The Safety of Keto Diets
What are the effects of ketogenic diets on nutrient sufficiency, gut flora, and heart disease risk? Given the decades of experience using ketogenic diets to […]

What are the effects of ketogenic diets on nutrient sufficiency, gut flora, and heart disease risk?
Given the decades of experience using ketogenic diets to treat certain cases of pediatric epilepsy, a body of safety data has accumulated. Nutrient deficiencies would seem to be the obvious issue. Inadequate intake of 17 micronutrients, vitamins, and minerals has been documented in those on strict ketogenic diets, as you can see in the graph below and at 0:14 in my video Are Keto Diets Safe?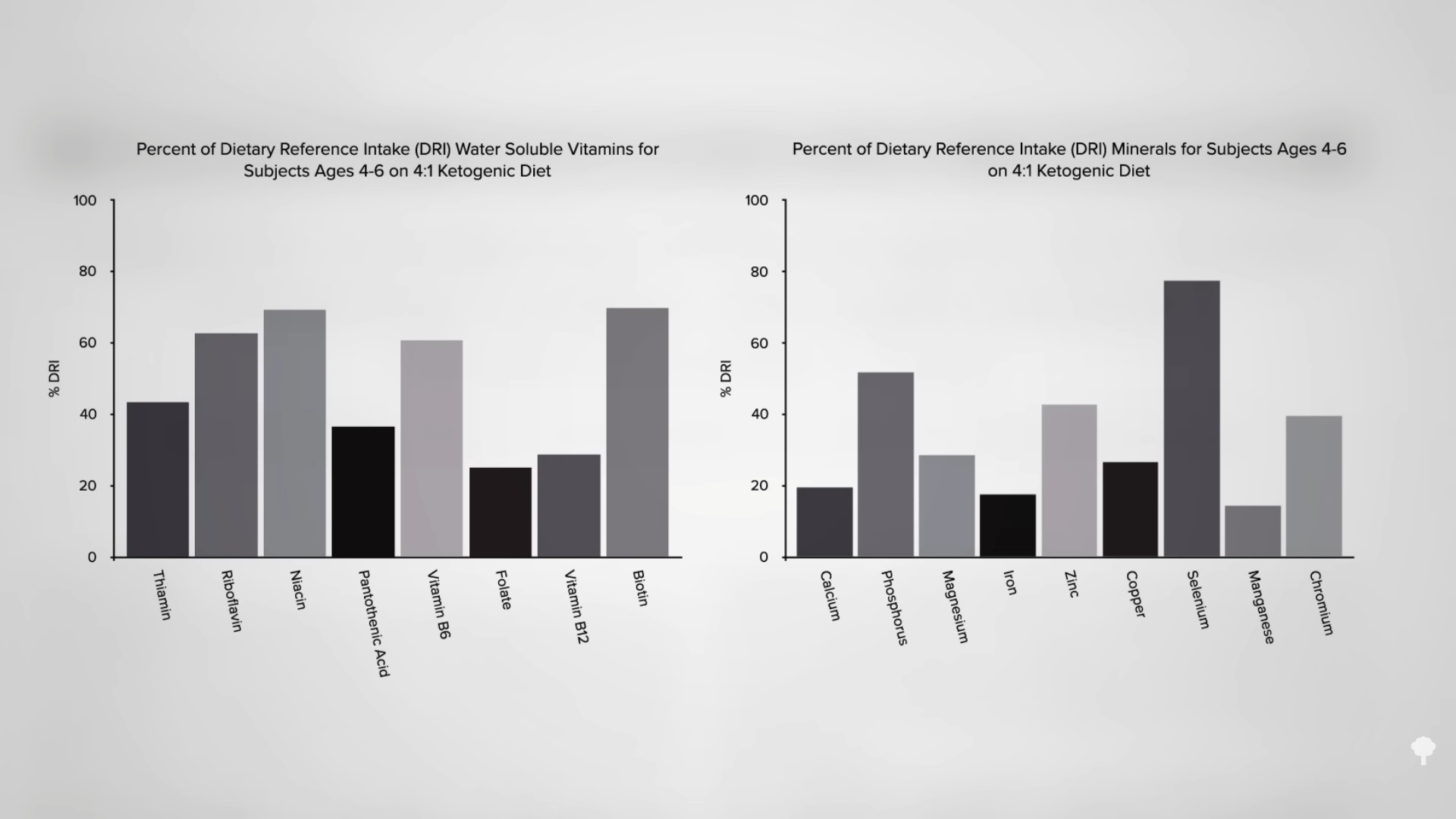
Dieting is a particularly important time to make sure you’re meeting all of your essential nutrient requirements, since you may be taking in less food. Ketogenic diets tend to be so nutritionally vacuous that one assessment estimated that you’d have to eat more than 37,000 calories a day to get a sufficient daily intake of all essential vitamins and minerals, as you can see in the graph below and at 0:39 in my video.
