SEO vs. GEO: 5 Key Differences Despite the Similarities
Want the full story? Read on. As you probably already know, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the practice of improving your website so it appears higher in Google, Bing, or other search engine results when people search for topics...

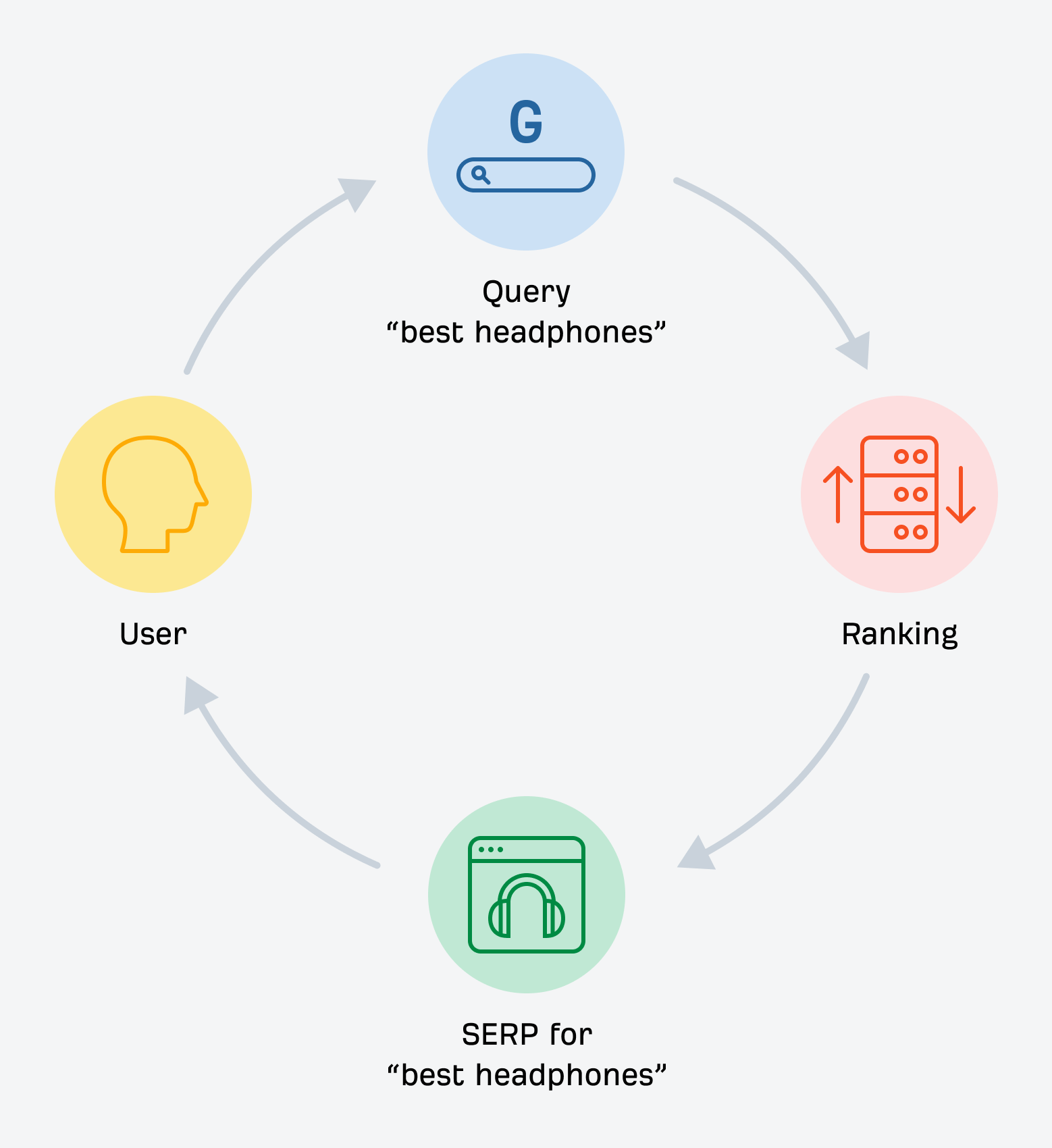
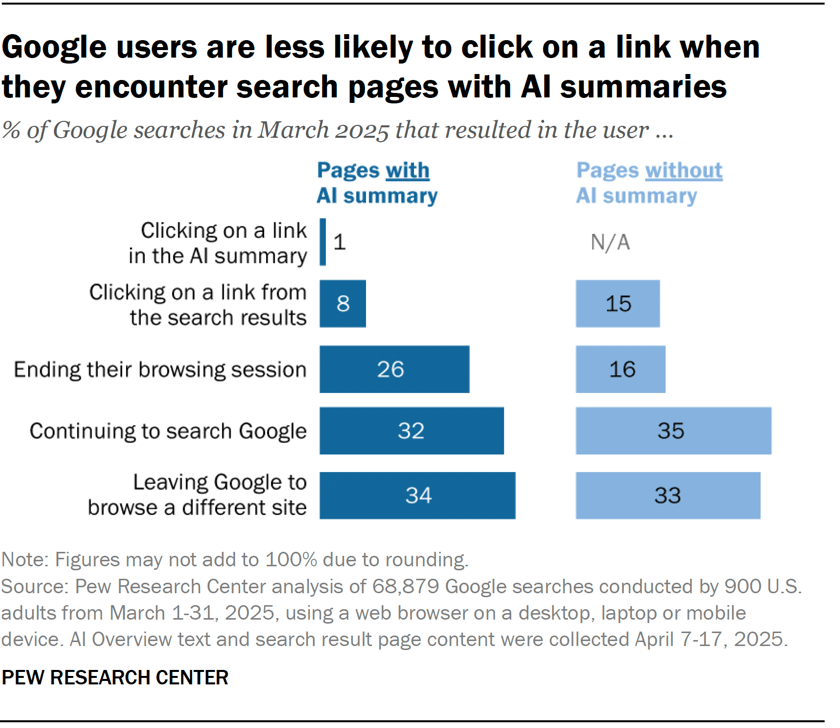
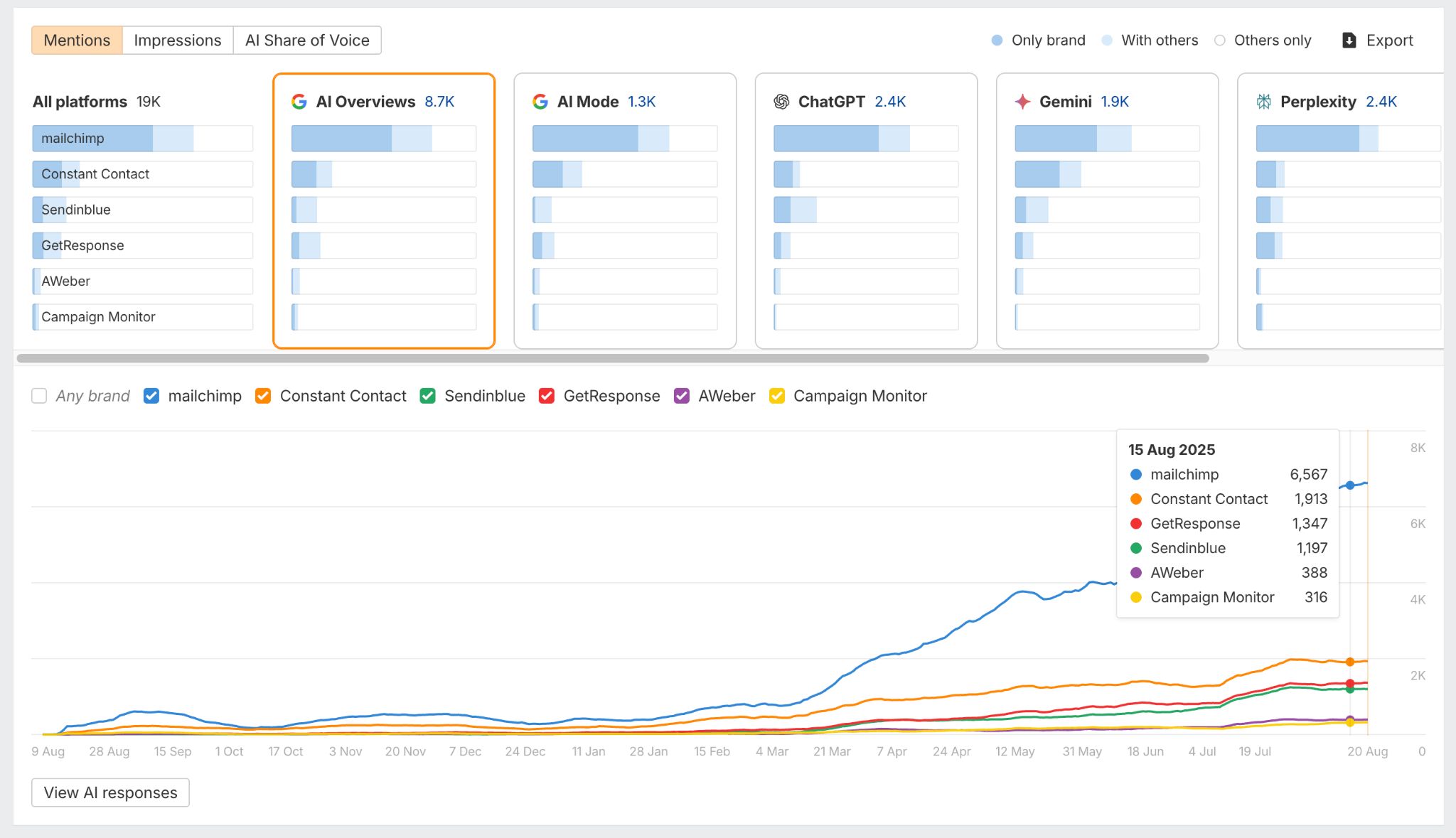
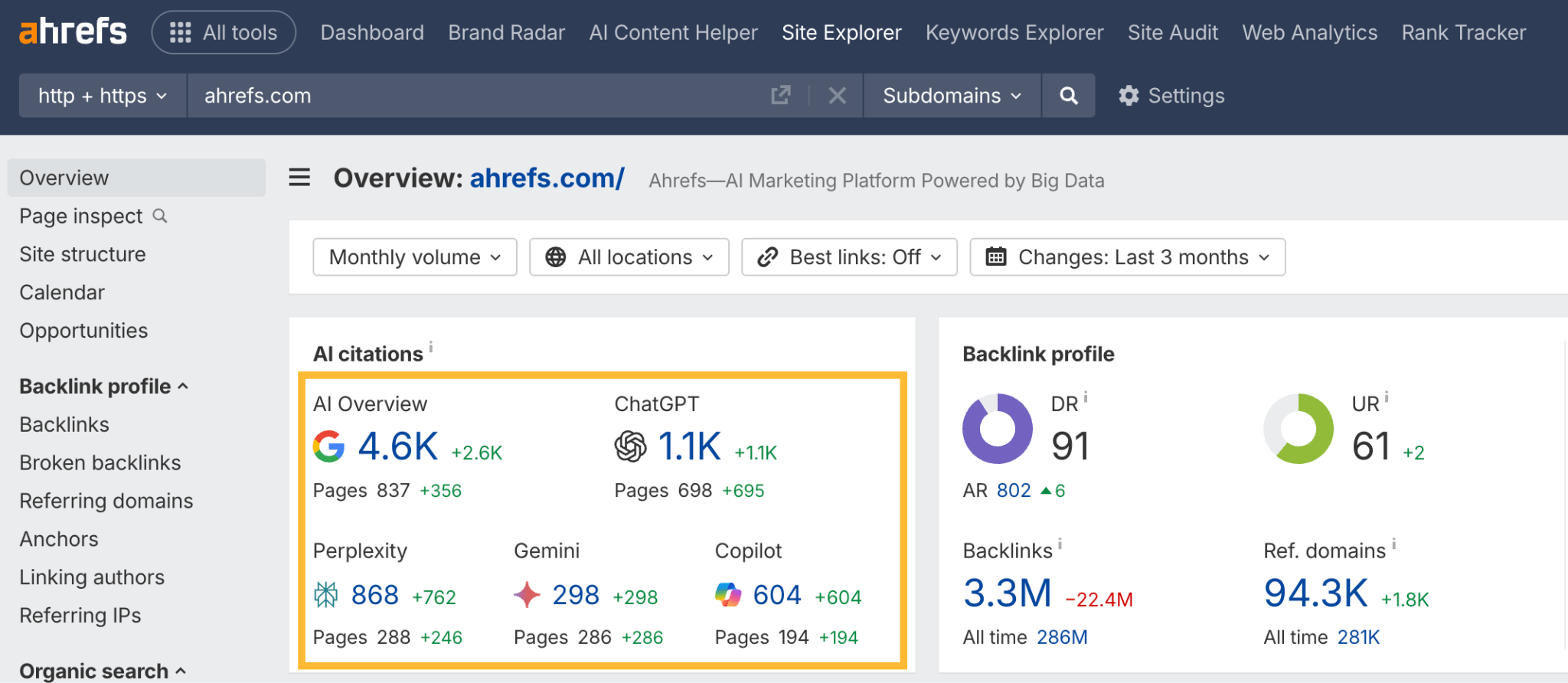
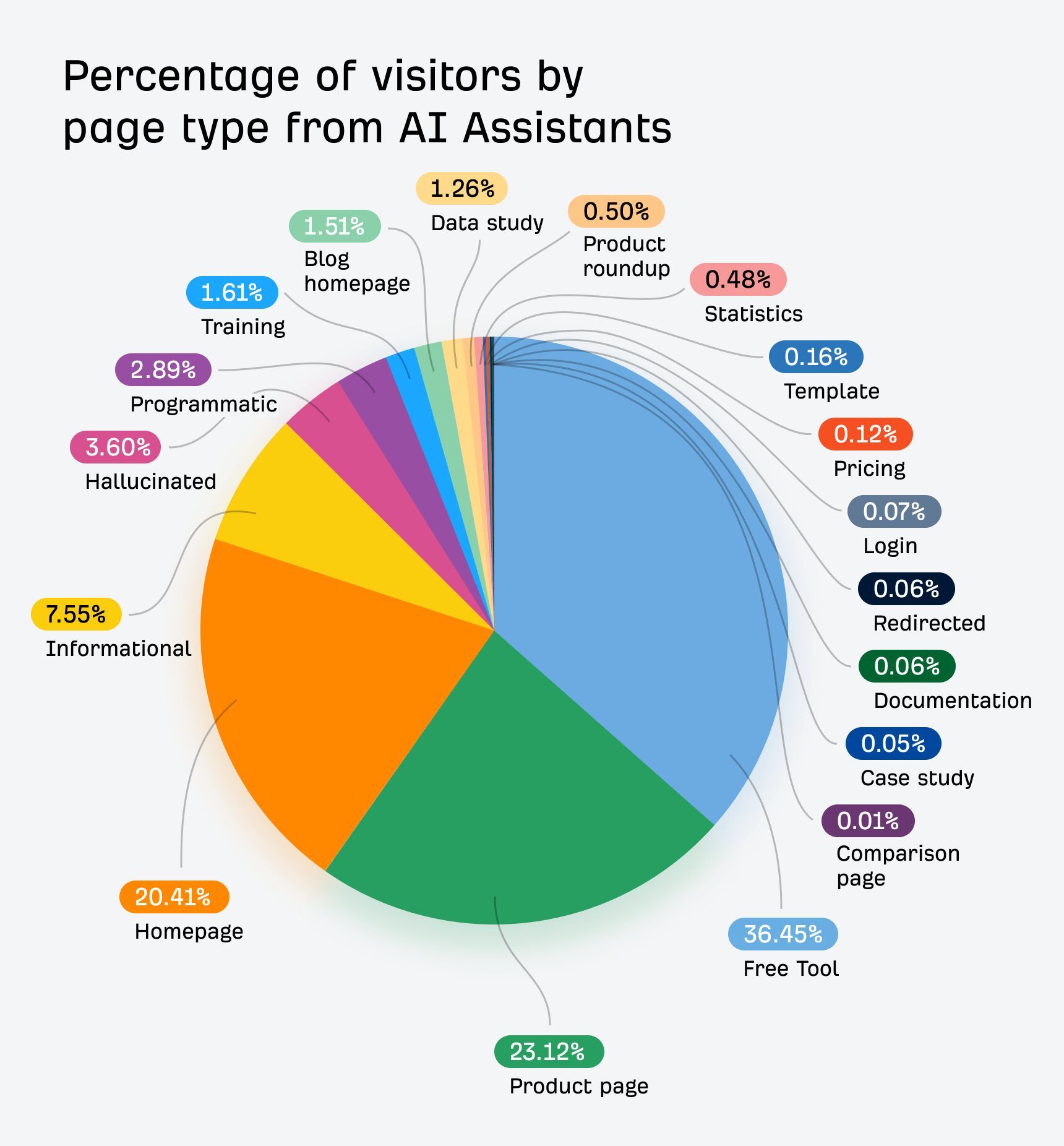
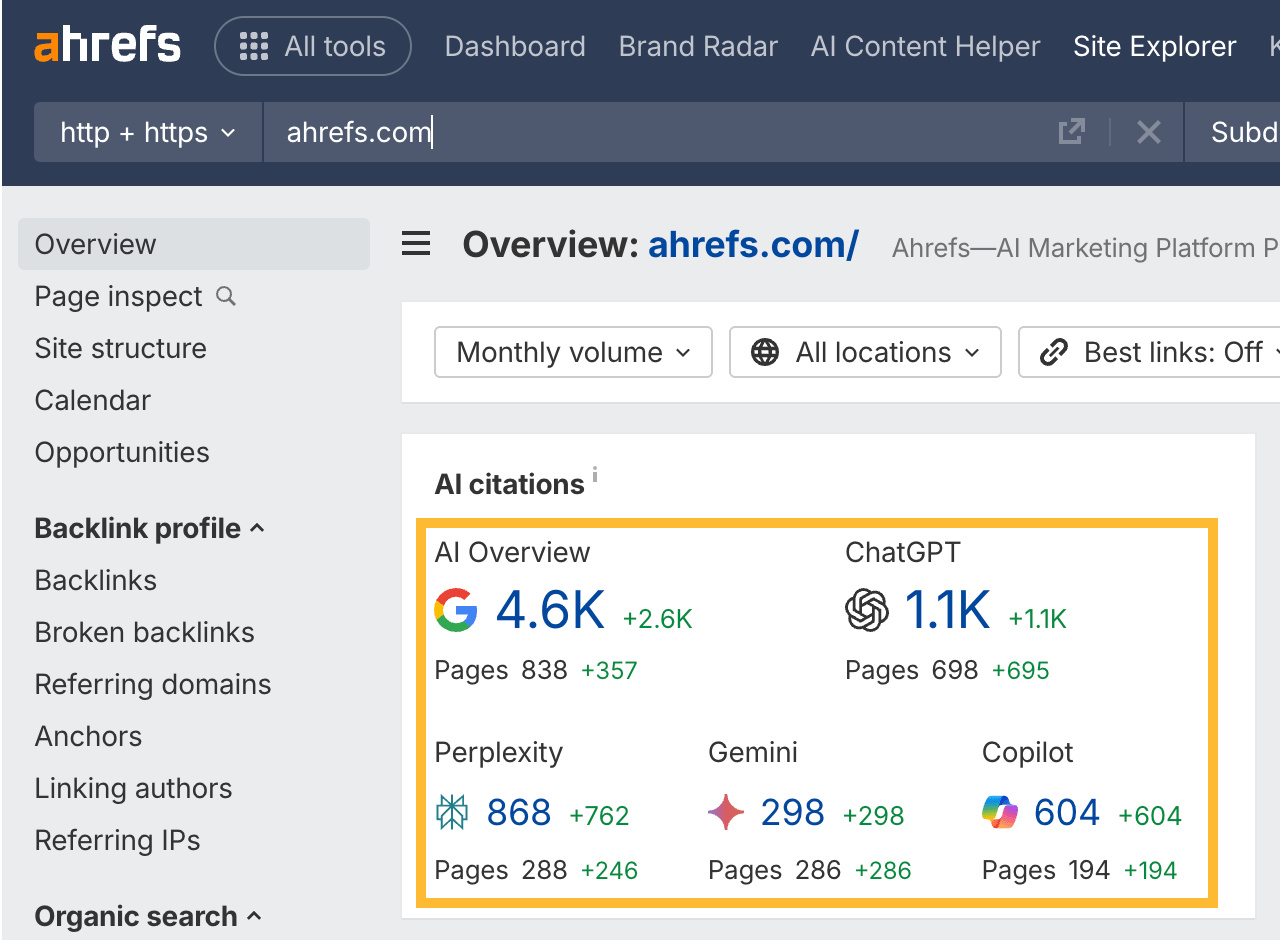
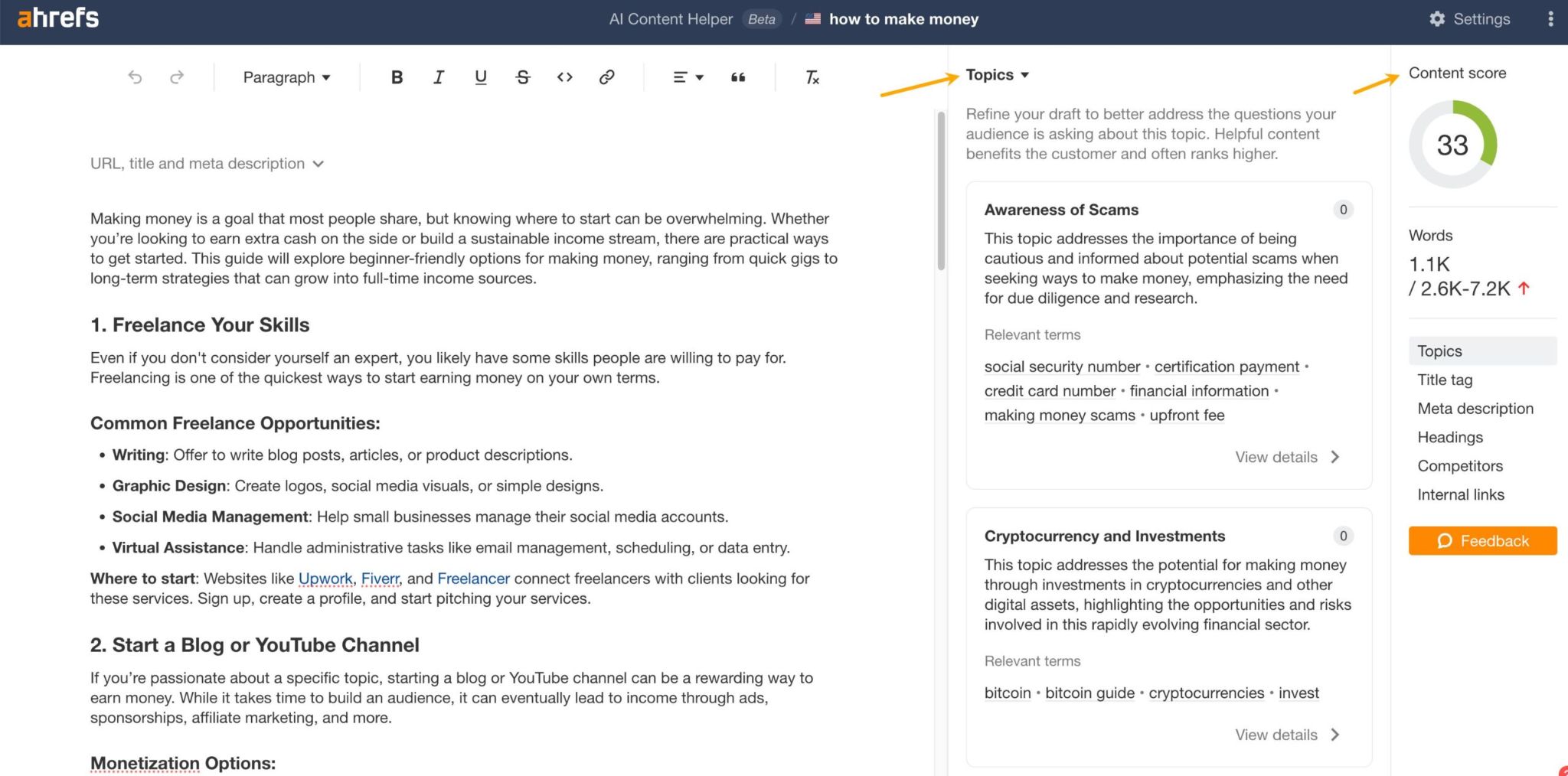
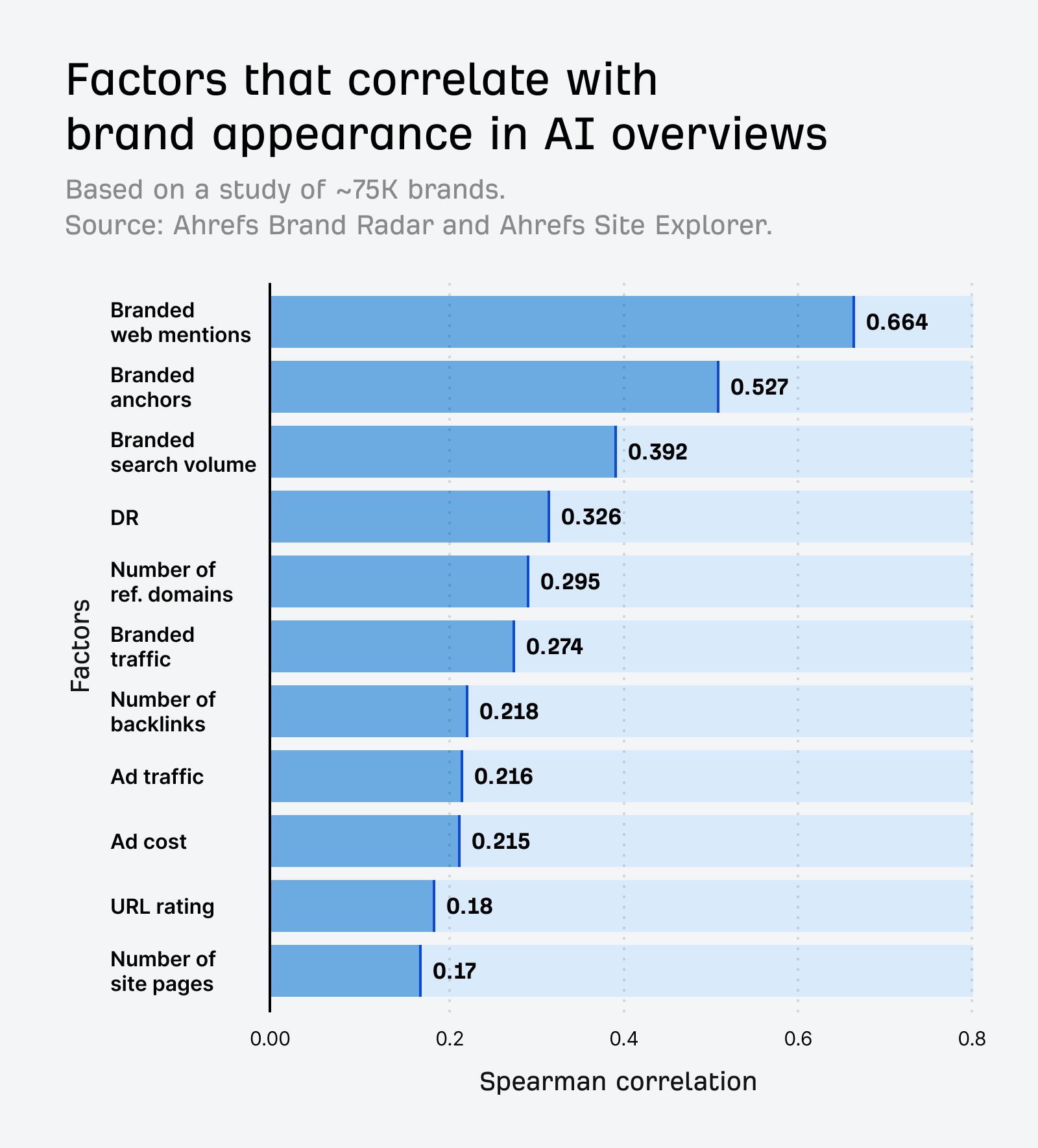
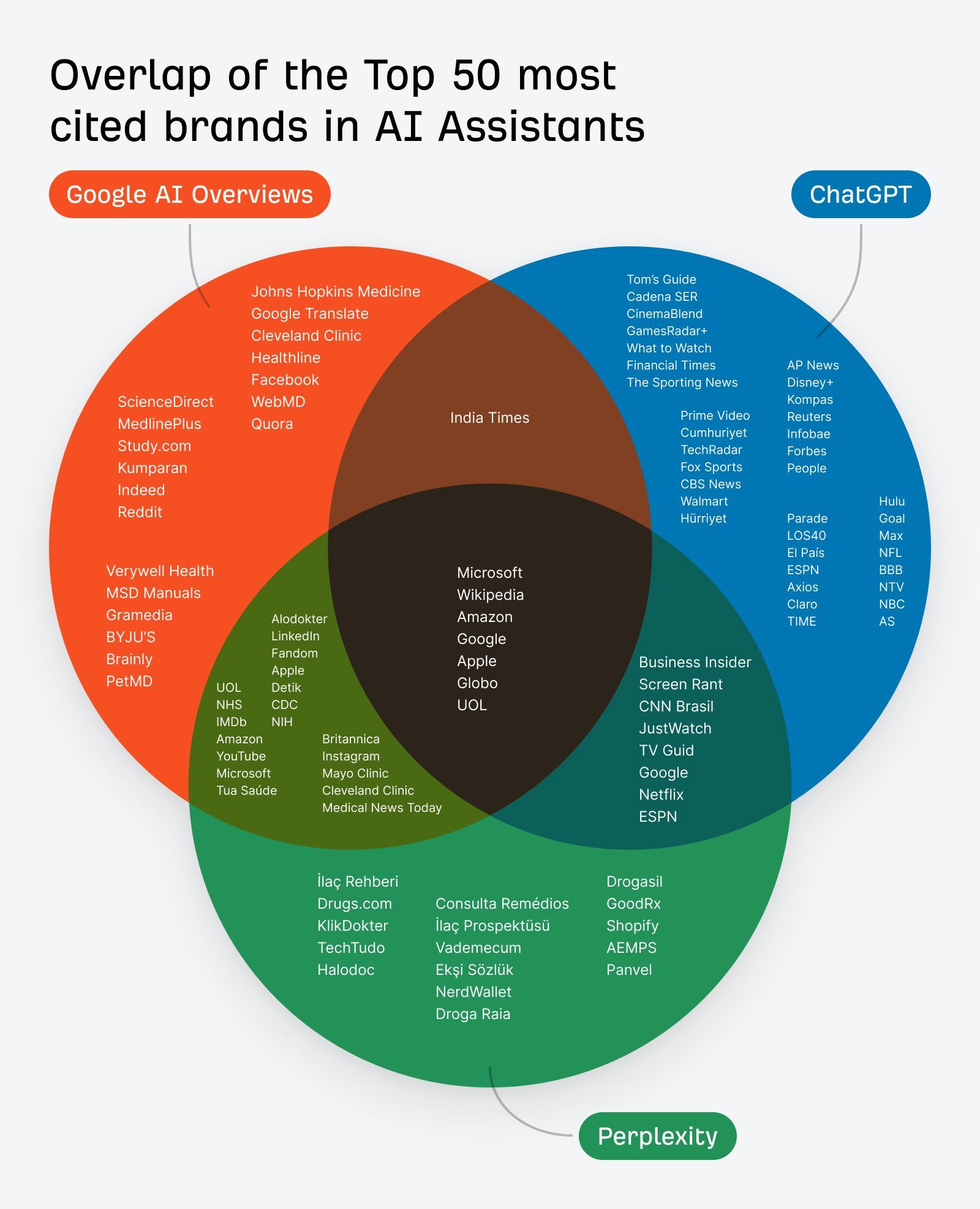
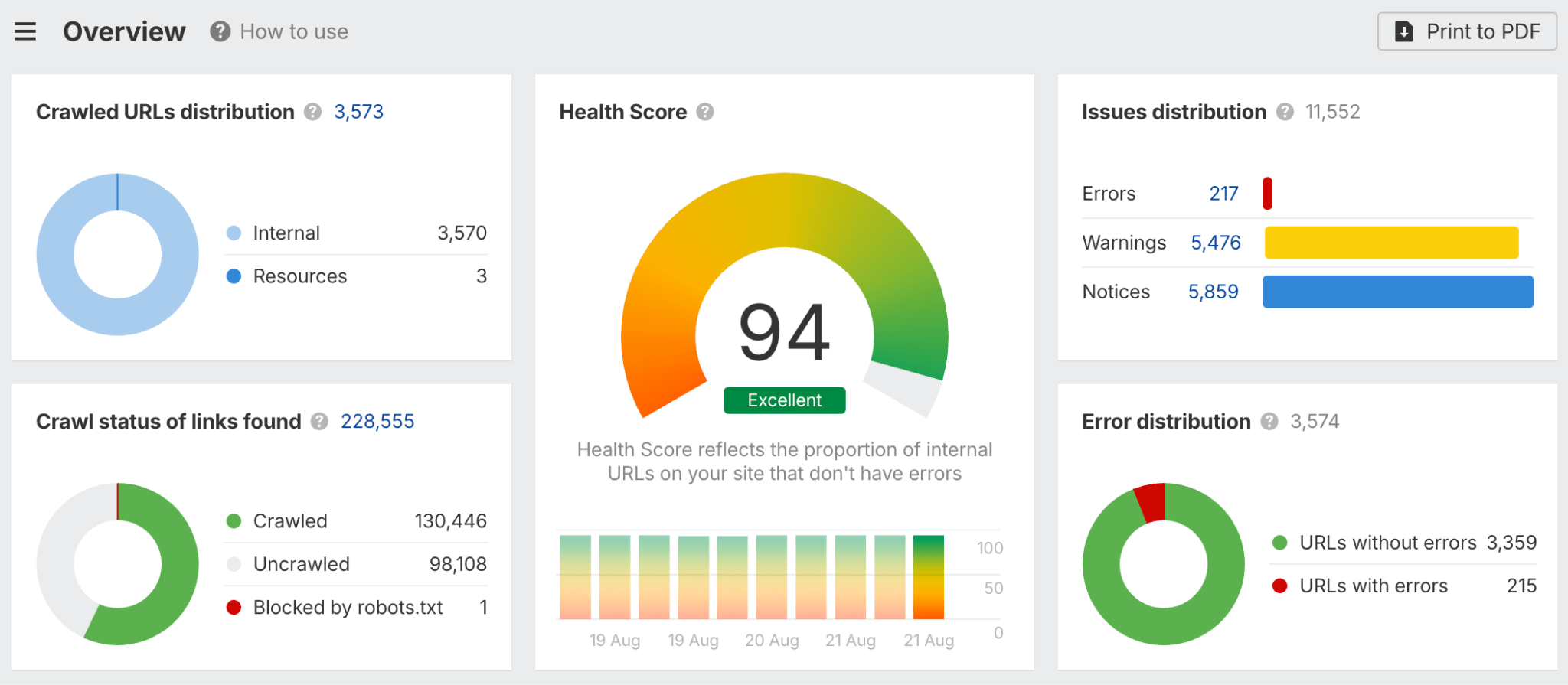
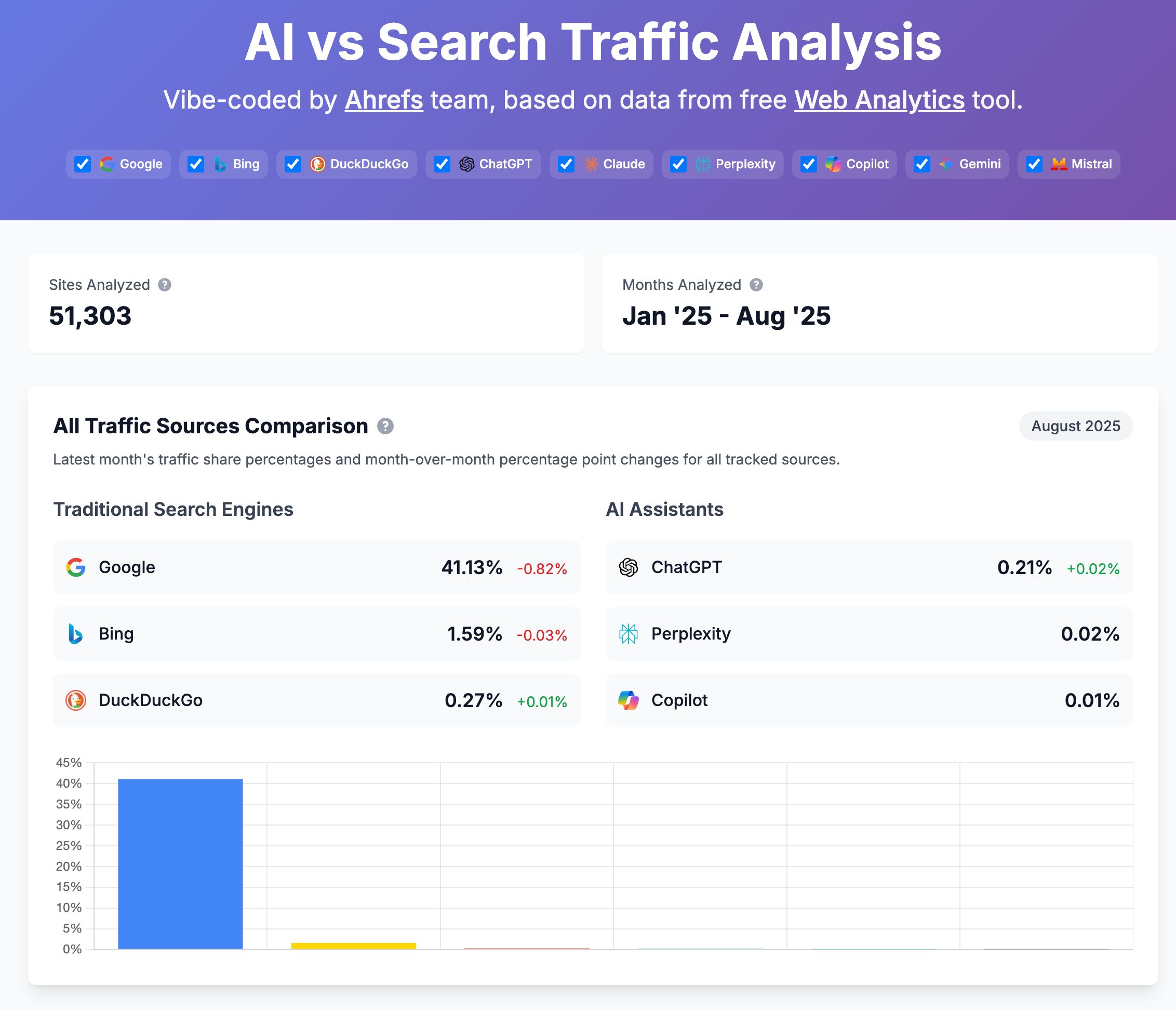
In 30 seconds, here’s what you need to know about the differences between SEO and GEO: Want the full story? Read on. As you probably already know, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the practice of improving your website so it appears higher in Google, Bing, or other search engine results when people search for topics related to your business. The goal: get people to click on your link in the SERPs and visit your website. Search engines work in three main steps: In short, when you search for something, the search engine scans its index for matches, ranks them by relevance, and then shows you the best results on the search engine results page (SERP). AI search