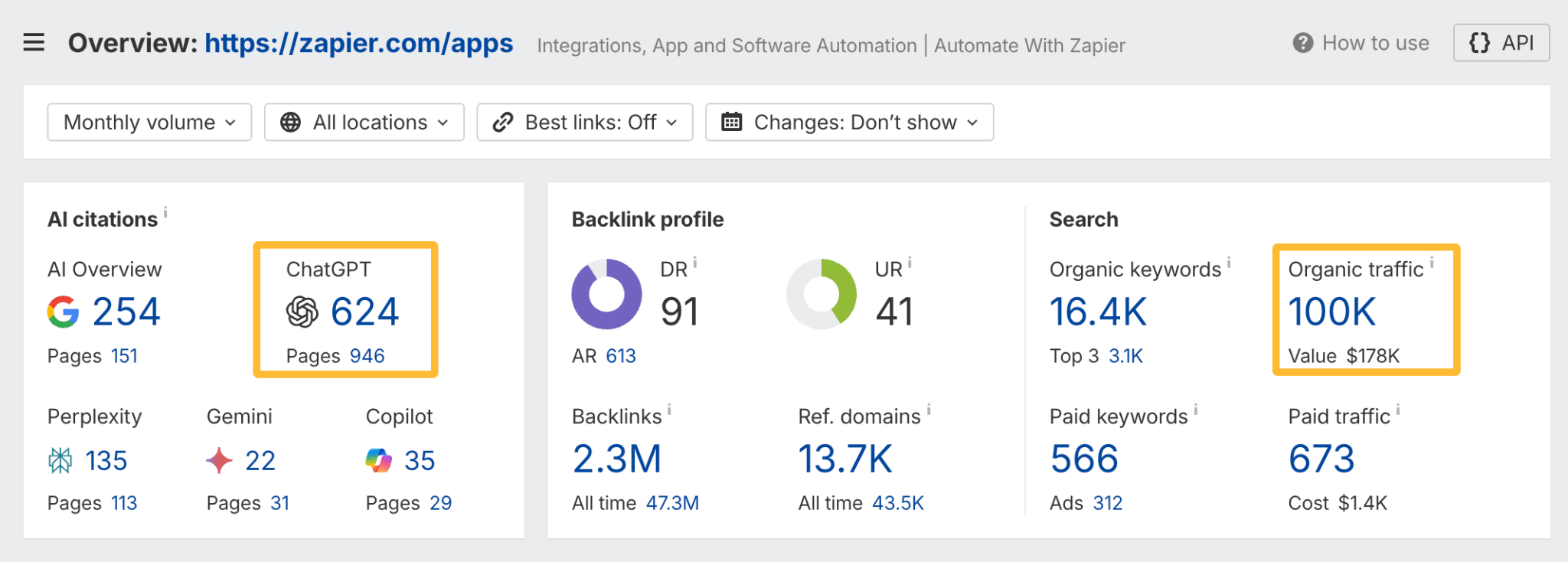
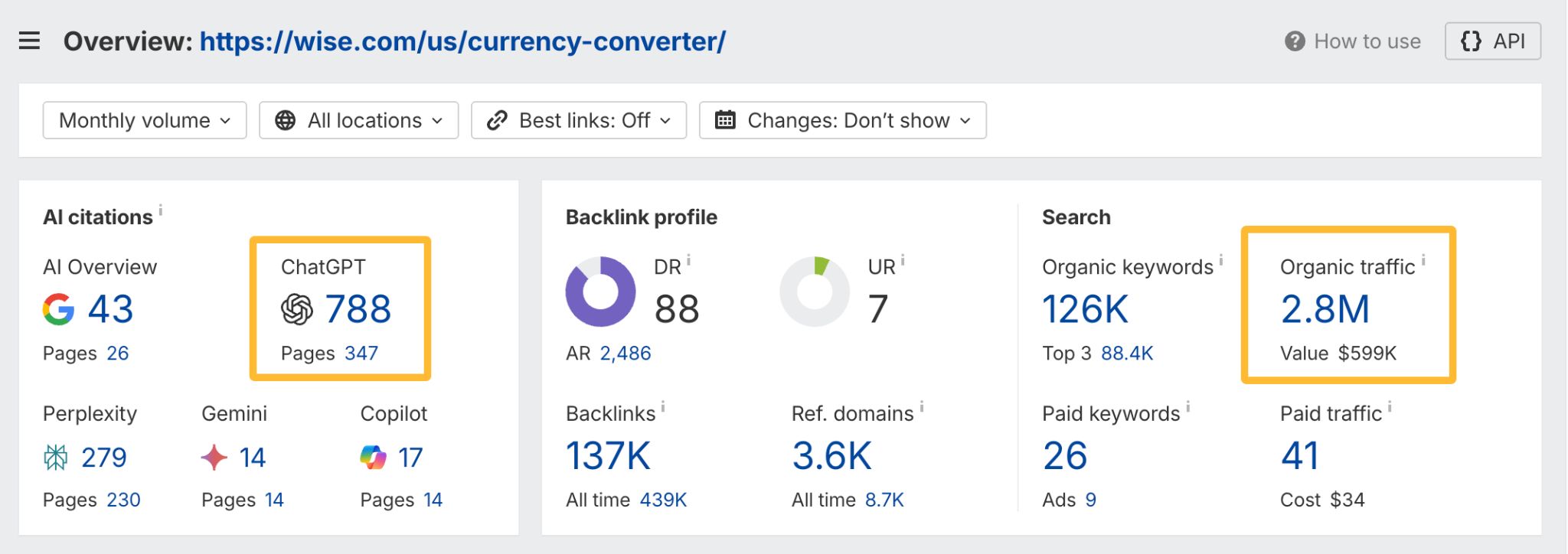
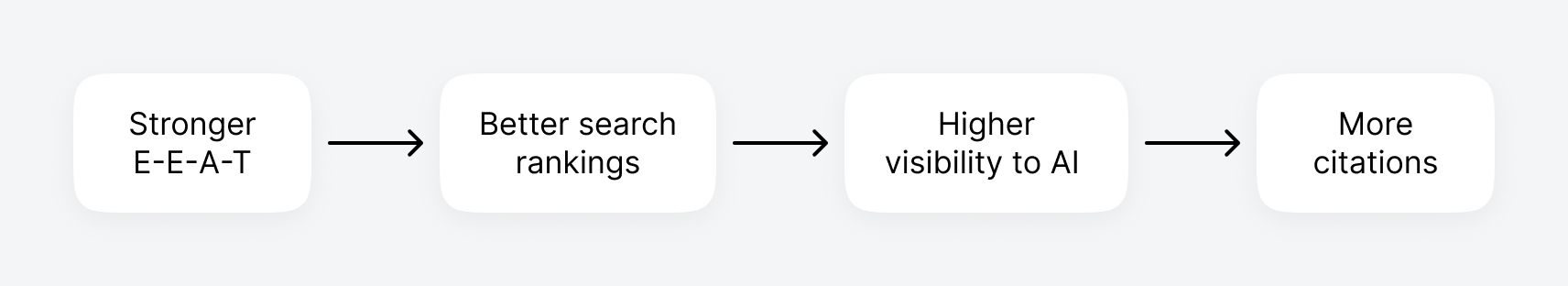
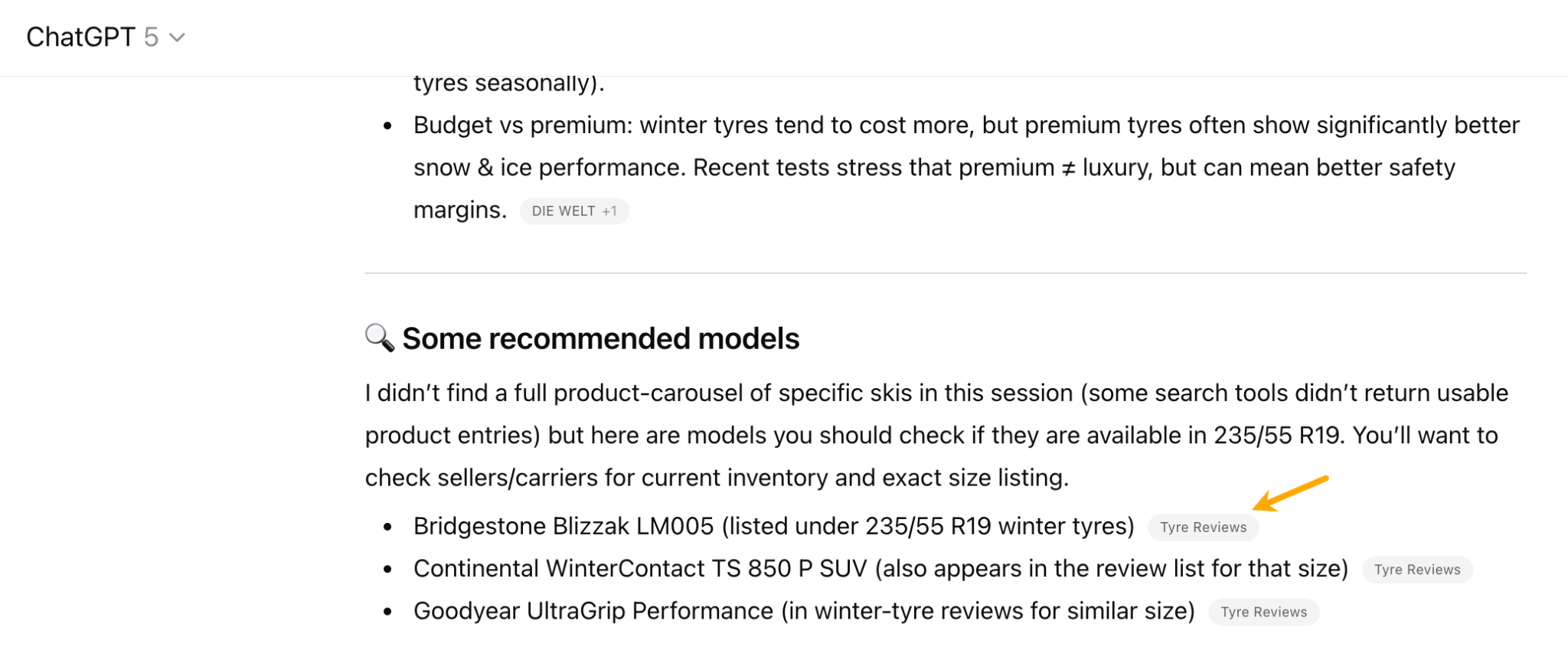
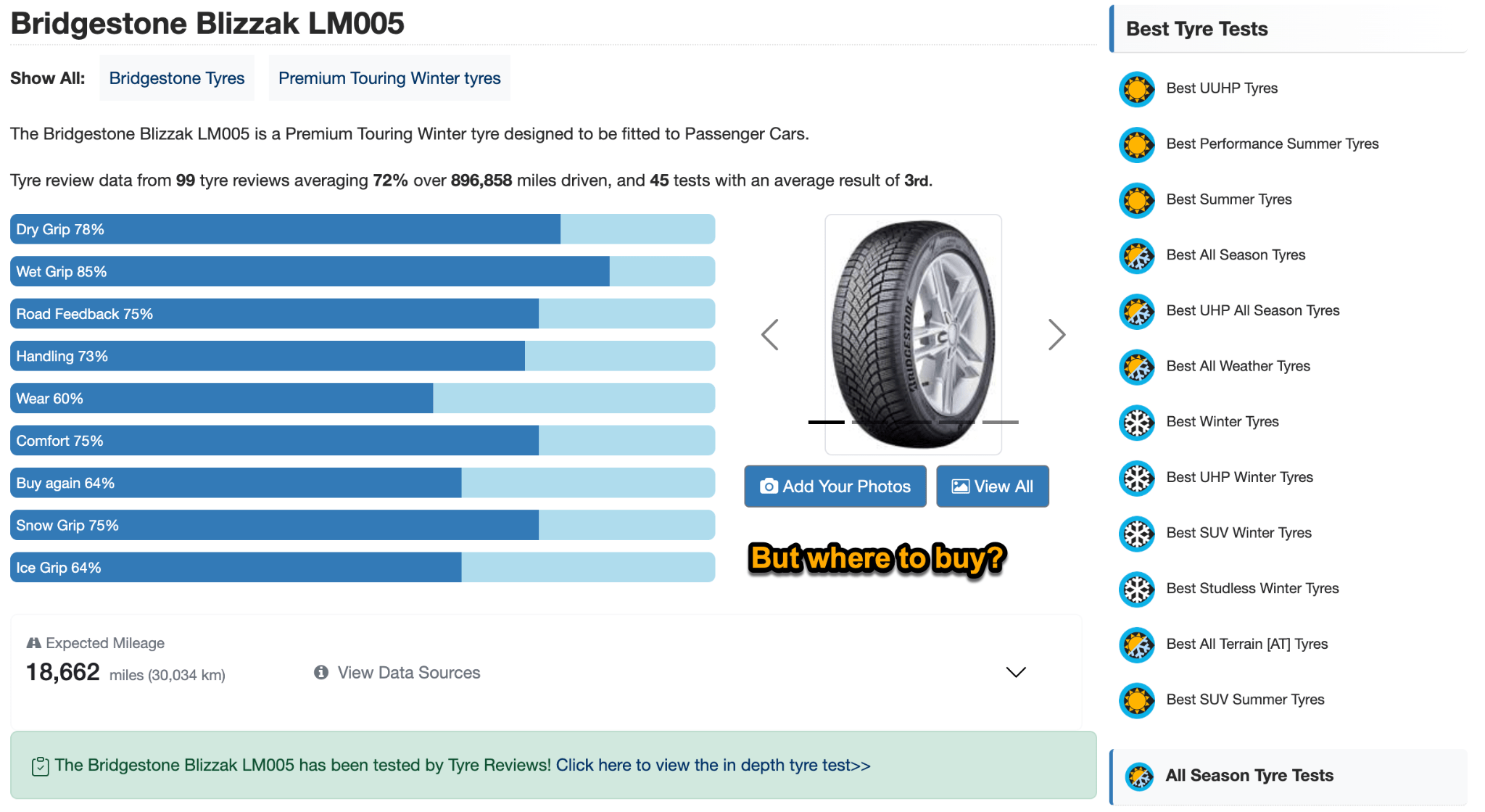
In October 2025, ChatGPT had more than 800 million weekly users; yet, most analytics dashboards don’t even list it as a traffic source. There’s an entirely new visitor channel quietly growing faster than Google Search, sending higher-intent users who convert at rates that make traditional search traffic look inefficient. In this guide, you’ll learn what makes ChatGPT traffic unique, how to track it in your analytics, and strategies to increase both direct and indirect visits from this AI assistant. ChatGPT traffic works differently from regular search engine traffic. Knowing how it differs can help you decide if and how you should adjust your strategy to make the most of it. When ChatGPT suggests your website, it usually explains what you offer and why it’s relevant. That means visitors click through already knowing what to expect—they’re there because the AI specifically recommended your solution. For Ahrefs’ own site, AI-search traffic was ~0.5% of visits but accounted for ~12.1% of sign-ups. That’s 23x higher rate than traditional organic search visitors in our case. And we’re not the only ones with higher conversion rates from LLM traffic. Recently, Buffer’s Director of Growth, Simon Heaton, reported similar results: Even some people in the comments chimed in similar data: Not everyone will get the same results, though. This study by Amsive suggested that LLM conversions depend on the business model. And there’s even a massive, 61-page research providing evidence that ChatGPT referrals convert worse when it comes to e-commerce. There’s mixed research on conversion rates across different websites, but visitors coming from ChatGPT might convert at much higher rates than those from regular search traffic. Either way, it’s worth running your own tests to see how it performs for your site. As AI assistants like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini continue to shape how people discover information, more brands will start optimizing for visibility within these tools. Within a year or two, we’ll likely see the same saturation that happened with traditional SEO. Getting in early means you can build a track record before the competition floods in. To illustrate this, just look at how demand for