Run An Ecommerce SEO Audit in 4 Stages [+ Free Workbook]
An ecommerce SEO audit is a 360-degree review of your website’s SEO performance in terms of technical setup, on-page optimization, site structure, backlink profile, and more. Think of it like a routine check-up for your online store. Instead of...
![Run An Ecommerce SEO Audit in 4 Stages [+ Free Workbook]](https://api.backlinko.com/app/uploads/2025/06/ecommerce-seo-audit-featured-image.png)
An ecommerce SEO audit is a 360-degree review of your website’s SEO performance in terms of technical setup, on-page optimization, site structure, backlink profile, and more.
Think of it like a routine check-up for your online store.
Instead of waiting for traffic to drop or sales to slow down, you can proactively find and fix problems before they spiral into revenue leaks.
Done right, an SEO audit helps you:
Identify ways to improve rankings and user experience Detect issues affecting your organic performance Protect and sustain long-term growthMore importantly, this audit creates an SEO strategy grounded in data, not guesswork.
In this guide, I’ll break down a 4-stage process for conducting an ecommerce SEO audit.
I’ve also prepared a free audit workbook to help you document findings, prioritize fixes, and drive measurable results.
Core Components of an Ecommerce SEO Audit
Unlike a traditional website audit, a well-rounded SEO audit for ecommerce focuses on five key components.
1. Technical SEO
Technical SEO ensures search engines can find, crawl, and index your website.
It prevents critical issues like:
Slow page speed Duplicate content Broken internal links Wasted crawl budgetThis is important for ecommerce websites since URL structures and large inventories can create crawlability concerns.
2. On-Page SEO
On-page SEO allows search engines to understand the content and purpose of each page on your site.
A strong on-page setup includes title tags, meta descriptions, headers, and more.
It also covers internal linking patterns to ensure link equity flows to your most important pages.
3. UX and Performance
This part of the audit evaluates:
Mobile responsiveness Core Web Vitals Overall usabilityIt helps optimize your UX, so visitors can easily navigate your store, stay longer, and convert.
4. Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO looks at external signals that influence your site’s authority, such as:
E-E-A-T Backlinks Online reviews Brand mentionsPut simply, off-page SEO covers everything outside your website that shows search engines you’re a trustworthy brand.
5. Competitive Analysis
Competitive analysis assesses how your site stacks up against other brands.
Benchmarking your performance against competitors helps you find gaps and opportunities to outrank competitors on organic search.
Now that you know what to audit, let’s walk through how to do it — step by step.
We’ll break it down into four practical stages that map back to the core components.
Download our free audit workbook to better understand every step and implement them for your business.
Stage 1: Can Google Find My Store and Products?
A good ecommerce SEO audit starts by checking whether search engines can actually find, crawl, and index your pages.
No matter how well you optimize pages, they won’t rank or drive traffic if they’re invisible to search engines.
In short: This stage lays the groundwork for everything else that follows.
Here’s what to look for in this stage:
Check If Your Pages Are Indexed in Google
A web page becomes visible in search results and starts ranking only after it’s added to a search engine’s index.
Start your audit by heading to Google Search Console (GSC) to review the index status for your pages.
Open your GSC dashboard and go to the “Pages” report under the index section.
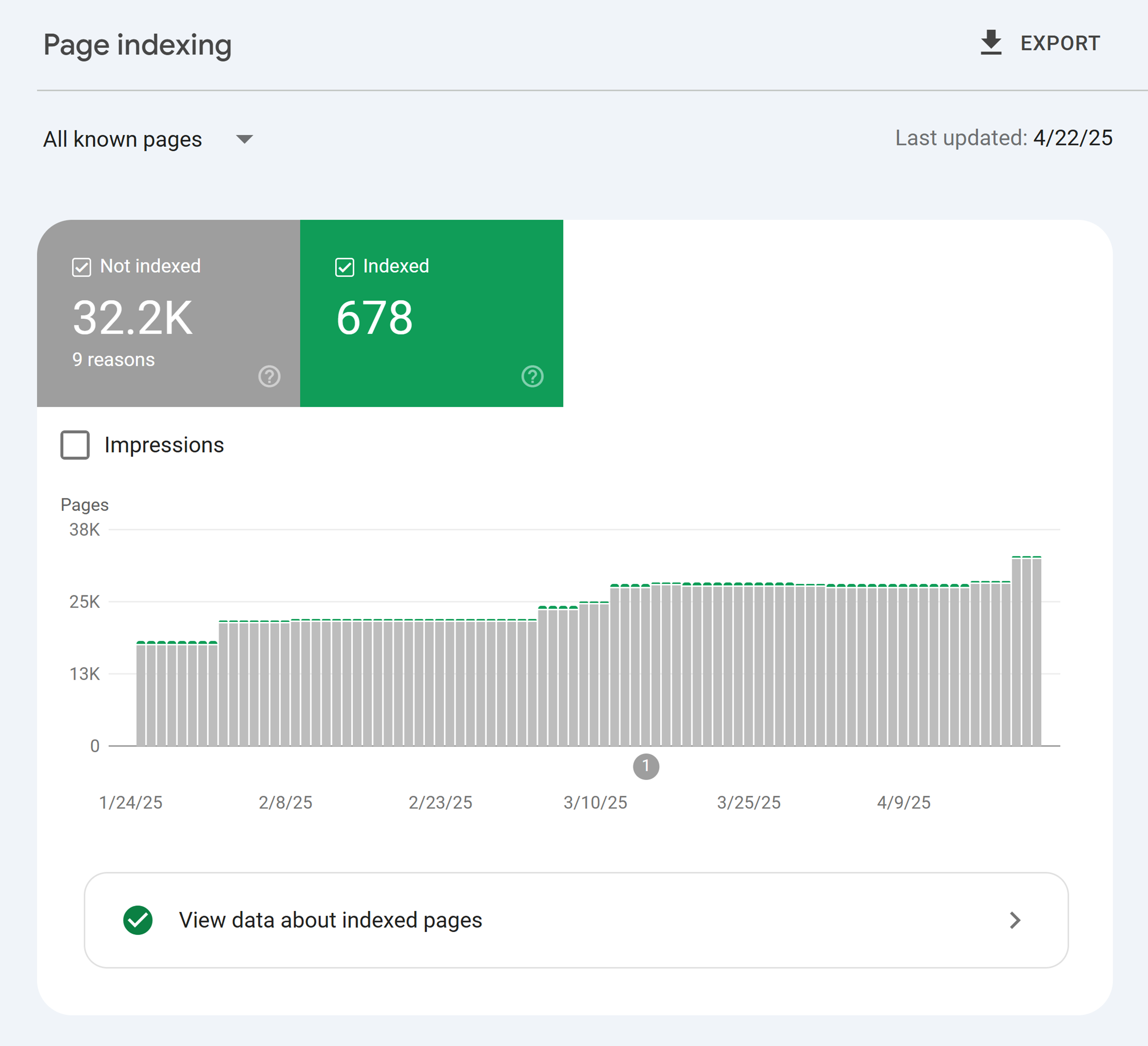
The report will list all non-indexed pages with specific reasons:
Discovered – currently not indexed Crawled – currently not indexed Excluded by ‘noindex’ tag Page with redirect
If pages aren’t added to Google’s index, it could be due to issues with page quality, crawl budget, or duplicate content.
Use the “URL Inspection” tool to learn why a page isn’t indexed yet.
In this example, the URL has been discovered but not indexed.

Press the “Request Indexing” button to manually submit a page for indexing.
Ensure Key Pages Are in Sitemap and Crawlable
A clean, accurate sitemap helps search engines discover your most important pages.
Your sitemap should include hierarchical URLs for all types of pages, like categories, products, product versions, and more.
Here’s what an ecommerce store’s sitemap looks like:

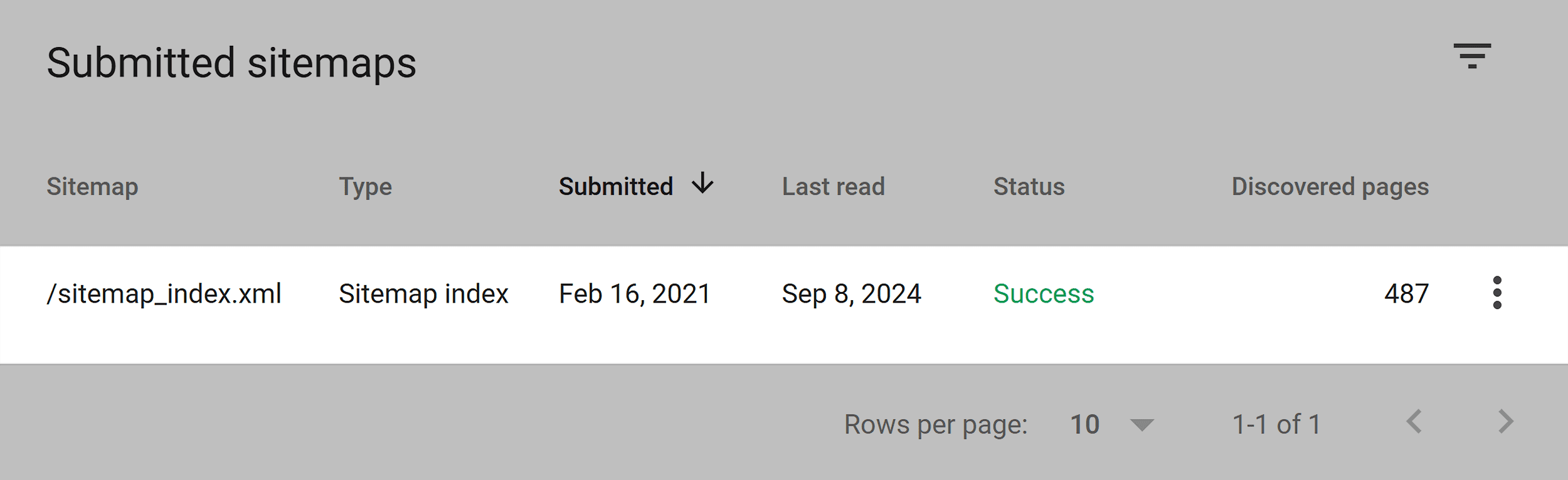
Check whether your sitemap is updated automatically whenever you add new pages.
Open Google Search Console and go to the “Sitemaps” section.
This report shows when your sitemap was last submitted and read by Google. It also highlights the status and number of URLs discovered.
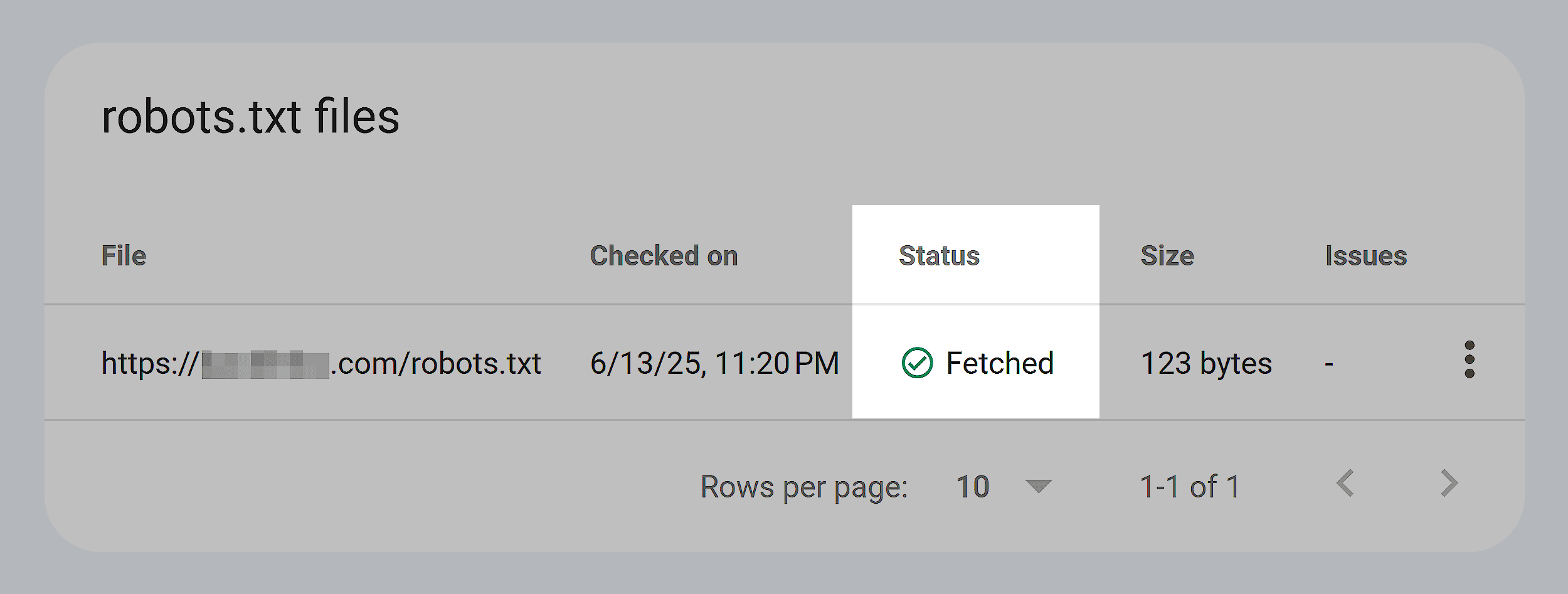
At the same time, check your robots.txt file.