works differently—more on that in a bit. In practice, SEO is about using the right keywords, creating helpful content, earning trusted links, and making sure your site is fast, safe, and easy to use. Here are the core strategies: GEO, short for Generative Engine Optimization (also known as AEO or LLMO), is the process of getting your brand mentioned, cited, and accurately represented in AI-generated answers. That includes results from AI assistants like ChatGPT, Google’s AI Overviews, and Google’s AI Mode. In other words, GEO is SEO for AI search. With ChatGPT, the way it responds depends on whether it uses web browsing (also called grounding) to find the answer: All of these are covered in detail in our GEO guide, but here’s the quick version: The key difference between SEO and GEO comes from how the search experience works. With AI answers, users don’t need to click links as often, but when they do, it’s usually because they want a deeper understanding or are ready to try the product the AI recommended. That in turn creates a different set of metrics to track. In SEO, your website appears as a link in search results. In GEO, your information or brand appears directly inside the AI’s answer. If links appear in AI-generated answers, they are far less visible (and redundant from the perspective of users who wanted a quick answer). In AI Overviews, they can appear contextually with a small link icon next to a term, on the right-hand panel, or at the very bottom. In SEO, the user journey typically looks like this: they search for something, see your link, click to your website, and read your content. In GEO, the journey is different: the user asks a question, the AI provides an answer using your information, and the user may never visit your site at all, at least not directly from the AI answer (this is called a ‘zero-click’ search). PEW Research Center recently studied how searches interact with Google’s AI Overviews, proving the “zero click” phenomenon. They found that users click on search results only 8% of the time when AI summaries appear vs 15% without them - that’s nearly 50% fewer clicks. Only 1% of users click on sources cited in the AI summary itself. What’s more, 26% of users end their session completely after seeing an AI summary (vs 16% for traditional search). Success in SEO is measured with metrics like keyword rankings, backlinks, organic traffic, and organic share of voice. This is part of the “click economics,” because your results depend on convincing people to click through to your site. By contrast, success in GEO is measured with metrics like brand mentions in AI answers, citations when your content is referenced, AI referral traffic, and AI share of voice. This is “visibility economics,” where the more often your brand appears in AI responses, the more likely users are to trust and choose you, even if they never click. Here’s