Deep Learning vs. Machine Learning: What Marketers Need to Know
Artificial intelligence continues to be a hot topic within the marketing industry. The market for AI in marketing will likely grow to $107.5 billion by 2028, up from $15.84 billion in 2021.

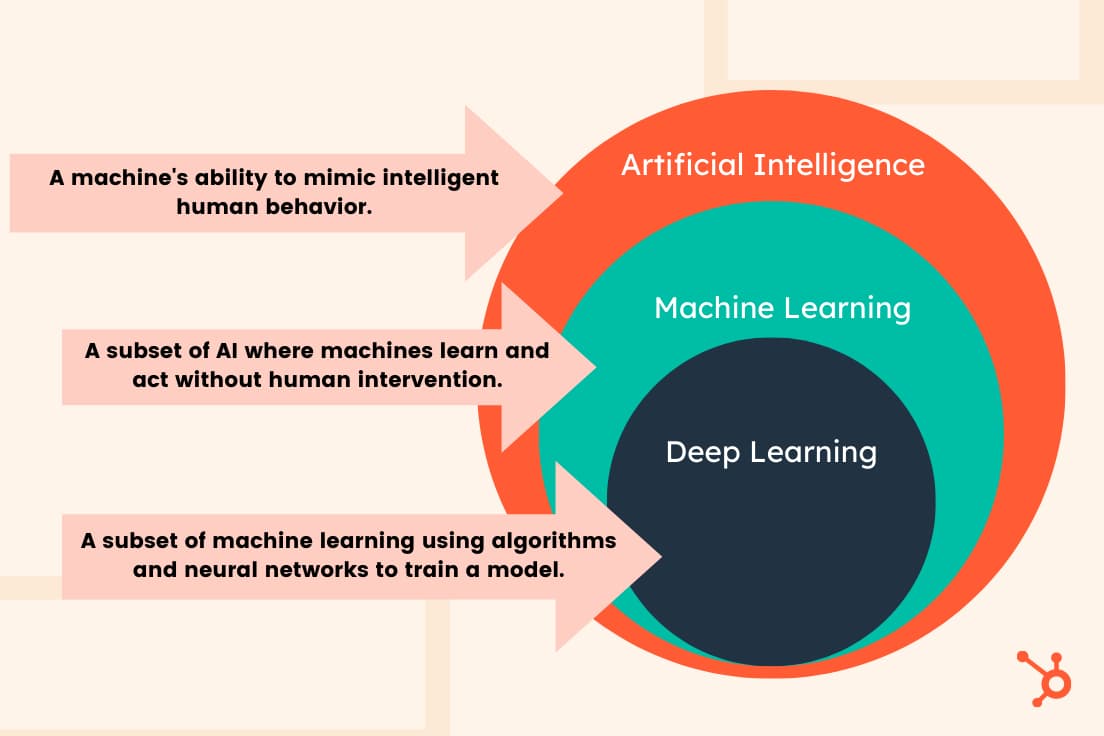
Artificial intelligence continues to be a hot topic within the marketing industry. The market for AI in marketing will likely grow to $107.5 billion by 2028, up from $15.84 billion in 2021. As the technology's role in marketing expands, you've probably heard the terms "deep learning" and "machine learning," — but what do these terms mean? Here's what marketers need to know about deep learning and machine learning. 3 Common Ways Marketers Use Machine Learning 3 Common Ways Marketers Use Deep Learning The Difference Between Machine Learning and Deep Learning Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence that uses data and algorithms to mirror how humans learn, gradually improving accuracy. The purpose is for a computer to learn without explicitly being programmed — in other words, without human intervention. An example of machine learning is speech recognition. Machine learning can translate speech into text; software applications can convert live voice and speech recordings into text files. Voice search, voice dialing, and appliance control are all examples of machine learning in speech recognition. So if you’ve ever listened to your favorite song by saying, “Alexa, play ____,” you can thank machine learning for the capability. Here are some ways machine learning is often implemented in marketing strategies. Predictive recommendation machines rely on data to predict what content or services a user would enjoy. A well-known example is Netflix's AI system that recommends movies and shows based on what a user has already watched. The AI reportedly saves Netflix $1 billion annually through decreased churn and higher retention. Some companies use machine learning to predict when a customer is about to churn so the company can take action before the customer leaves. They achieve this by examining demographics, past user actions, and other data to predict future behavior. For example, if a customer's behavior indicates they may end their subscription to a music stream. In that case, the service may offer an exclusive deal — such as a temporarily discounted subscription rate — to keep them from churning. This type of machine learning helps companies keep high retention rates, which leads to increased revenue. Leading scoring predicts which leads are likely to convert into customers. This form of machine learning helps sales teams avoid manually sorting and reviewing thousands of leads every month. Teams can use a lead scoring model to automatically identify and prioritize the most promising, thus boosting productivity while reducing costs. Deep learning is a discipline of machine learning that uses algorithms and data to mimic the human brain to train a model. This discipline uses neural networks to learn a specific task. The neural networks comprise interconnected neurons that process data in the human brain and computers. Here are some ways marketers use deep learning in their strategies. Deep learning models can find patterns in data to initiate advanced segmentation. This allows marketers to easily and quickly identify the target audience for a campaign and predict potential leads. Deep learning can develop personalization engines that help marketers streamline the process of delivering hyper-personalized content. Examples of hyper-personalized materials are websites that show content that varies depending on who's browsing or push notifications for customers who leave without making a purchase. Marketers can use deep learning to predict a customer's actions by tracking how they move through the brand's website and how often they purchase. In doing so, AI can tell companies which products and services are in demand and should be the focus of future campaigns. Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence, while deep learning is a subset of machine learning. Machine learning means computers learn from data using algorithms to learn and act without being programmed — in other words, without human intervention. And deep learning uses algorithms and neural networks to train a model. The image below illustrates the relationship between artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning. Machine learning can also train on smaller data sets, while deep learning requires large amounts of data. Deep learning improves via its environment and by learning from past mistakes, but machine learning requires more human intervention to learn and correct itself. Here are some other key differences between machine learning and deep learning: As artificial intelligence further integrates into various industries and our daily lives, marketers must understand its basic principles and learn how to leverage it for their brands. Both deep learning and machine learning will create new possibilities in marketing by streamlining tedious processes and predicting audience behavior. AI can help marketers improve their strategies and ensure they're always on trend with consumers.
What is Machine Learning?
3 Common Ways Marketers Use Machine Learning
1. Predictive Recommendations
2. Churn Prediction
3. Lead Scoring
What is Deep Learning?
3 Common Ways Marketers Use Deep Learning
1. Segmentation
2. Hyper-personalization
3. Predicting Customer Behavior
The Difference Between Machine Learning and Deep Learning

 MikeTyes
MikeTyes ![How to Use AI in Content Marketing [Download Now]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/3e25e192-30c3-40c1-a7da-a4d054c9e157.png)












_2.jpg)




