This file tells search engines which parts of your site they shouldn’t crawl.
Go to yoursite.com/robots.txt to see if you’re unintentionally blocking any pages or folders.
You can use Google’s robots.txt Tester to validate your setup.
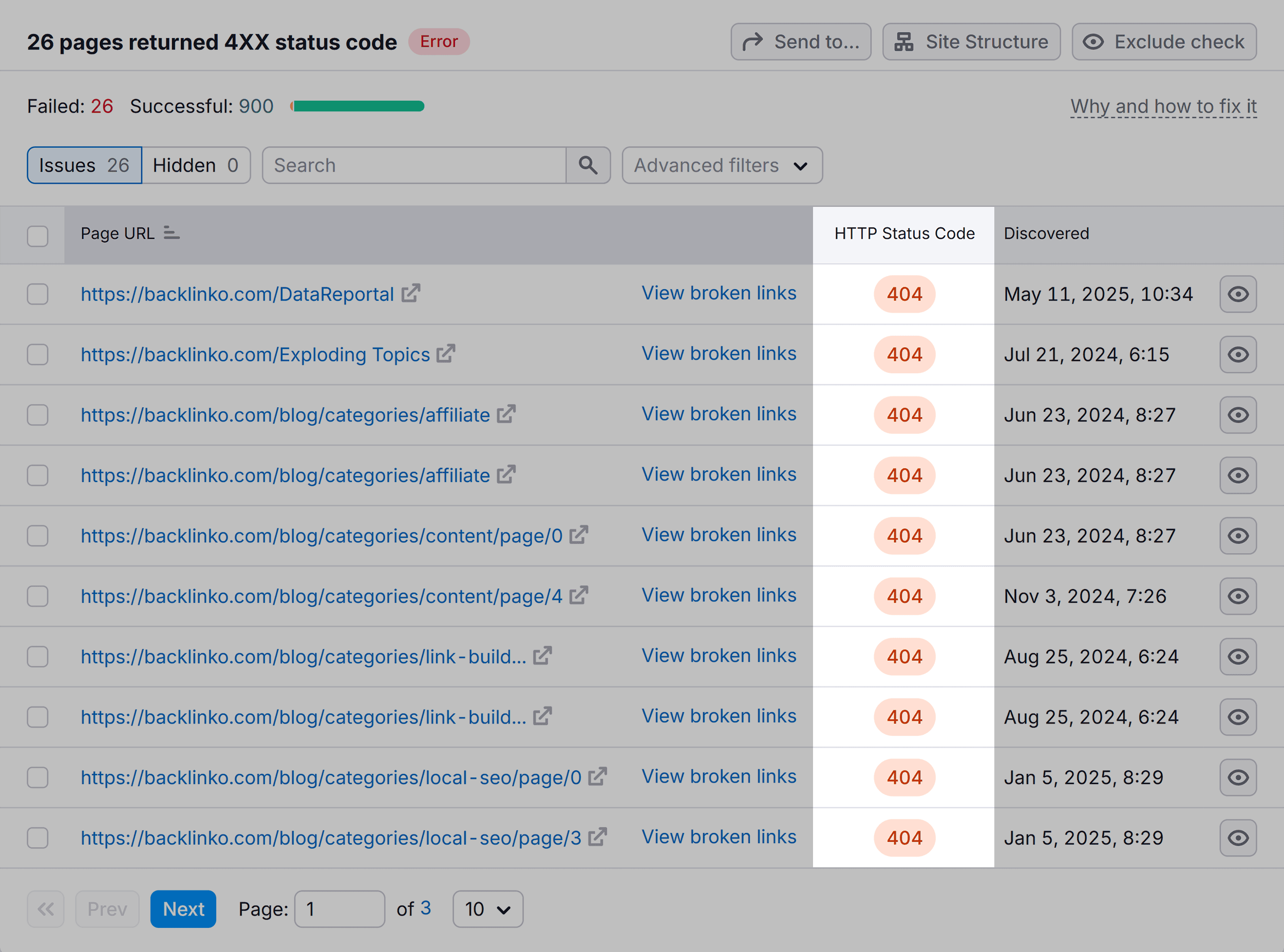
Identify and Fix 4xx/5xx Errors That Hurt Visibility
Check your HTTPS status codes to discover pages with 4xx or 5xx errors.
These errors explain why search engines can’t access your pages.
Use tools like Screaming Frog and Semrush Site Audit to check your HTTPS status codes.
Here’s how to do it with Semrush:
Go to the Site Audit tool, and add your domain.
Follow the steps in this guide to configure and customize your Site Audit project before running the crawl.
When you’re ready, hit “Start audit.”
Once the results are in, navigate to the “HTTPS” part of the audit overview.
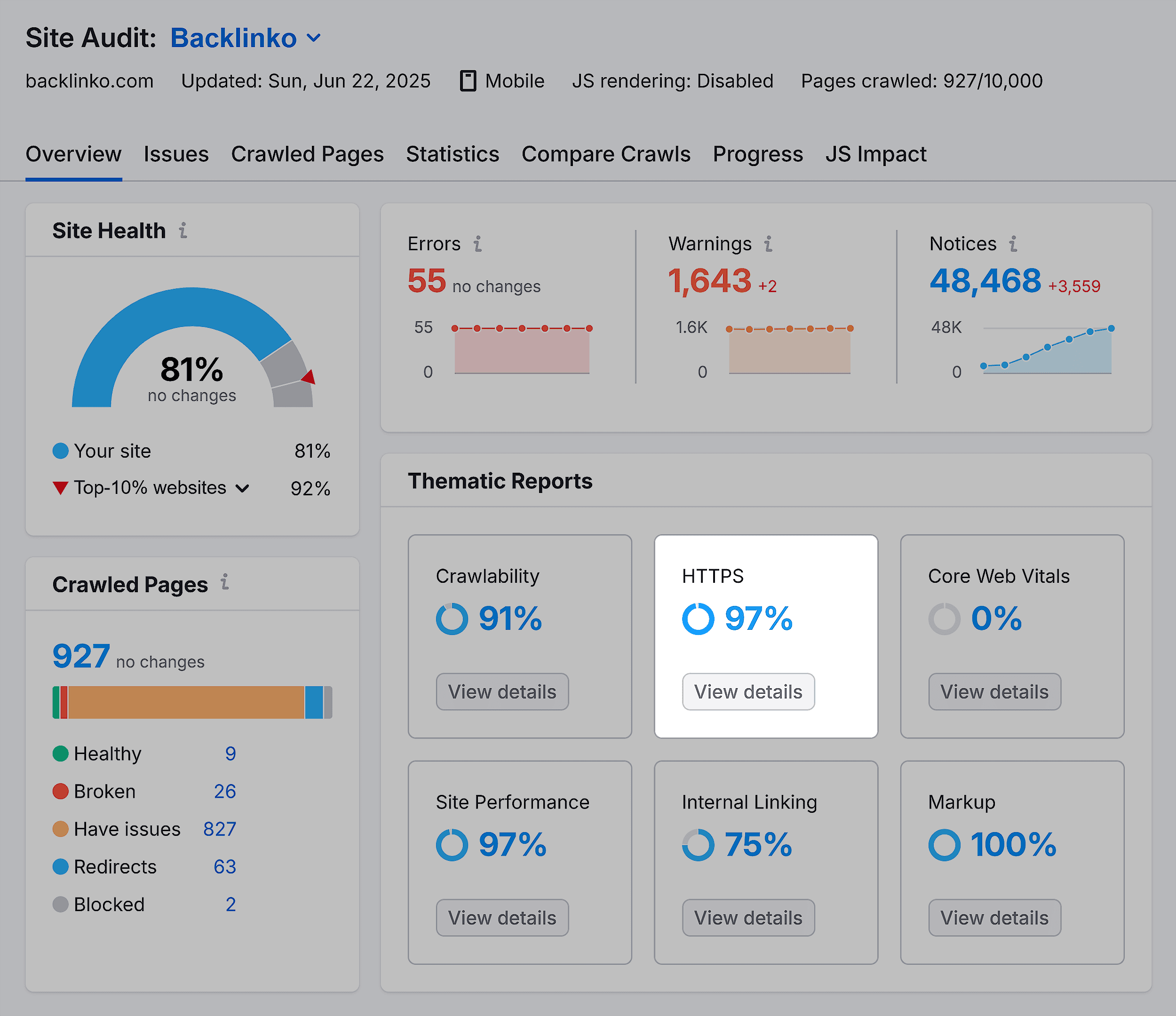
Here, you’ll see any issues with HTTPS status codes and how to fix them.
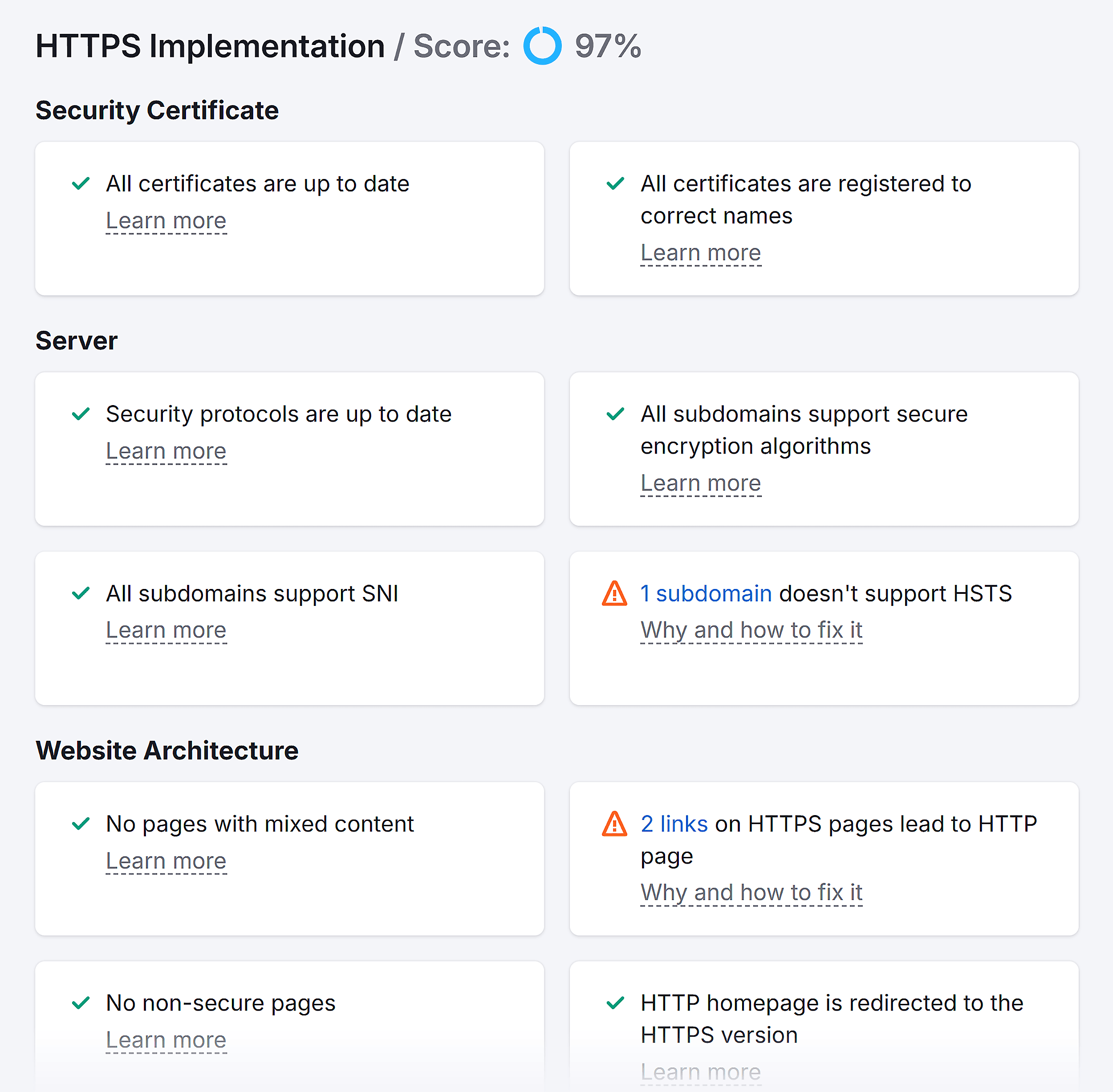
You can also go to the “Crawled Pages” section in your report and filter data based on status codes.
For example, I applied the “Issue Status” filter to find pages with broken or blocked status codes.
