Typos can get you hacked in latest cybersecurity threat
Fake websites look just like the real ones, but steal your logins, harvest cryptocurrency, and infect your computer and phone in the latest cybersecurity threat.

By
Alan Truly
October 24, 2022 7:33AM 
Even a simple and common error like mistyping a domain name can lead to cybersecurity attacks, the latest in the ongoing barrage of malware. Known as URL hijacking or “typosquatting,” this social engineering technique is built upon the knowledge that it’s easy to hit the incorrect key and end up visiting the wrong website.
With very little effort, a hacker can copy images, fonts, and text to construct a malware website that looks like PayPal, Google Wallet, Microsoft Visual Studio, MetaMask, and other popular websites. These fake websites are also used in phishing campaigns of all sorts since the similarity of the domain name is useful for a whole variety of confidence stings.

URL hijacking and phishing campaigns aren’t new, but there has been a recent increase in them. Bleeping Computer, with a little help from the security firm Cyble, discovered over 200 domains that impersonated popular websites for Android and Windows apps, cryptocurrency and stock trading, as well as subscription services apps.
The goal of fake websites for apps would be stealing credentials and infecting your computer or phone with viruses. Any website that involves subscriptions or payments would have the more direct approach of taking your money or cryptocurrency.
A common technique with URL hijacking is to add or change one letter. Bleeping Computer gave an example of a trustworthy website for the popular Windows text editor, notepad-plus-plus.org. A malware website exists that simply adds the letter S to the end of “notepad” to create the deceptive domain name.
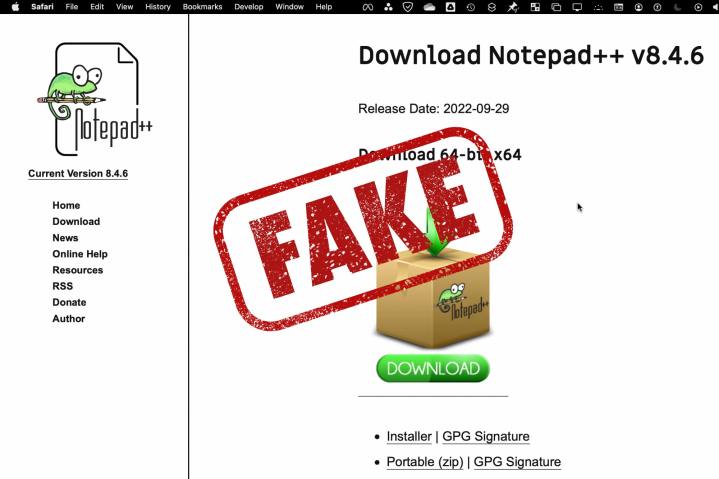
Major browsers include a degree of protection, identifying some fake websites while missing others. To protect yourself, have a close look at the domain name shown in the website address box or do an internet search for the website, app, or service you want to visit. You can’t trust that you’re at an authentic website based on appearance alone.

 Konoly
Konoly 































