Health Experts Want You To Stop Tossing The Most Nutritious Part Of Your Fish
Don't miss out on this healthy source of fat and protein.


mbg Contributor
Emma Loewe is the former Sustainability and Health Director at mindbodygreen. She is the author of "Return to Nature: The New Science of How Natural Landscapes Restore Us" and the co-author of "The Spirit Almanac: A Modern Guide To Ancient Self Care." Emma received her B.A. in Environmental Science & Policy with a specialty in environmental communications from Duke University. In addition to penning over 1,500 mbg articles on topics from the water crisis in California to the rise of urban beekeeping, her work has appeared on Grist, Bloomberg News, Bustle, and Forbes.
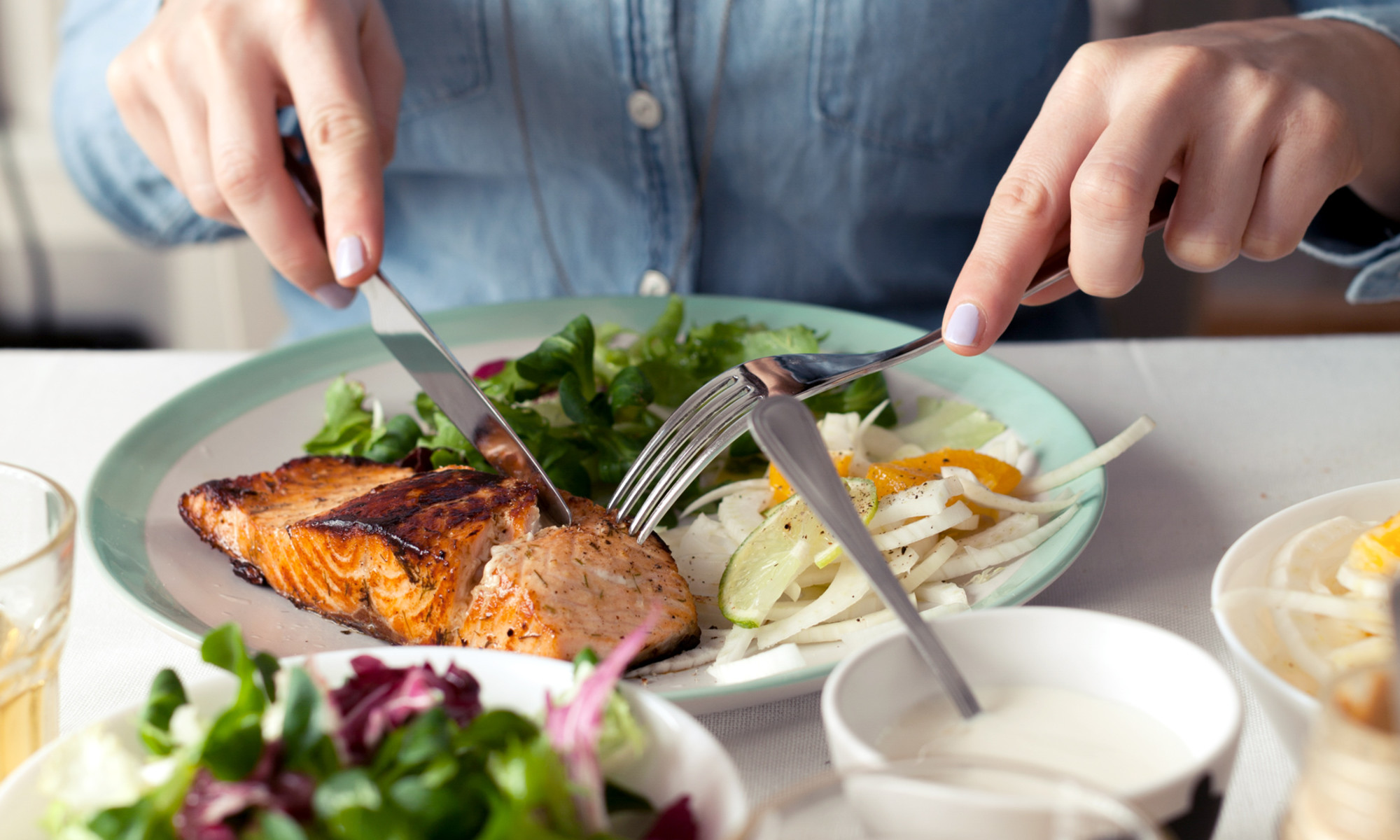
Image by Davide Illini / Stocksy October 29, 2024 Salmon skin is polarizing. While some people consider it the tastiest part of the fish, others are averse to its funky texture and salty bite. If you fall somewhere in the middle, you're probably wondering whether there are any health benefits to leaving the skin intact. As it turns out, there are! Salmon skin is a good source of healthy fats and proteins, and it helps lock in the nutritional value of your filet. Here, nutritionists explain why you should eat salmon skin and how to prepare it for maximum crispy deliciousness.