the term “geo agency” has taken off lately. It’s still a low-volume keyword, but interest is climbing fast. Moreover, the top results are already focused on AI search optimization agencies—not the old “geographic” meaning of the word—showing that user intent is shifting quickly in the SERPs. One of the best things about optimizing for AI is that it doesn’t come at the expense of traditional SEO. In fact, many of the same best practices improve your performance in both, creating a multiplier effect where one effort pays off across multiple channels. At its core, SEO has always been about two main things: content and backlinks. In ChatGPT’s world, great content helps your site get cited and makes it easier for AI models to understand what your brand is about. Backlinks, meanwhile, still boost your Google rankings—which also helps AI tools find and reference your content when they pull information independently. Even better, backlinks often lead to more brand mentions across the web. And interestingly, those mentions seem to play a role in why AI assistants like ChatGPT choose to reference certain websites in their answers. For example, our own site has been cited thousands of times across different AI assistants—and that happened before we ever optimized for LLMs. It turns out, solid content and organic visibility still go a long way. ChatGPT introduces new attribution challenges. When an AI mentions your brand, it can drive awareness and traffic—but those visits don’t always show up in your analytics the same way traditional referrals do. Here’s an example: when ChatGPT recommended the top tool in my test, none of the mentions linked directly to the tool’s homepage. The first mention wasn’t even a clickable link, and the only actual link pointed to a review page, not the main site. So, if that AI-recommended tool gets visitors through this path, the traffic won’t appear as coming from ChatGPT—it’ll look like it came from the review site instead. Before you can optimize for ChatGPT traffic, you need to see it in your analytics. Here’s how to set up proper tracking and identify which metrics actually matter. Some tools, like GA4, don’t include ChatGPT or other AI assistants as default traffic sources. To track them, you’ll need to set up a custom segment or use regex to filter referrals from chatgpt.com (here’s a detailed guide by Amsive). An easier option is to use tools like Ahrefs’ Web Analytics, which already