what a GEO dashboard looks like, a screenshot from Ahrefs’ Brand Radar. The core difference is that there are no keyword rankings. Instead, you see how popular a brand is within a specific AI’s responses, and how that popularity changes over time. Another key difference is where mentions come from. In SEO, your own site is the primary asset—you optimize your pages to rank as links in search results. In GEO, however, most brand mentions in AI responses originate from third‑party sites rather than your own domain. For this reason, GEO may turn out to be a more interdisciplinary effort than SEO (requiring, for example, PR and influencer marketing). Industry rankings, “best of” lists, review platforms, PR coverage, and customer case studies often dominate as the top sources AI assistants rely on. For example, in Google’s AI Overviews, the top pages mentioning Ahrefs didn’t include ahrefs.com at all. These mentions don’t even need to be linked. AI can pick up unlinked references just as easily. This makes broad visibility across the web more important than ever. To find sites that often appear in AI answers, just plug their domain in Ahrefs’ Site Explorer and look at the AI citation count in the Overview report: Traffic from AI search looks different from traditional organic search. Visitors from AI tend to view fewer pages (4 vs. 5.2) but spend slightly more time on them (86s vs. 78s). They also have a higher bounce rate (67.8% vs. 63.7%), suggesting they arrive with a clear, specific goal (source). AI search also drives users to homepages, product pages, and tools more often than organic search, while organic search brings more traffic to international pages. Most importantly, AI traffic can convert at a much higher rate. In the case of Ahrefs, it was 23x more than organic search; despite being just 0.5% of traffic, it generates over 12% of signups. That said, conversion rates will vary by site. As this recent study from Amsive shows, not every website sees the same uplift from LLM-driven traffic. Despite their differences, SEO and GEO share important common ground based on content quality and brand authority. Both SEO and GEO depend on having useful content, which builds topical authority. At the end of the day, search engines and AI tools are designed to bring people the information they’re looking for. The key difference is in how the answer is delivered: search engines point you to links, while AI often gives you the answer directly. Case in point, Ahrefs’ content and product pages were mentioned 7,470 times across 2,309 pages without any special effort to optimize for AI. That’s because new search technologies still rely on the same foundation: quality, useful content. Both strategies focus on understanding what people are really looking for and providing the best answer (the search intent). Whether someone searches Google for “best