Salmon skin health benefits
Salmon skin is made of collagen, phospholipid molecules1, and mucus cells1 that give the fish structure and protect it from various pathogens. It's a good source of proteins and healthy fats, including the omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA.
These fatty acids are present in the skin itself and abundant in the fatty layer right underneath the skin known as the "fat line."
Many people don't get enough omega-3s in their diet, but it's essential for heart health and brain health. "People who have higher omega-3 intake have a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases2, basically across the board," Penny Kris-Etherton, Ph.D., RDN, LDN, FAHA, a professor of nutritional sciences at Penn State and past chair of the AHA Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health, tells mindbodygreen. "Beyond that, omega-3 fatty acids seem to play an important role in cognition3, especially in the young."
All this is to say, it's worth leaving the skin on if you can. It'll help take salmon—which is already a very healthy food—to the next level nutritionally. "I tell people, if [salmon] comes with skin on, leave it on—there's no need to remove it," says registered dietitian nutritionist Roxana Ehsani, M.S., R.D., CSSD, LDN.
If you end up cutting the skin off, do so carefully to protect the gold mine of healthy fats underneath it. Glide a sharp knife underneath the skin, getting as close to it as possible, before cooking your salmon. You can also use your hands to peel the skin off after the salmon is cooked—again, ensuring to protect the layer of flesh underneath.
Summary
Salmon skin is a healthy source of protein and omega-3 fatty acids. It's best to leave it on your salmon. If you do remove the skin, do so carefully to protect the nutritious fatty layer right underneath it.
If you've disliked salmon skin in the past, chances are it wasn't cooked properly. Try these techniques and recipes to ensure a crispy skin and juicy flavorful flesh:
How to prevent sticking:
If you've tried to make crispy salmon on the stovetop only to have the skin stick to the bottom, try this viral chef tip: Cut a sheet of parchment paper so it's slightly larger than your filet. Place some oil in your pan, then place the parchment paper on top of it. Add more oil on top of the paper and cook your salmon as normal. The parchment paper will form another barrier between the skin and your pan, preventing any accidental stickage.
One argument against eating salmon skin is that it contains toxins from the fish's environment. While it's true that skin does hold on to lipophilic (fat-loving) organic contaminants7 like PCBs, this won't be an issue as long as you're buying salmon from clean waters.
Farmed salmon has a higher concentration of pollutants than wild-caught salmon in some cases, but again it depends on where the fish comes from. While wild-caught Chinook salmon from Alaska tends to be lower in PCBs8 and pesticides than farmed salmon, wild Atlantic salmon can actually be up to three times higher in PCBs, mercury, and arsenic9 than farmed salmon, according to research.
To be safe, look for skin-on salmon that is certified by the Marine Stewardship Council (which monitors illegal fishing in sketchy waters) and/or the Monterey Bay Aquarium's Seafood Watch. In the U.S., wild-caught Pacific salmon from Washington and Alaska consistently ranks as the best choices, thanks to the region's clean, cold waters.
Summary
Salmon skin can trap contaminants that are present in the fish's environment. If you're concerned about things like PCBs and pesticides, buy salmon that's been certified by the Marine Stewardship Council or ranks highly on the Monterey Bay Aquarium's Seafood Watch.
FAQ
Is it healthy to eat wild-caught salmon skin?
Yes! Salmon skin is rich in healthy protein and omega-3 fats, and it can help lock in the nutrients of your fish. Look for wild-caught Pacific salmon, as its skin tends to be lower in contaminants like PCBs and pesticides.
How should you cook salmon skin?
Salmon skin is crispy and delicious when cooked under the broiler or lightly fried in healthy oil with a high smoke point on the stove.
Is salmon high in mercury?
No, salmon is a lower-mercury fish since it falls pretty low on the aquatic food chain. It's considered a safer choice than larger fish like tuna in this regard, especially for those who are nursing or pregnant.
The takeaway
Salmon skin is packed with healthy fats and proteins, making it a nutritious addition to your plate. The next time you're tempted to remove it, fire it up under the broiler or in a hot skillet instead and enjoy the crispy, crunchy health food.

 ShanonG
ShanonG