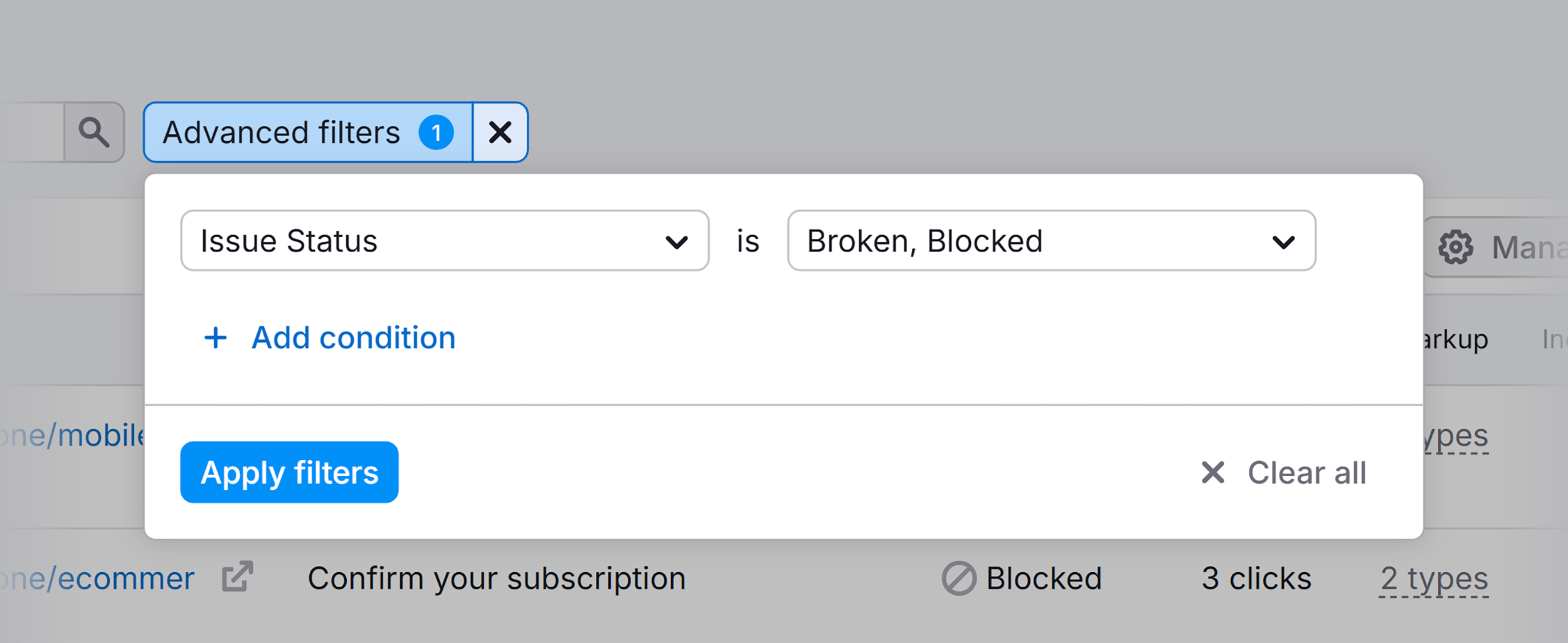
Here are the filtered results showing all the pages meeting this criteria:
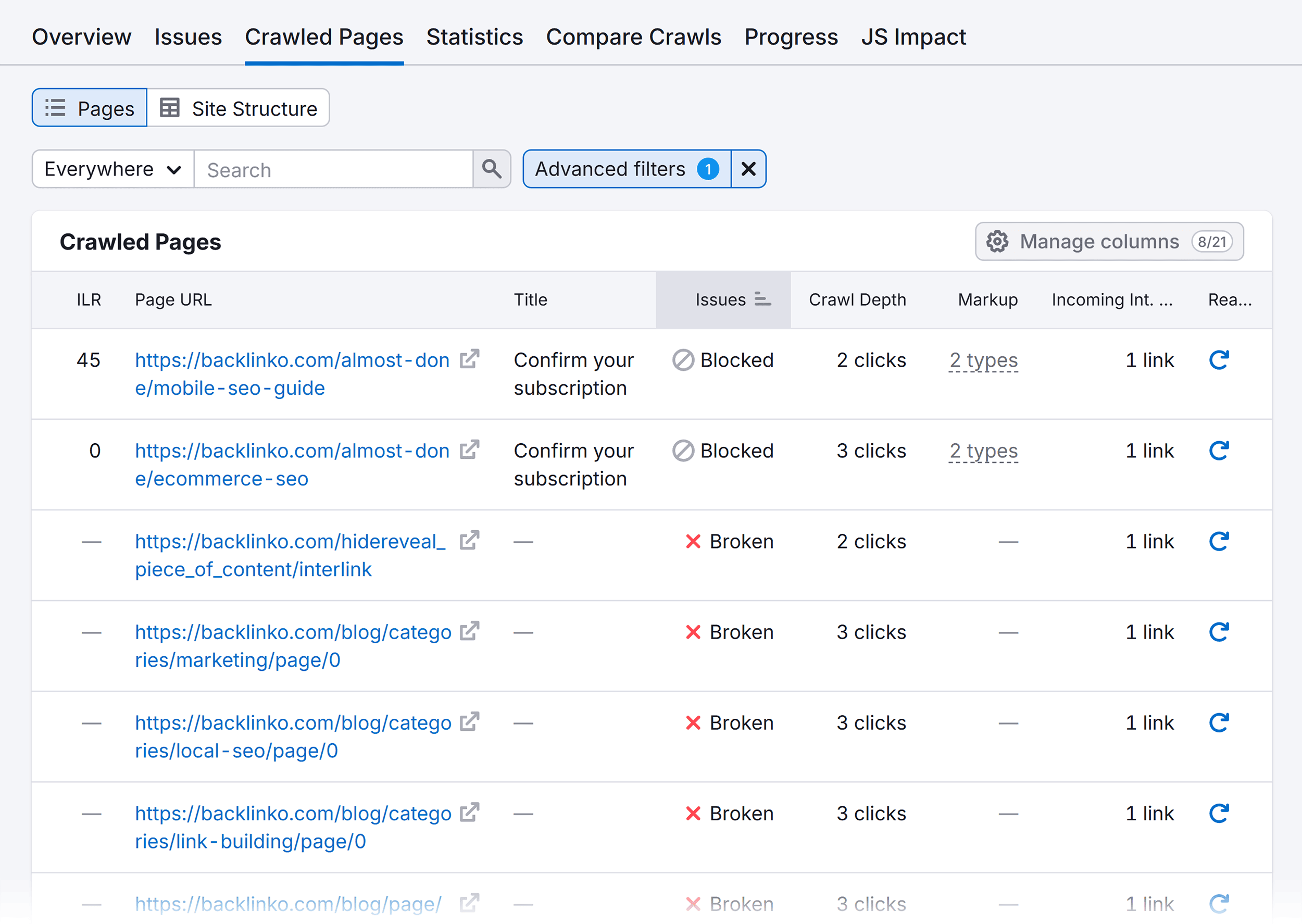
Review all the pages showing errors and plan ways to fix each type of error.
For example, if a page showing the 404 error is outdated and no longer needed, you can remove it from your sitemap.
Use Canonical Tags to Avoid Duplicate Content
Ecommerce sites often struggle with duplicate content due to multiple product variants or filtering options.
This can confuse search engines and affect your rankings.
That’s why canonical tags are important to tell search engines your
preferred version of a page.
For example, the athleisure brand Alo Yoga uses canonical tags for color variants, such as:
Steel grey: airlift-intrigue-bra-steel-grey Anthracite: airlift-intrigue-bra-anthraciteTo prevent search engines from seeing these pages as duplicate content, each product variant includes a canonical tag pointing to a single, main product URL.
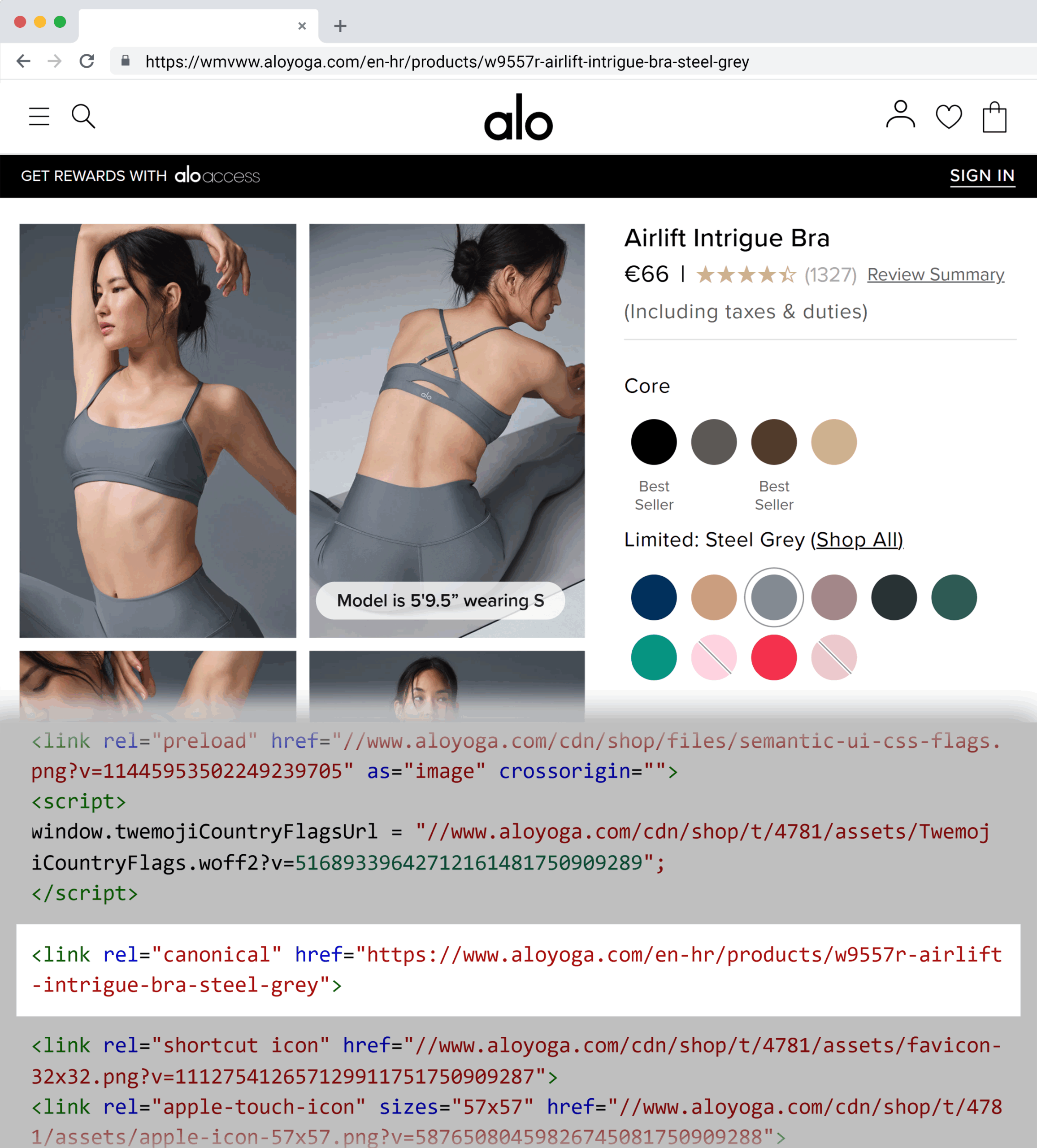
Use free canonical checker tools like Detailed to check whether all product variants are canonicalized to the main URL.
Stage 2: Do People Discover and Visit My Pages?
Your next step is optimizing your pages to rank well and appeal to searchers.
Focus on improving how your listings appear in search engine results pages (SERPs) and matching them to the right search intent.
This optimization can boost impressions, traffic, and, ultimately, revenue.
Here’s what to check in this stage:
Optimize Titles and Meta Descriptions for Clicks
Title tags and meta descriptions are often the first thing searchers see.
Are yours compelling enough to earn the click?
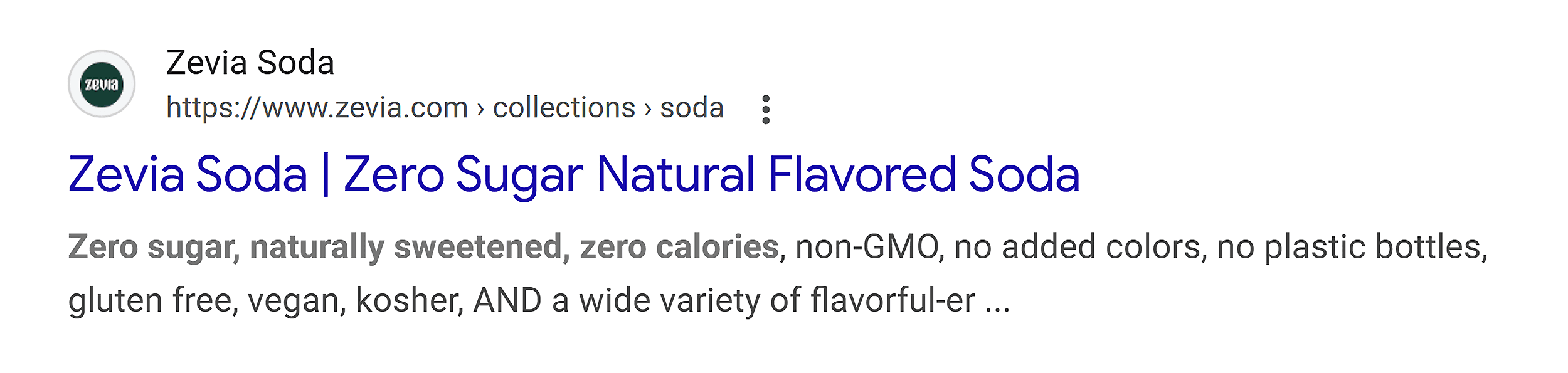
For example, when I search for “healthy soda,” I find this page by Zevia Soda.