project management software” or asks ChatGPT something more specific like “What’s the best project management tool for a team of 30 under $50?”, the intent doesn’t change. They’re looking for the top options, the reasons behind those recommendations, and a clear comparison to help them decide. Tip Use Ahrefs’ AI Content Helper to take the guesswork out of content planning. Find the main topics (not just keywords) for your keyword by analyzing top-ranking pages. As you write, see your content rated in real time and adjust instantly. Create new articles or update old ones with ease. When search results mix different intents, simply pick the intent you want to optimize for and let the tool guide you. Google Search and AI assistants both rely on outside content; they don’t generate answers out of thin air. That means they face the same challenge: deciding which sources to trust. This is where your reputation as an expert becomes valuable for both SEO and GEO. Just like in traditional SEO, brand authority is a major factor in GEO. Branded mentions across the web show a strong connection to visibility in AI Overviews (correlation of 0.664). Furthermore, brands in the top 25% for web mentions earn over 10x more AI Overview placements than the next tier down. And that’s not just true for AI Overviews. AI Assistants also lean heavily on well-known sources. The main difference is that they tend to cite a slightly different set of sites. Simply put, the more people talk about your brand online, the more likely AI is to feature you. Search engines and AI assistants still rely on crawlers to fetch and process pages. AI struggles with heavy JavaScript, but it typically respects robots.txt rules. If they can’t access or interpret your content correctly, neither SEO nor GEO will work. Tip Keep your site in good SEO health with Ahrefs’ Site Audit. It monitors your site on autopilot for over 170 SEO issues, showing where exactly they happen and suggesting how to fix them. Free in Ahrefs Webmaster Tools. Think of SEO as your foundation and GEO as the upgrade. You need SEO first because it’s established, drives most web traffic, and provides the base that AI systems often learn from. But GEO matters too, because AI search is growing, and the “zero-click” trend is accelerating as more AI Overviews roll out. What’s more, Adobe’s recent study found that three in 10 U.S. respondents trust ChatGPT more than other search engines, and 36% of the people surveyed discovered a new product or brand through ChatGPT. If you’re curious about the global traffic shift, check out our AI vs. Search Traffic Analysis dashboard, which pulls data from over 50,000 sites. For instance, from January to August 2025, Google held a 41.13% traffic share, while ChatGPT accounted for 0.21%. Worried you’re falling behind? Don’t panic. SEO dies every year and lives forever. The same qualities that make content strong for SEO also work for GEO. By adding GEO strategies to your SEO efforts and keeping an eye on your AI visibility, you’ll be well-positioned for today and prepared for what’s next. Got questions or comments? Let me know on LinkedIn.How search engines work
Key SEO strategies
How AI search works
Key GEO tactics

AspectSEO (Search Engine Optimization)GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) Goal Get clicks to your website Get AI to mention your brand/content Where you appear Blue links in search results Inside AI-generated answers Primary mention source Your own website pages and content Third-party sites (industry lists, reviews, PR coverage) User journey Search → Click link → Visit site Ask → Read AI summary → May never visit site Traffic volume High Low Conversion quality Standard rates Can be much higher (23x higher in case of ahrefs.com) Visitor behavior More pages viewed, shorter time Fewer pages, longer time, clearer intent Success metrics Rankings, backlinks, organic traffic, share of voice Mentions, citations, AI referral traffic, AI share of voice Trust signals Backlinks from reputable sites, EEAT Unlinked mentions, brand authority, multi-platform presence Foundation Essential starting point Built on top of SEO; future-proofing Shared principles Quality content, trust/authority, intent focus, strong technical foundation Same — GEO builds on SEO Final thoughts

 ShanonG
ShanonG