have AI traffic sources built in and automatically categorize these visits. Once you’re tracking ChatGPT traffic, measure its performance using the same analytics framework you already use for Google Search or social media. The key difference: pay attention to how ChatGPT visitors behave compared to other channels. All of these metrics can be tracked in Ahrefs’ Web Analytics. Chances are, the tool you’re already using can do it too—as long as it supports event tracking and can identify LLM-driven traffic. This part gets a little nuanced, but it’s key to understanding how ChatGPT (and other LLMs) actually send traffic to your site. The pages ChatGPT cites most aren’t the ones driving the most traffic. At Ahrefs, there’s only a 10% overlap between our most-cited pages and highest-traffic pages from ChatGPT. Users click ChatGPT citations when they need to take action. Sometimes they ignore citations for background reading but click through when they need to actually do something—use a tool, sign up for a trial, compare options. That 10% overlap is likely the actionable citations—where ChatGPT both cites us AND users need to visit our site to complete a task. But here’s the kicker: ChatGPT often mentions brands without citing them, especially for actionable recommendations. It might say “try Ahrefs’ keyword tool” without including a link. Users then find you through Google or type your URL directly. That creates two main types of traffic: If you optimize only for citations, you’re missing the bigger picture. You need to optimize for actionable mentions—both cited and uncited. Focus on being ChatGPT’s go-to recommendation when users need to take action, not just its reference source for information. In this section, I’ll explain how to increase both direct traffic (from citations) and indirect traffic (from mentions). Study which types of content perform best in your industry and focus your efforts there. Not every kind of content works equally well in AI search; and some formats might not make sense for your niche at all. To give you a quick idea, the types of content I’ve most often seen cited tend to be: Here’s a straightforward way to find out which content types perform best in your niche using our AI search visibility tool, Ahrefs Brand Radar: You can narrow the analysis down to a single competitor (or a few competitors) and find their best-performing content in ChatGPT: Long-tail keywords—those specific, lower-traffic