The title tag emphasizes its main value proposition: Zero Sugar Natural Flavored Soda.
And the meta description doubles down on this, highlighting zero calories and the variety of flavors.
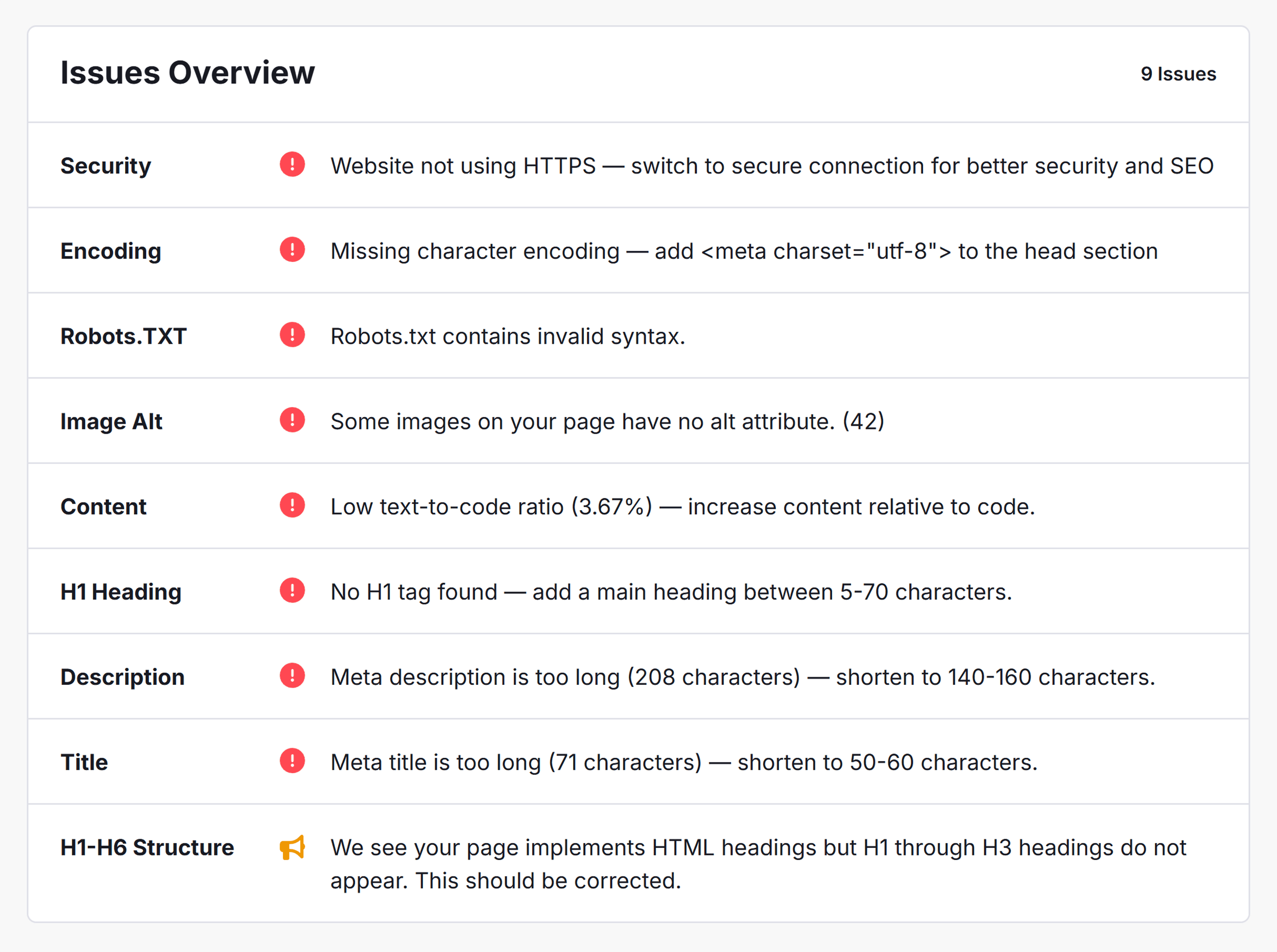
Use Backlinko’s free SEO checker to find any critical issues here.
Add any page and hit “Check SEO” to get started.

Here’s how the tool flags issues related to your page’s title, headings, meta description, and other elements:
Add Structured Schema for Rich Results
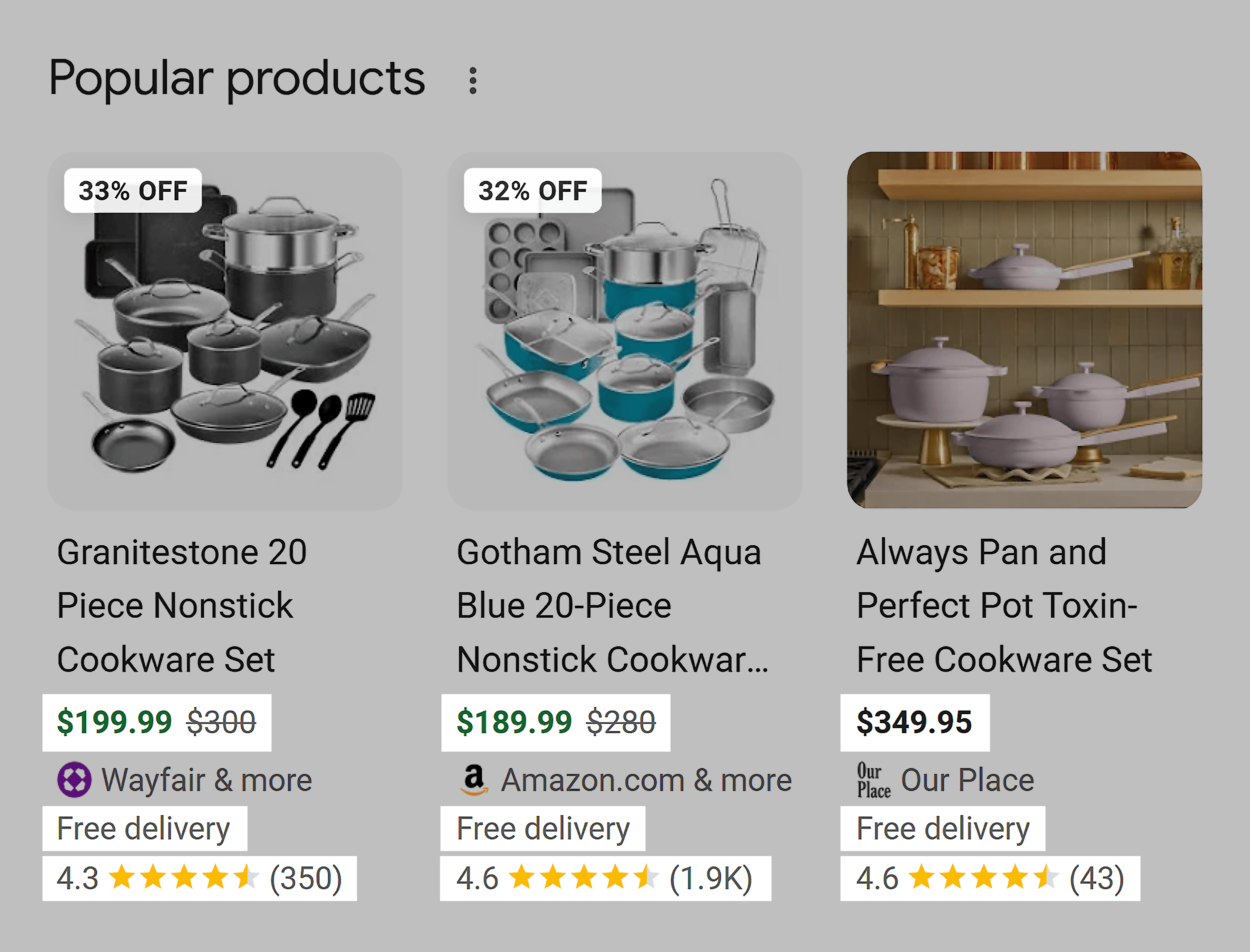
Schema markup with tags like Product, Review, and FAQs can enhance your listings with rich snippets.
Visual cues like pricing, ratings, discounts, and delivery details simplify the shopping experience and can boost CTR for your pages.
Here’s how they look:
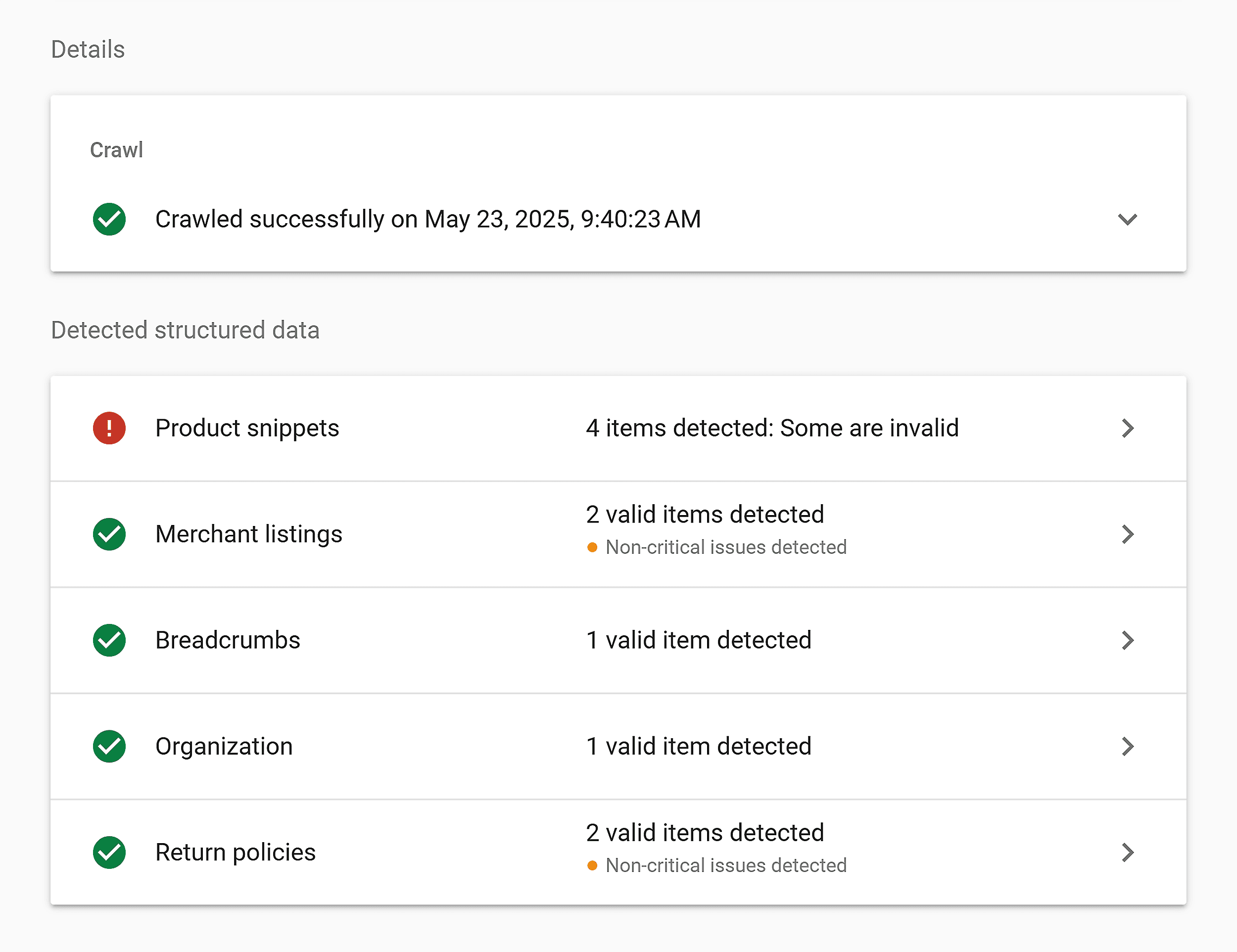
Google’s Rich Results Test is a helpful tool to validate your schema markup with all these elements.
For example, I ran a test for a hair oil product page to see what kind of rich snippets it has.
The report indicated that this page has four snippets, but some of them are invalid.
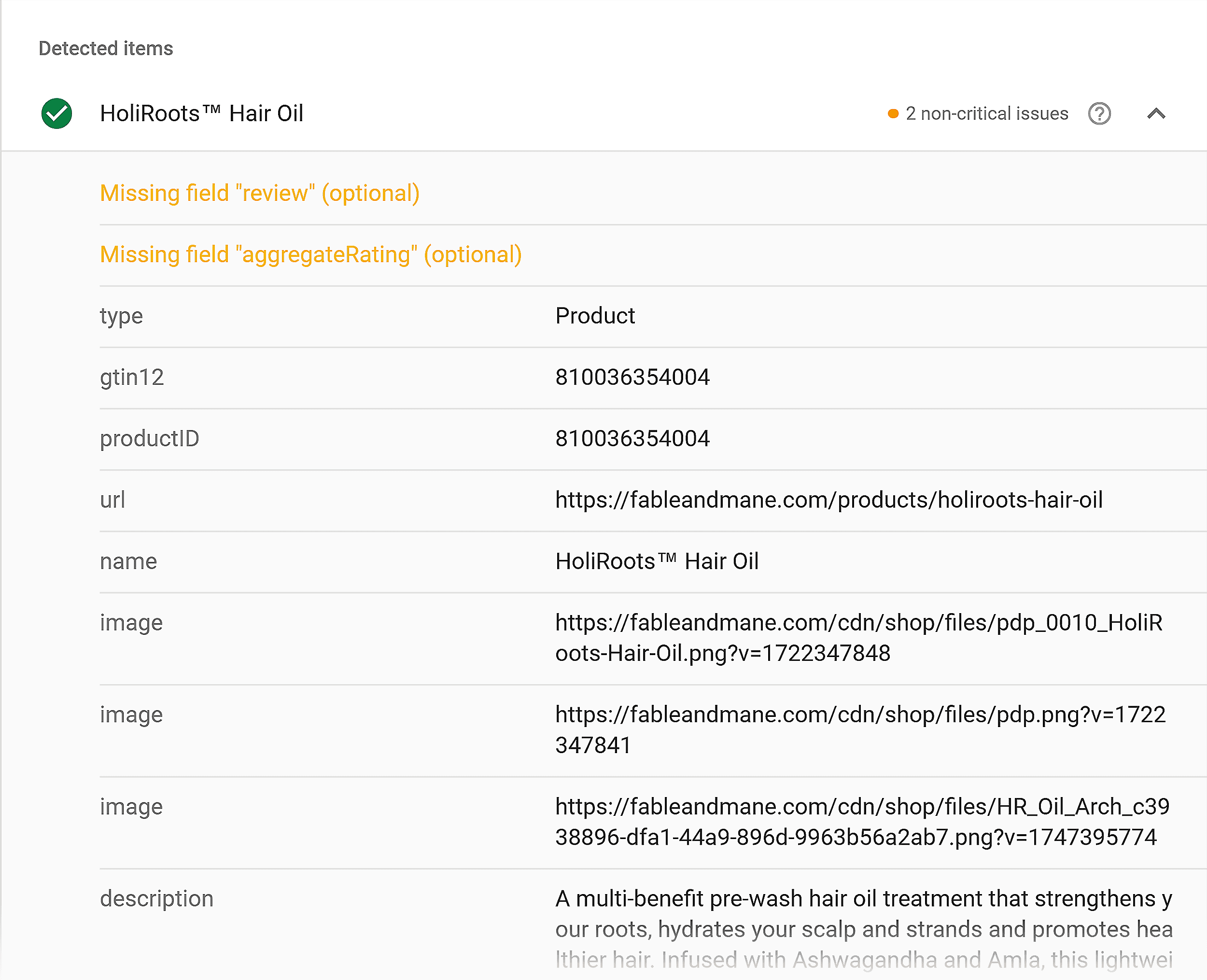
On further analysis, I discovered that one of the snippets is missing the review and rating fields.
This product listing won’t qualify for full rich results unless you add such required fields to your schema.
That’s how you can review schema markup for individual pages.
To check the schema for all your pages, revisit your Site Audit report on Semrush.
In the Overview section, you’ll see data for the “Markup” category.
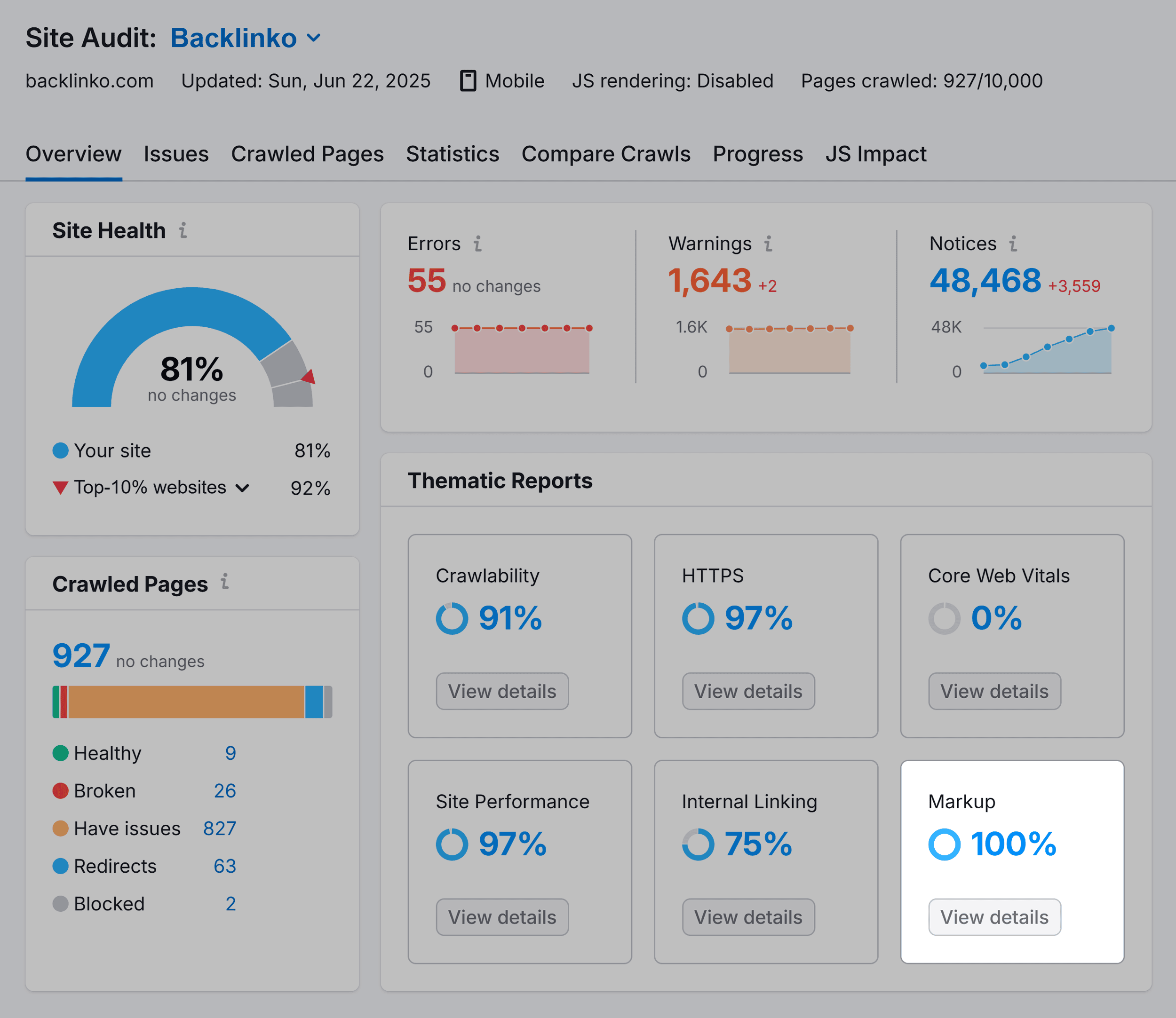
Press “View details” to get deeper insights about your site’s schema.
For example, the report shows:
Number of pages with markup Kind of schema markup for all pages Type of structured data available for your pages.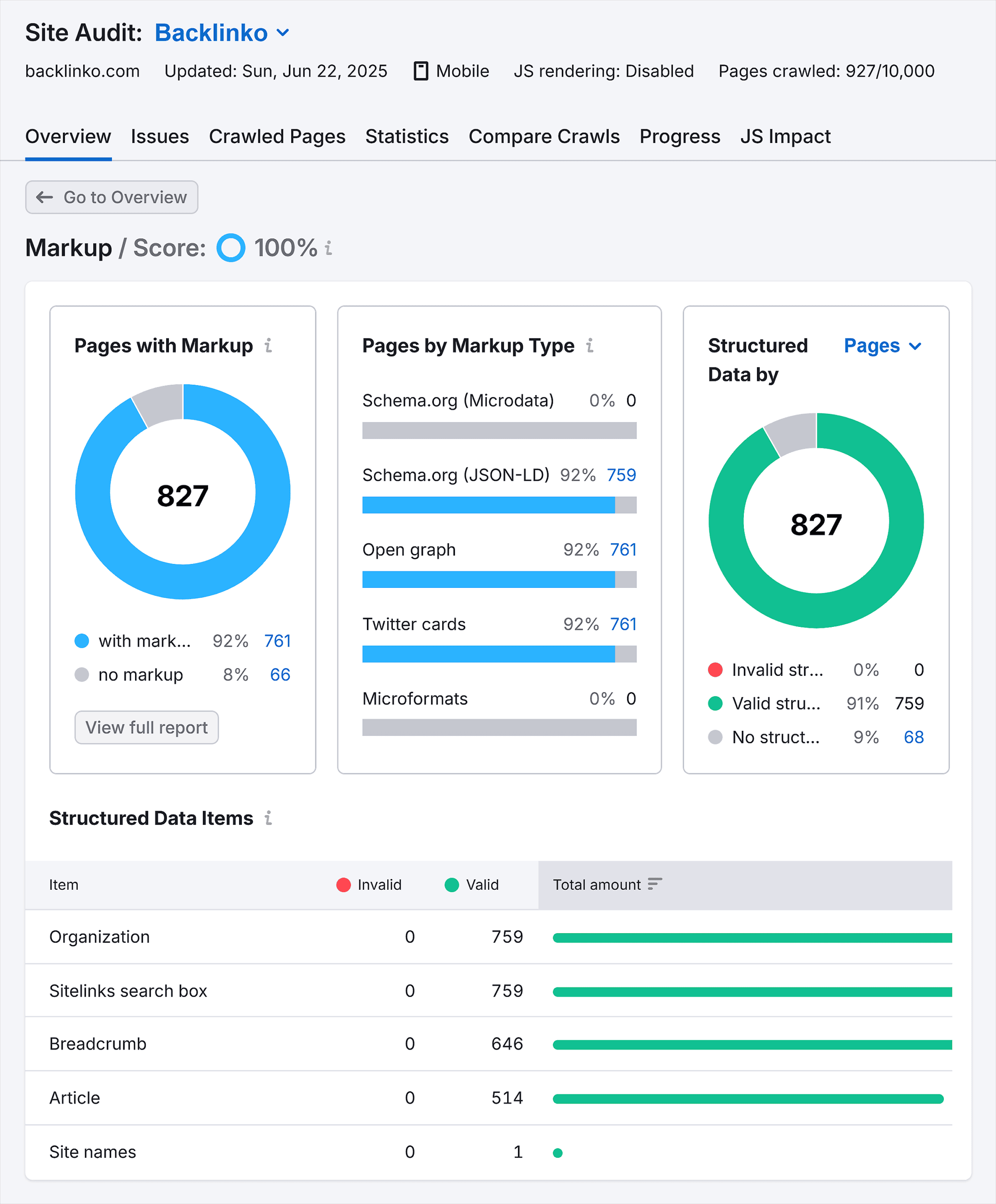
Map Target Keywords to the Right Pages
Another crucial task in this stage is checking whether your keywords align with the actual user behavior and intent.
Map each page to its target keywords and search intent.