phrases—have always been an SEO secret weapon, and they’re becoming even more valuable in the age of AI. People tend to ask AI tools longer, more detailed questions than they type into search engines. These in-depth prompts often align perfectly with long-tail keywords, making your content easier for AI to surface and recommend. This happens thanks to query fan-out—when an LLM takes one prompt and expands it into multiple related ideas or sub-questions, boosting the chances of matching niche keywords. So, it’s smart to create content that covers: That’s why long-tail keywords matter more than ever in AI-driven search. Start with Brand Radar—it’s not just useful for tracking mentions, but also great for keyword research for AI search. From there, you can either create content that directly targets the topic, try to get featured on the pages already cited for it, or do both. This is a smart first step if you want to boost your visibility in ChatGPT results. Next, expand your research with a tool like Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer to pull data from Google’s much larger keyword database, giving you plenty of new ideas. Since what people search on Google often overlaps with what they ask ChatGPT, it’s a great way to spot additional opportunities. Here’s how: If you see an “x” under ranking position, it means you don’t currently have a page targeting that keyword, and you can consider creating one. If the ranking position is greater than 10, you can likely improve your existing content (click the SERP icon on the right to see which URL is ranking). Recommendation There’s a simple trick to see which queries ChatGPT uses when it searches the web for a prompt—check out this short video to learn how it works. ChatGPT usually performs query fan-out on longer prompts, breaking them into several related searches to find the best-fitting information. So when you get an idea—say, from a social media comment or customer feedback—try this: Fresh content matters more for AI than you might think. Our research shows AI assistants like ChatGPT strongly prefer recently updated content. Here are the types of pages worth updating regularly: Refreshing these pages helps you attract more traffic from both LLMs and Google. While Google Search doesn’t heavily favor recency, updating content is still a proven way to maintain first-page rankings. Moreover, if you find that ChatGPT cites an outdated study