Evaluate this map to find pages targeting the wrong keywords or intents. Here’s an example:
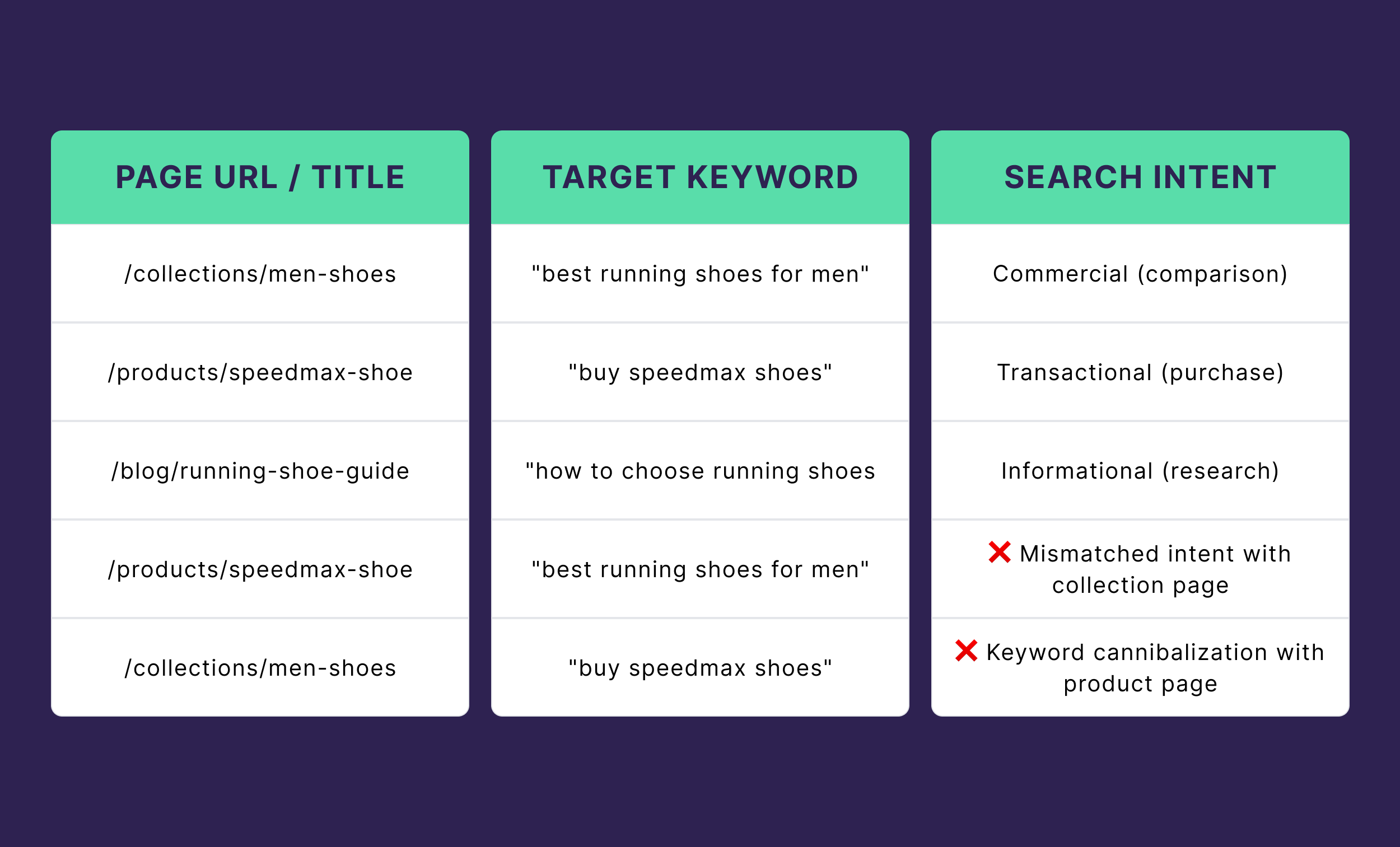
You can also run a Google search for your low-ranking keywords and see the kind of pages appearing in SERPs.
Then, compare these top-ranking pages with your content to find areas of improvement.
Optimize Images and Add Alt Text
Your online store can drive significant traffic by optimizing images and multimedia assets.
Image optimization can:
Improve search visibility Rank for visual search terms Help search engines understand your contentI searched “blue ceramic dinner plates” to see this in action.
Below the usual product listings, the images section also shows product listings for people to browse more options.
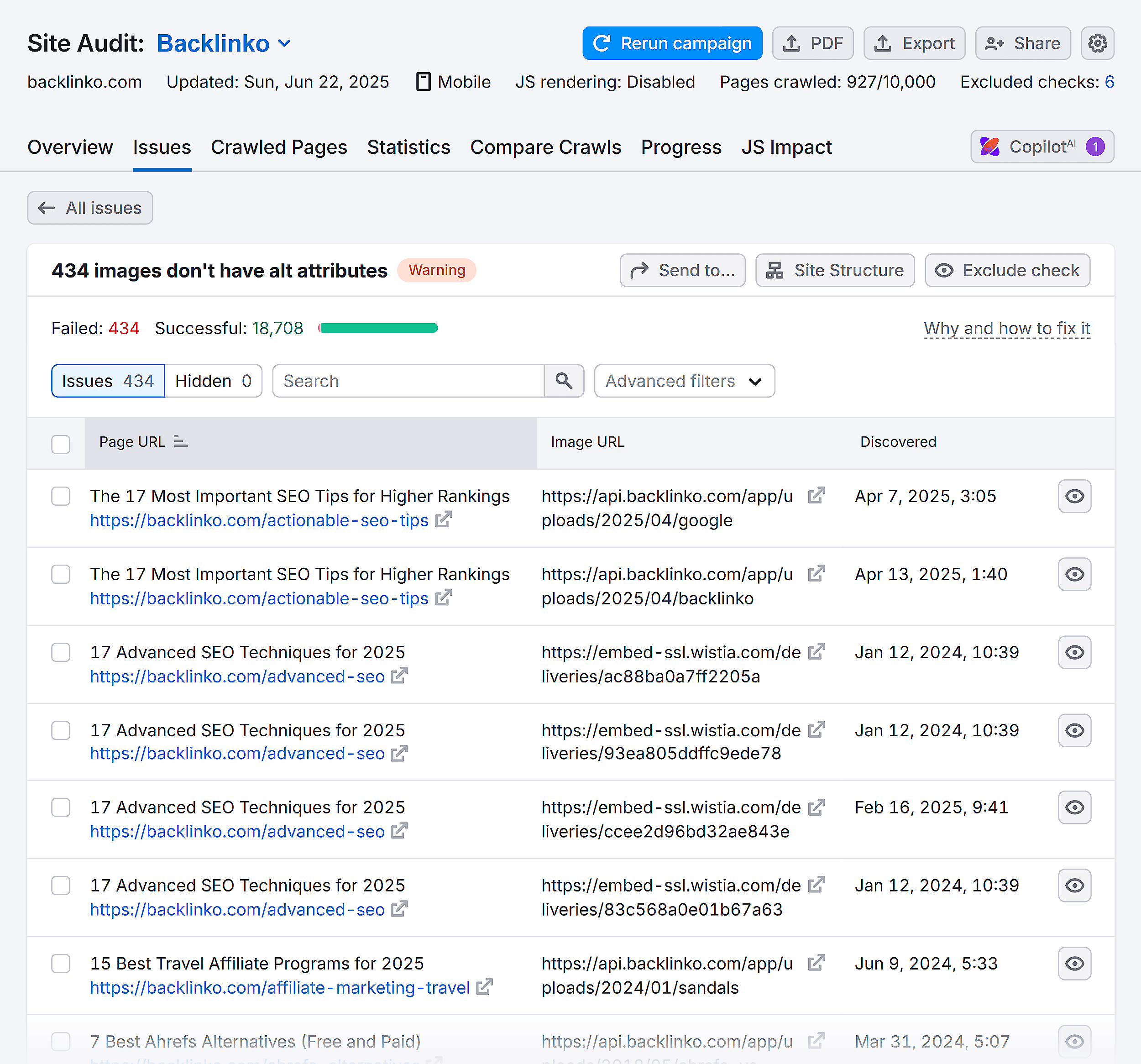
As a part of your audit, check whether your images have relevant file names and keyword-rich alt text.
Semrush’s Site Audit report will also flag images missing alt text attributes.
Stage 3: Are Visitors Staying and Buying?
The next part of your audit explores how shoppers interact with your site and whether they convert or bounce.
You want to know:
Are people spending enough time in your store? Are they dropping off after viewing one product? Is something in the user journey causing friction?If people constantly leave your store without buying, your site’s UX might need help.
Here’s what to check in this stage:
Improve Load Times and Mobile Usability
Slow pages = Poor experience = Higher bounce rate.
An ecommerce site audit reveals which pages are loading slowly and need your attention.
It also tests your website’s responsiveness across different screens, especially mobile devices.
Google PageSpeed Insights is a trusted tool for evaluating your store’s user experience based on Core Web Vitals:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading speed First Input Delay (FID): Tracks time to interactivity Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Checks visual stability during loadHere’s an example report I generated:

This page failed to meet the benchmark for a good user experience for mobile devices.
Remember to check the page speed specifically for mobile since Google’s mobile-first indexing approach prioritizes mobile devices.
Simplify Page Design and UX
Design plays a crucial role in instilling confidence among potential customers.
When you deliver a frictionless user experience with good design elements like CTAs, trust badges, and accessible navigation, users stick around for longer.
This sends powerful signals to search engines and improves SEO metrics like dwell time, page views, bounce rate, and more.
In fact, our ranking factors study reveals that pages with a higher “time on site” tend to rank higher in Google.
Fix Pages Targeting the Same Keyword
Ecommerce sites often have multiple pages targeting the same keyword, like category filters or similar products.
As a result, many pages compete against each other for a keyword.
Since search engines can’t decide which page to rank higher, your rankings are diluted.
Refer to your Site Audit report to find errors pointing to duplicate content and identify:
Near-identical pages competing for the same keywords Variants (color, size) are published as separate URLsAdd Internal Links to Boost Relevance
Strategic internal links create logical paths between pages, keep users engaged longer, and distribute authority.
So, even if searchers land on one of your blog posts, they can find their way to a relevant product page and make a purchase.
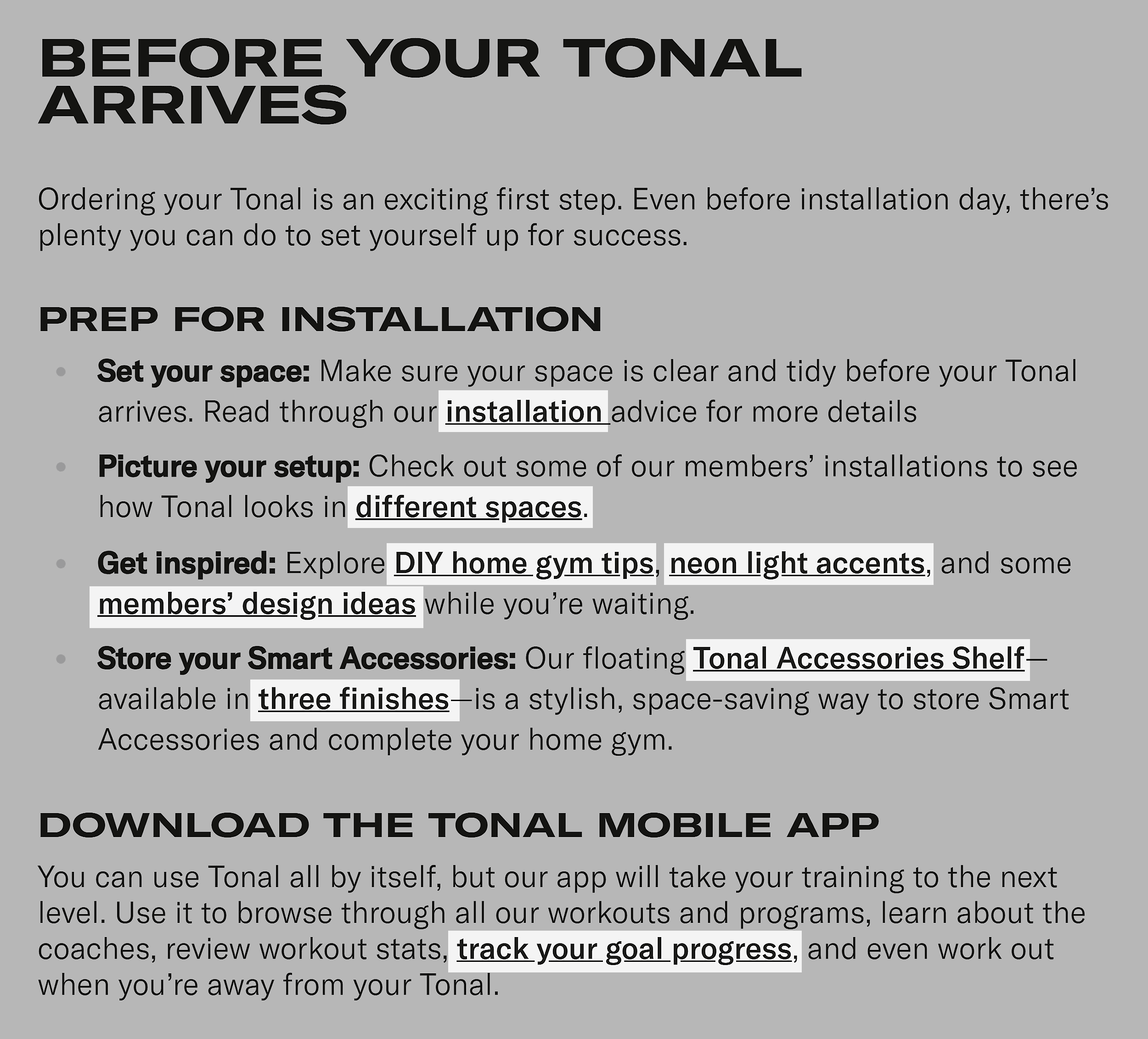
Here’s how Tonal, a fitness equipment brand, does this in its articles:
Stage 4: Where Am I Behind My Competitors?
In the final stage of your ecommerce SEO site audit, broaden the scope and look at the competition.
If a competitor ranks above you for key terms or earns better backlinks, they’re claiming traffic that could be yours.
So, understand your competitive landscape to identify missed opportunities for your SEO efforts.
Audit and Strengthen Your Backlink Profile
Backlinks are another critical ranking signal.
If you operate in a competitive category, backlinks can have a decisive impact on your organic visibility and traffic.
Start with a backlink audit to see where you currently stand.
This audit will help you discover:
High-authority domains are already linking to your site Toxic or spammy links that may hurt your rankings Pages earning the most backlinks (and why) Opportunities to reclaim or build new backlinksYou can also benchmark your backlink profile against competitors and plan the next steps.
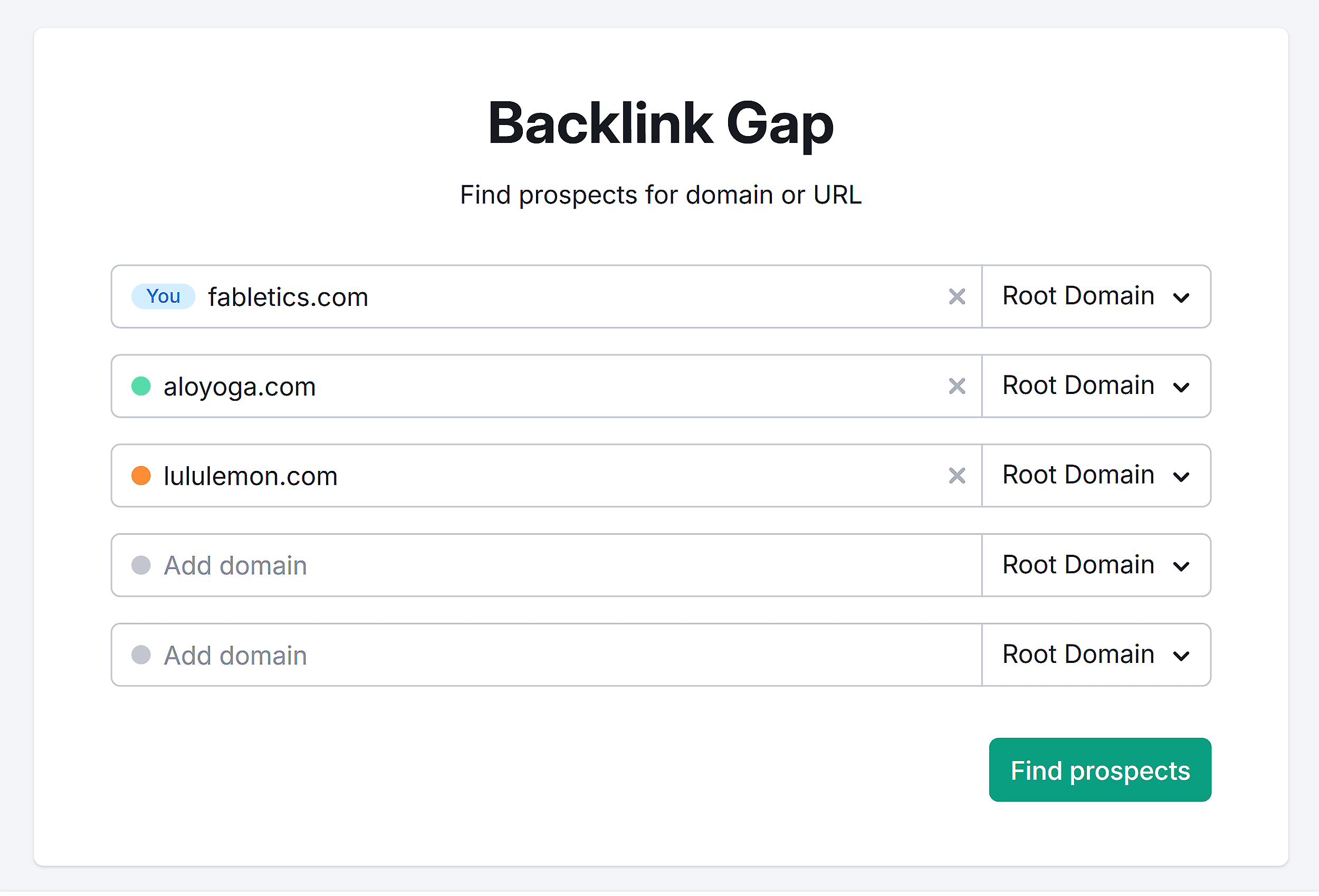
I used Semrush’s Backlink Gap tool to compare Fabletics’ backlink profile with two competitors.
You can add up to four main competitors and press “Find prospects.”
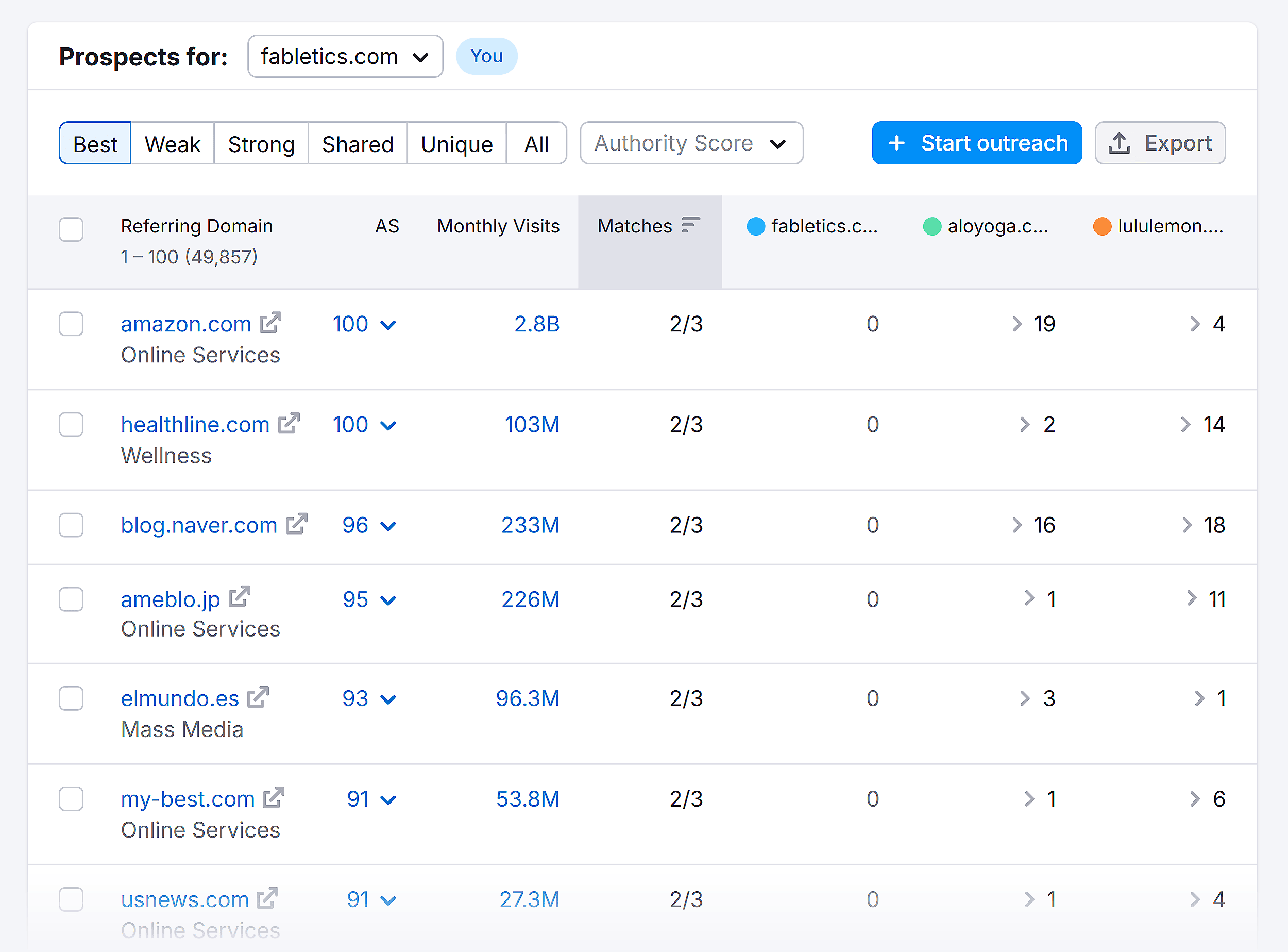
The tool will analyze every site’s backlinks and show you curated prospects for your site.
You can find the best, strong, weak, shared, and unique domains that link to your competitors but not to you.
For Fabletics, the tool suggests domains like healthline.com, usnews.com, americanexpress.com, and more.
Use this data to prioritize outreach or content partnerships for your link-building efforts.
Uncover Keyword Gaps and Ranking Opportunities
Use tools like Semrush’s Keyword Gap or SimilarWeb to see which keywords your competitors rank for but you don’t.
This can help you:
Identify new content opportunities Strengthen underperforming pages Reclaim rankings for keywords you’ve lost visibility onFocus especially on high-intent, bottom-funnel terms that drive conversions, not just traffic.
For example, let’s say a competitor ranks for “buy minimalist running shoes.”
If you sell the same type of product but don’t appear in search, that’s a clear gap — and a chance to win back visibility.
How to Prioritize SEO Issues You Identify in a Site Audit
When you’re looking at a laundry list of issues from your SEO audit, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed.
Everything looks important. Where do you even begin?
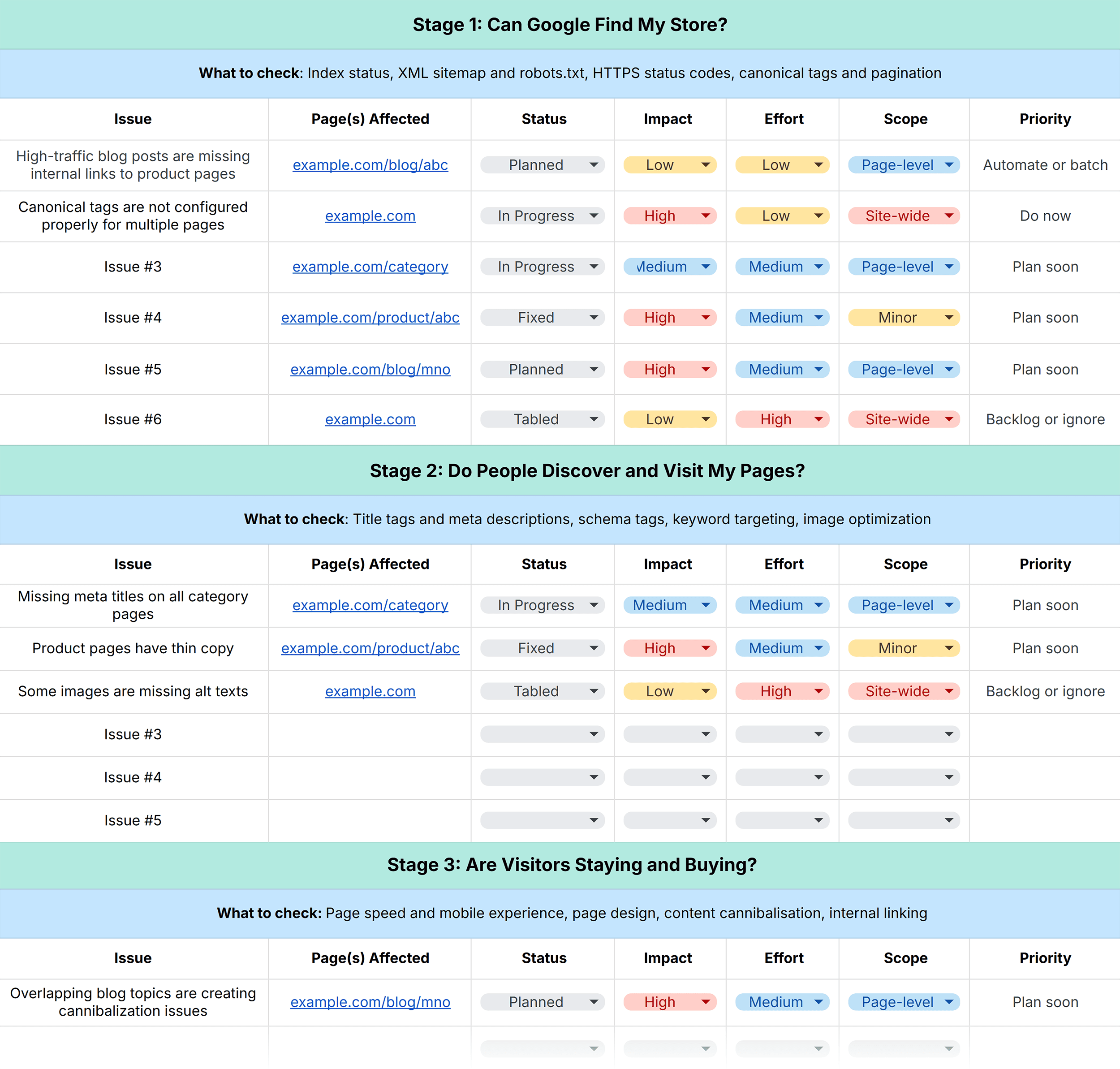
Our SEO audit workbook automatically calculates the priority level based on every issue’s impact, effort, and scope.