in an important topic for you, there’s a chance to replace it with your own or be cited next to it. If you know a popular study made by your competitor, simply plug it into Site Explorer and see if it gets cited in any of the 6 AI indexes we track. The more your content and brand appear across the web, the more chances AI tools have to find and recommend you. Keep in mind—this kind of visibility often leads to indirect traffic. These visitors discover your brand through ChatGPT, but don’t click directly from there. Instead, they might search your brand on Google or type your URL manually. This could change soon as large language models evolve. Right now, the main limitation is the interface—AI mentions your brand but doesn’t link to it. Once platforms like OpenAI start adding links, those mentions could instantly turn into direct traffic. You don’t have to guess which pages are helping you show up in AI-generated answers. Try running a mention gap analysis in Brand Radar to see which pages mention your brand but not your competitors. Here’s how: You can also do a quick check anytime you find a review that should mention your brand but doesn’t. Just paste the page’s URL into Site Explorer to see whether ChatGPT or other AI tools are already referencing it as a source. Another smart tactic is to tap into Reddit, which happens to be one of the most frequently cited sources by ChatGPT. Brand Radar lets you find Reddit threads that ChatGPT cites in its responses—especially those related to your business but mentioning your brand. There’s a technical side to the process, too. Start by checking if you’re not blocking ChatGPT (and other LLMs if you want traffic from them as well) with a tool like AI Crawler Access Checker. Then, you need to ensure ChatGPT can easily find and understand your content. Here’s how: AI assistants generate broken links about 2.8 times more often than Google (yes, we tested it). And actually, ChatGPT is the one that hallucinates the most. Start by monitoring your 404 errors to spot issues like: In Ahrefs Web Analytics, there’s a dedicated report for potential 404 errors hallucinated by AI. Pages in this report may still receive traffic, but their title includes “404,” indicating that users (or AIs) are trying to access pages that don’t exist. If you don’t have a closely related page to redirect that traffic yet, you can create one so visitors (and search engines) land somewhere useful instead of hitting a dead end. However, prioritize URLs that are generating meaningful traffic. If a hallucinated URL only gets a handful of visits, it may not be worth the effort to create a new page for it (you can redirect to your resources directory instead). ChatGPT is quickly becoming a comparison shopping assistant. Instead of browsing through multiple reviews and spec sheets, users now get a single, summarized answer that compares options and highlights trade-offs based on their needs. But here’s the catch—AI assistants still need reliable source material to build those answers. If your site doesn’t offer clear comparison content, ChatGPT will pull from competitors or third-party sources instead, or just “hallucinate” it. You can already see this happening in industries like consumer electronics, where brands like Samsung and LG are frequently cited when users ask about TV models or appliance features. In general, these kinds of product comparisons and buying guides should work for companies with: And it can also work for SaaS companies with competitor comparisons, FAQ pages, product academies, and product support pages. While programmatic content (templated pages generated automatically) may not perform as strongly in AI search as it does in traditional search, it can still earn citations and drive steady traffic. Interestingly, some of the examples that succeed here are the same ones that worked well in classic SEO—brands like Wise, Nomad List, and Zapier have all seen solid results from this approach. We’ve got a full guide explaining how to make programmatic content work, including how to find keywords with traffic potential that scale to populate dozens of pages. Here are two extra points to keep in mind with this approach: For example, if you ask “cost of living in different cities,” ChatGPT will pull information from a webpage it finds through a web search, rather than relying on built-in data. It will also note that the information is for 2025 and may change the following year. Stronger expertise, experience, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness create a virtuous cycle: The higher your E-E-A-T, the better your content performs in search, and the more likely it is to be found and cited by ChatGPT when it pulls data from the web to deliver accurate answers. At its core, E-E-A-T is about trust—proving to both users and Google that your content is credible and reliable. You can show this