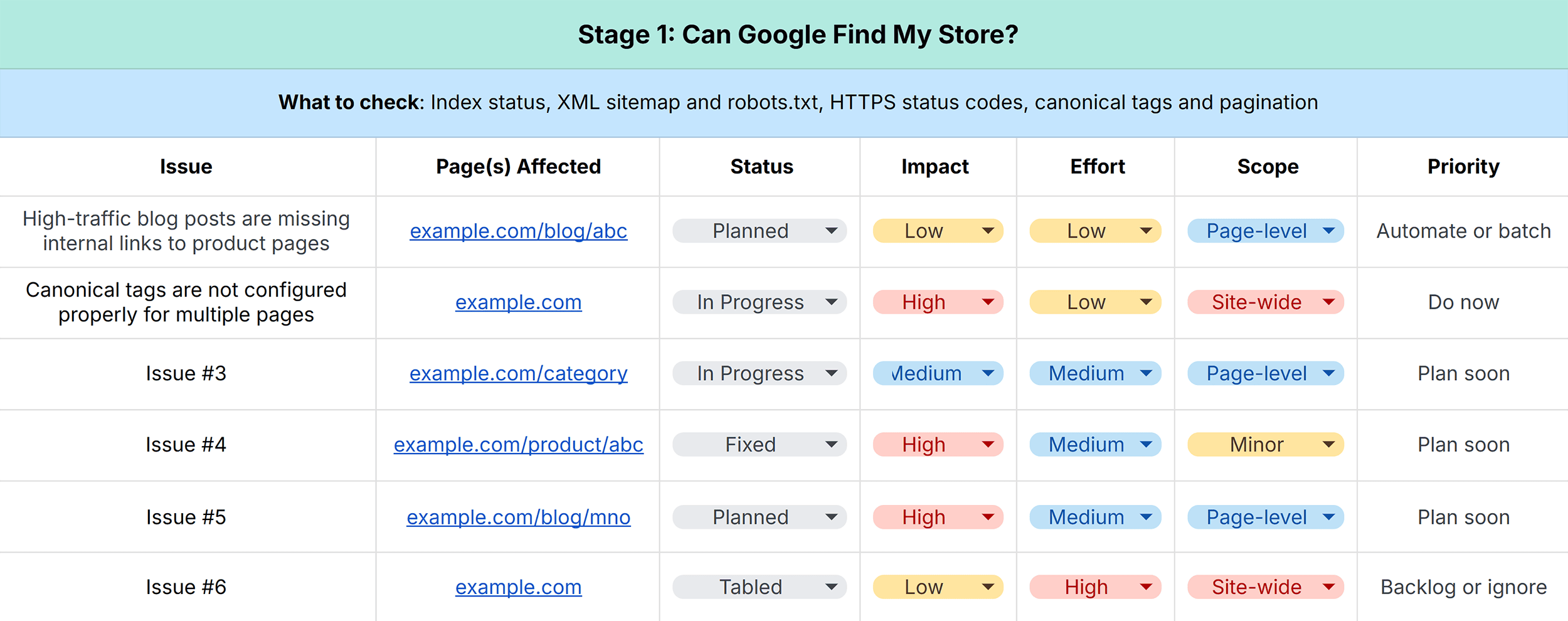
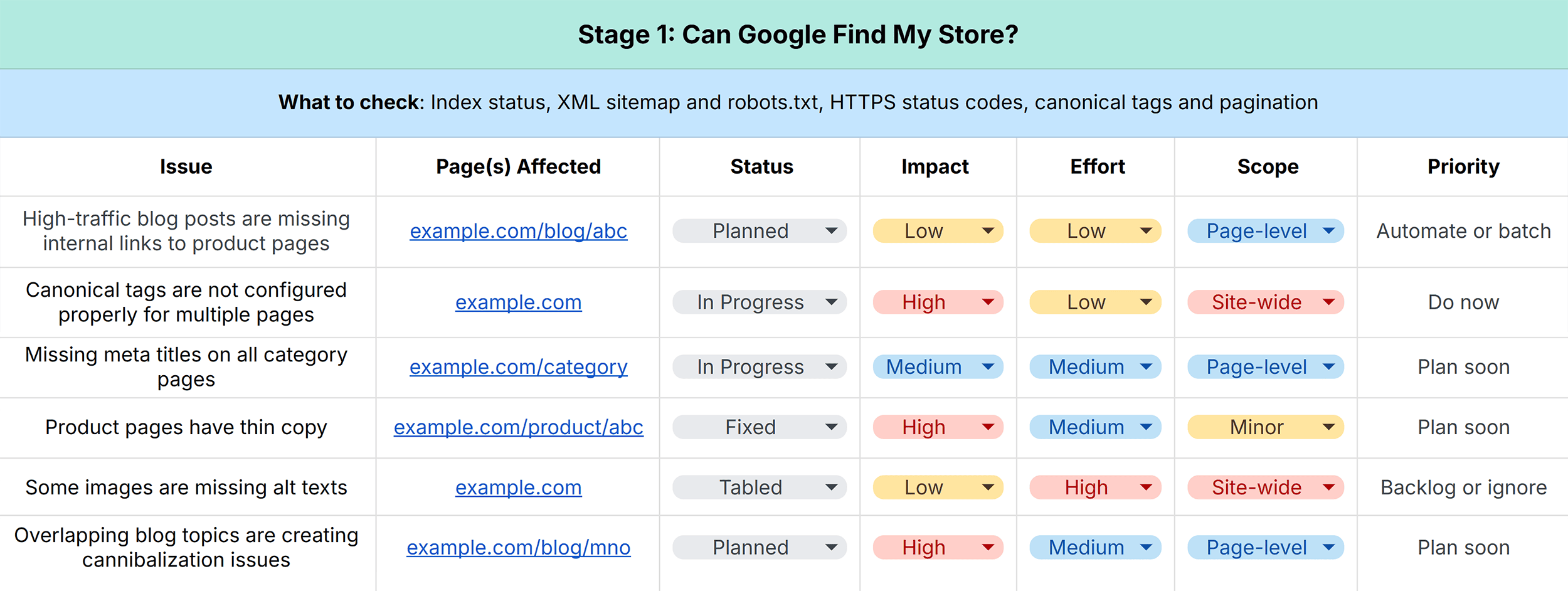
Impact
Find out how fixing an issue will move the needle for your business.
Will it increase traffic, rankings, or conversions? Or, will it go largely unnoticed by search engines and shoppers?The easiest way to determine impact is by looking at which pages are affected.
If high-revenue category or product pages are at stake, it’s a high-impact problem.
But if the problem is restricted to low-ranking blog posts, then the stakes are lower.
Effort
Once you’ve categorized issues on a scale of low to high impact, consider the effort required to fix each one.
Realistically calculate effort in terms of time, technical complexity, and capacity required to resolve a problem.
Scope
Scope looks at scale.
Estimate how big the problem is by checking if it’s:
Isolated Page-level Site-wideAnd if it’s a page-level concern, you want to zoom into the type of pages affected.
Prioritization Framework
Here’s how you can prioritize issues based on impact, effort, and scope:
Priority 1 (Quick wins): Resolving these concerns can lead to significant SEO gains without draining resources Priority 2 (Can be urgent): Some of these issues need attention because they can affect your key revenue drivers Priority 3 (Rarely urgent): Automating or handling these issues in monthly cycles is a good bet Priority 4 (Low impact): Spending resources on these time-consuming tasks can delay more meaningful workHere are a few examples to see this prioritization framework in action:
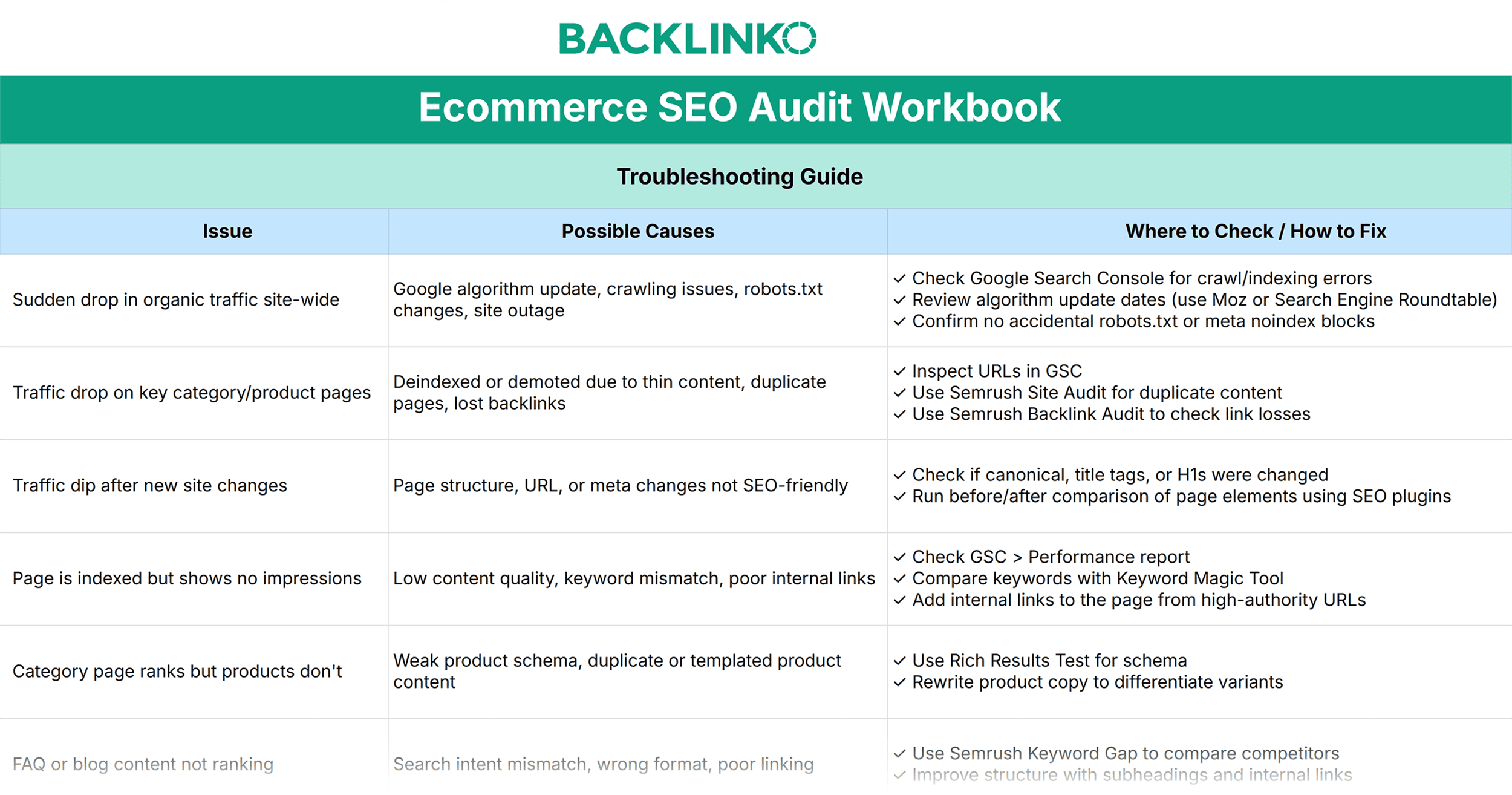
Troubleshooting Guide
We created a quick guide listing the solutions for some of the most common SEO issues for ecommerce stores.
When you’re ready with a prioritized list, refer to this guide to find potential causes and solutions quickly.
Build a Store That Google (and Shoppers) Love
Your online store has untapped potential.
A structured SEO audit gives you clarity to realize this potential.
It pinpoints where you’re losing traffic, which pages are underperforming, and what fixes will move the needle.
Work through our ecommerce SEO audit checklist to identify issues and implement solutions.
And when you’re ready to level up your strategy, check out our guide on the best strategies for ecommerce SEO.
It’s packed with examples, workflows, and tools to help you turn organic traffic into your best-performing channel.
Backlinko is owned by Semrush. We’re still obsessed with bringing you world-class SEO insights, backed by hands-on experience. Unless otherwise noted, this content was written by either an employee or paid contractor of Semrush Inc.

 FrankLin
FrankLin