by including author credentials, expert reviews, and earning backlinks from reputable sources. To dive deeper into what E-E-A-T means and how to strengthen each part, check out our complete guide to E-E-A-T. Once visitors arrive from ChatGPT, make sure your site is ready to turn that interest into action. These users often have higher intent, so your landing pages should: Here’s an example: imagine you’re using ChatGPT to find recommendations for winter tires. You notice one of the cited pages looks promising, so you click through. Turns out, there’s no link to buy the tires. The content is great, but the experience falls flat because it doesn’t help you take the next step after reading the AI’s summary. This kind of situation will likely become more common. AI tools like ChatGPT often send users who are already close to making a purchase decision, so it’s smart to design for that audience. By thinking ahead—adding relevant links, simplifying actions, or including affiliate CTAs—you not only improve the user experience but also open up more opportunities to increase revenue. I hope you found this guide useful. Before we wrap up, let’s look at what’s coming. Here are four trends that will likely shape ChatGPT traffic over the next few years: Got questions or comments? Find me on LinkedIn.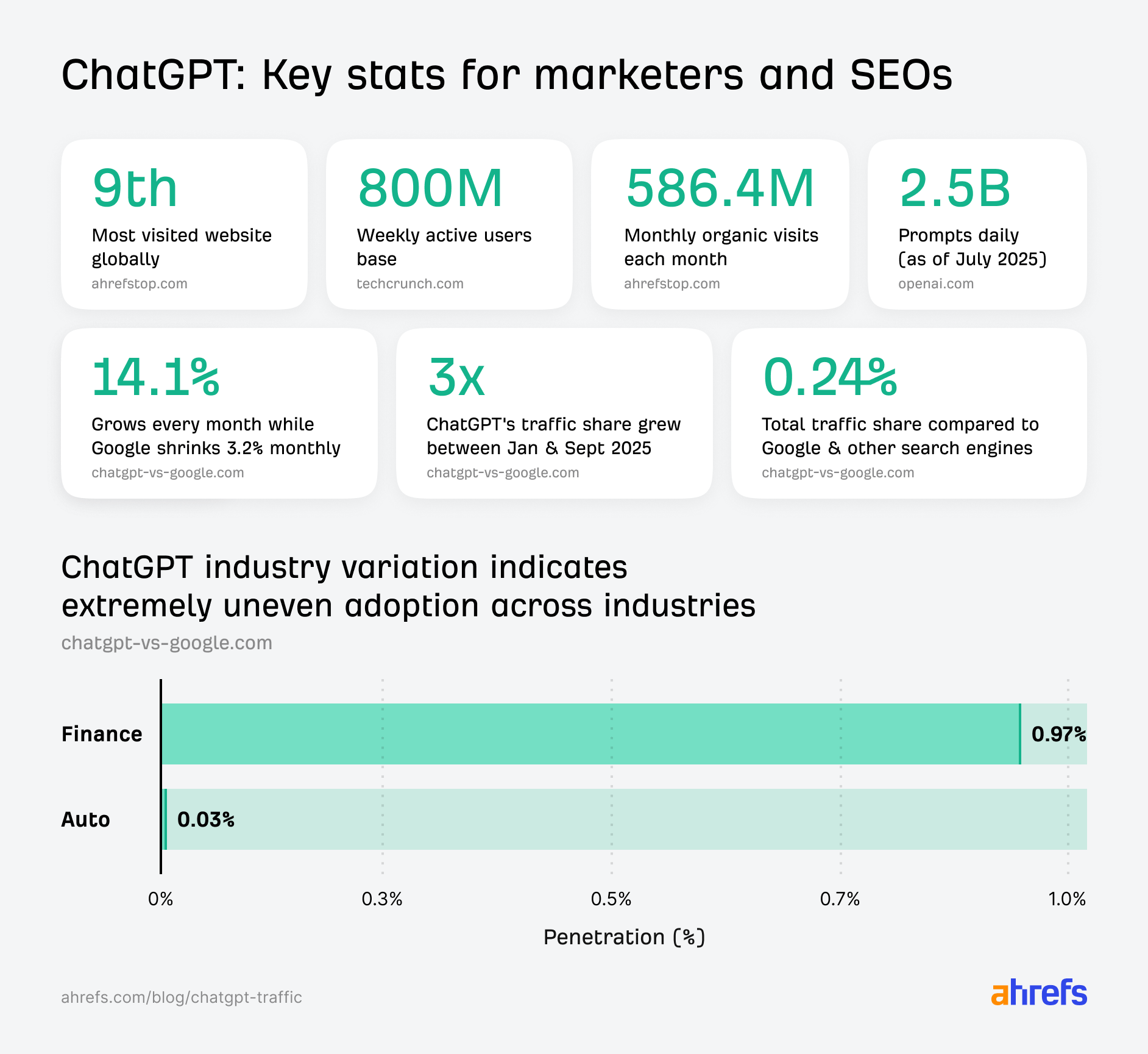 Market share: ChatGPT holds 0.24% of total traffic share compared to Google and other major search engines (source: chatgpt-vs-google.com)Growth trajectory: ChatGPT’s traffic share grew 3× between January and September 2025 (source: chatgpt-vs-google.com)Monthly growth: ChatGPT grows 14.1% every month while Google shrinks 3.2% monthly (source: chatgpt-vs-google.com)Industry variation: ChatGPT shows 32× higher penetration in Finance (0.97%) compared to Autos (0.03%), indicating extremely uneven adoption across industries (source: chatgpt-vs-google.com)User base: 800 million weekly active users (source: techcrunch.com)Daily usage: 2.5 billion prompts daily (as of July 2025) (source:openai.com)Web presence: chatgpt.com is the 9th most visited website globally with an estimated 586.4M organic visits each month (source: ahrefstop.com)Search interest: The term “ChatGPT” gets searched on Google an estimated 326 million times globally each month (source: Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer)
Market share: ChatGPT holds 0.24% of total traffic share compared to Google and other major search engines (source: chatgpt-vs-google.com)Growth trajectory: ChatGPT’s traffic share grew 3× between January and September 2025 (source: chatgpt-vs-google.com)Monthly growth: ChatGPT grows 14.1% every month while Google shrinks 3.2% monthly (source: chatgpt-vs-google.com)Industry variation: ChatGPT shows 32× higher penetration in Finance (0.97%) compared to Autos (0.03%), indicating extremely uneven adoption across industries (source: chatgpt-vs-google.com)User base: 800 million weekly active users (source: techcrunch.com)Daily usage: 2.5 billion prompts daily (as of July 2025) (source:openai.com)Web presence: chatgpt.com is the 9th most visited website globally with an estimated 586.4M organic visits each month (source: ahrefstop.com)Search interest: The term “ChatGPT” gets searched on Google an estimated 326 million times globally each month (source: Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer)

Set up tracking in your analytics
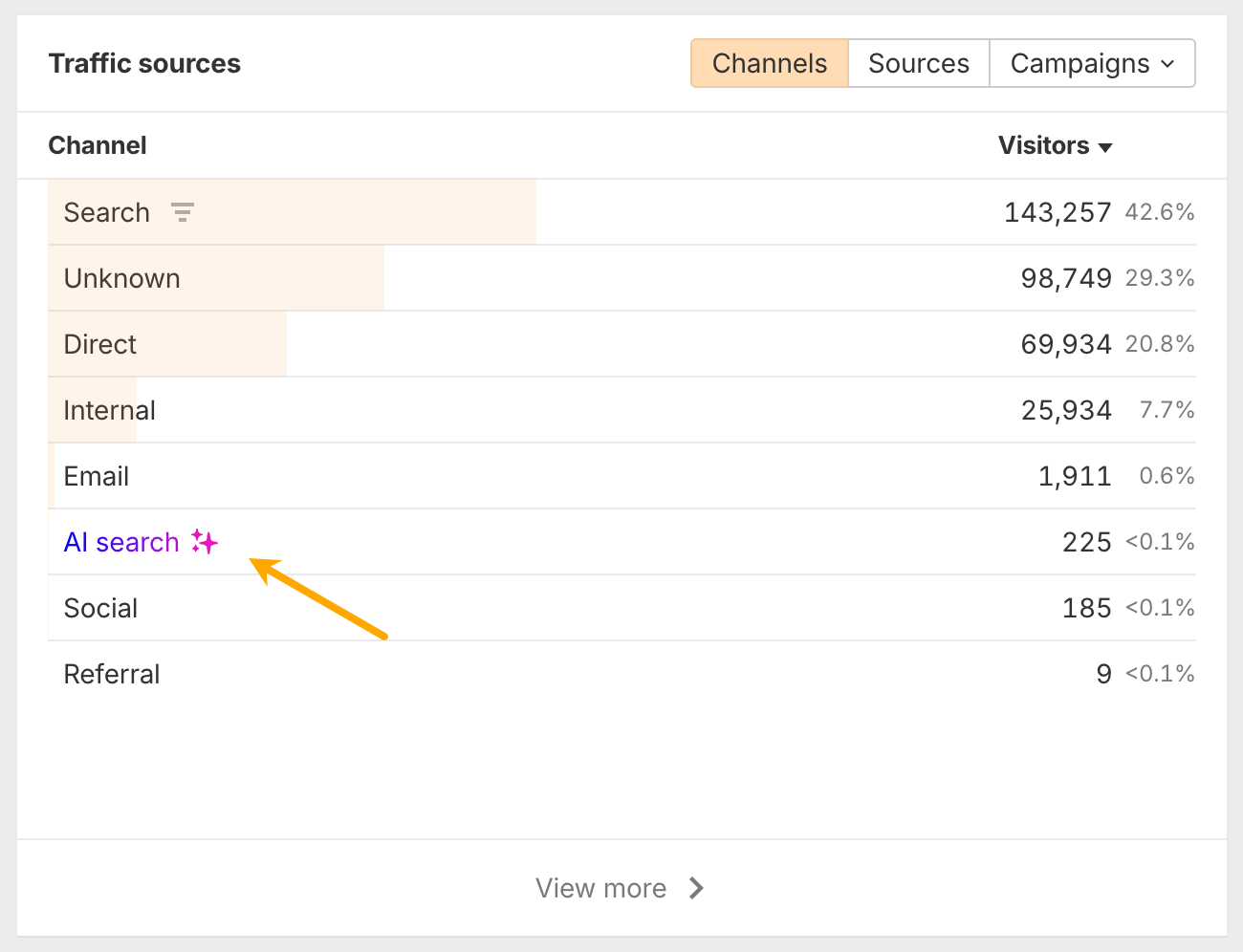
Monitor the same metrics you track for other channels
Metric categoryWhat to trackWhy it matters Volume metrics (establish baseline) Total visits from ChatGPT; Unique visitors; Week-over-week and month-over-month growth rate Shows how much traffic you’re getting and whether it’s growing. Even small numbers matter since ChatGPT traffic typically represents just a fraction of total traffic but is growing rapidly. Engagement metrics (validate quality) Time on page; Bounce rate; Pages per session Reveals whether ChatGPT visitors are genuinely interested in your content. AI-referred visitors often spend more time and explore more pages because they arrive pre-qualified with clear intent. Conversion metrics (measure impact) Goal completions (leads, downloads, signups); E-commerce transactions; Conversion rate vs other channels Connects ChatGPT visibility to business outcomes. AI traffic often converts at dramatically higher rates—for Ahrefs, ChatGPT traffic was ~0.5% of visits but ~12.1% of signups (roughly 23× higher conversion rate than organic search). Content performance (reverse-engineer what works) Pages receiving ChatGPT traffic; Top landing pages from AI referrals; Topics generating the most visits Identifies patterns in what ChatGPT cites so you can replicate success. Helps you prioritize which content types and topics deserve more investment. 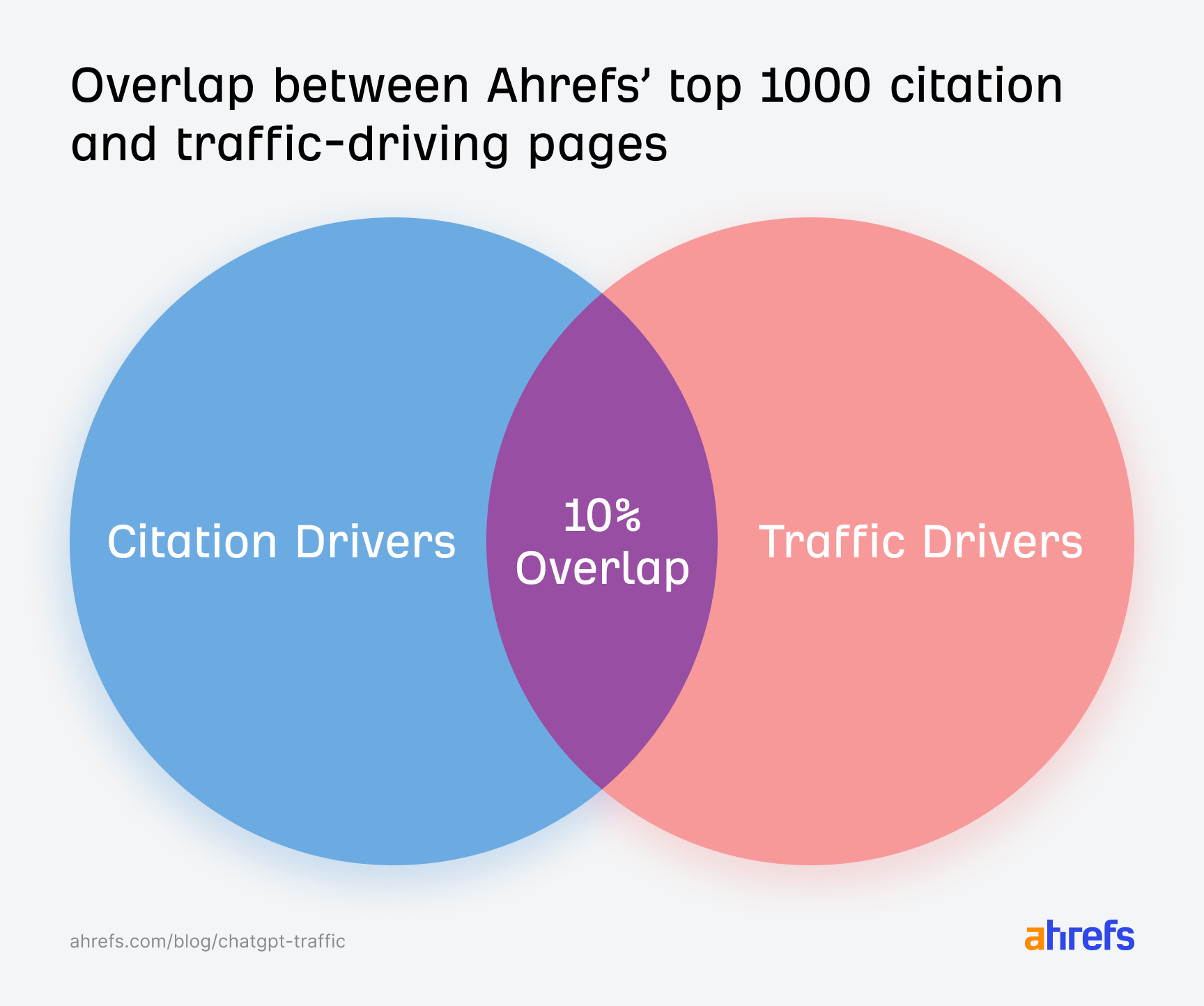



Final thoughts

 ValVades
ValVades