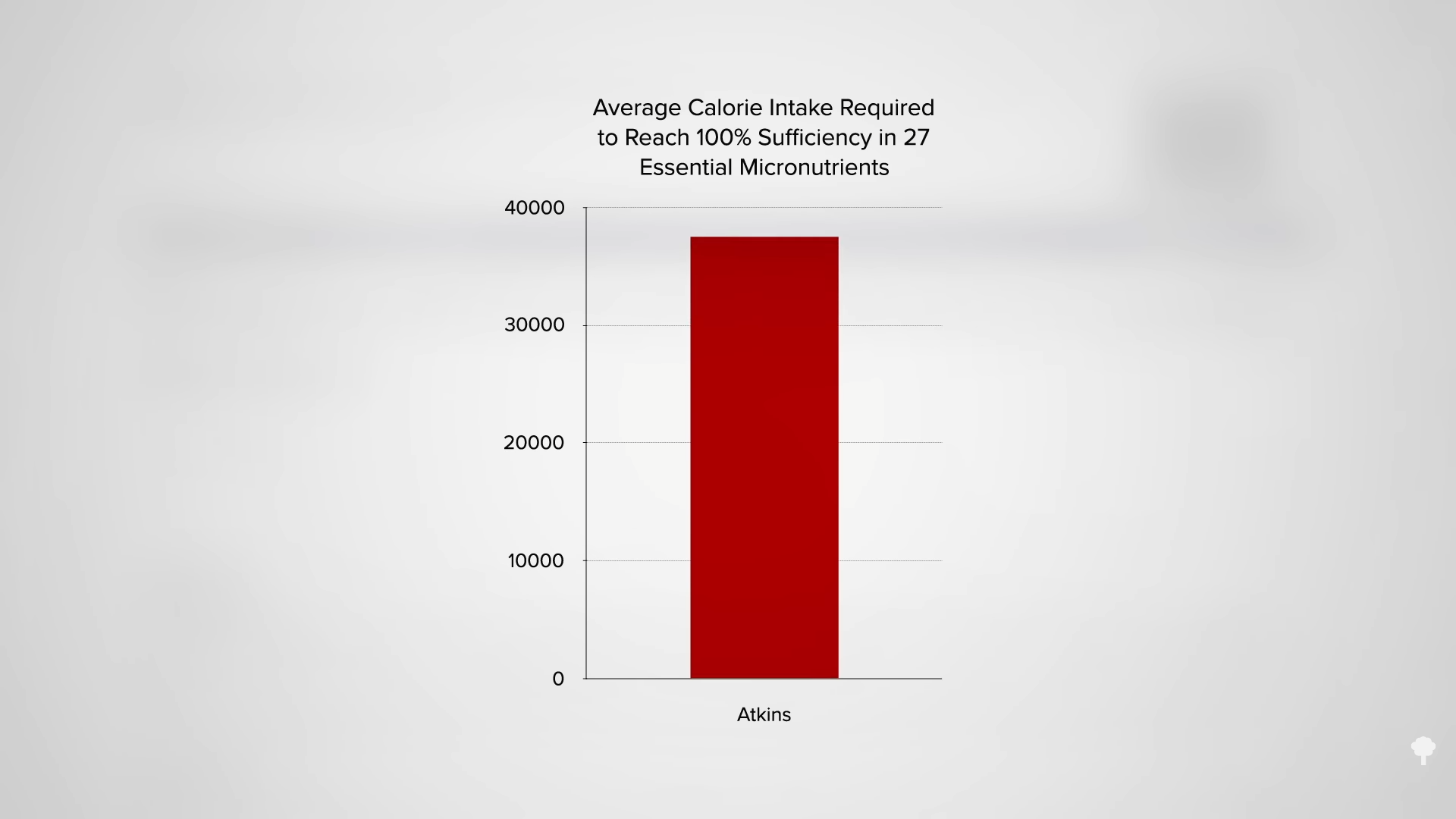
That is one of the advantages of more plant-based approaches. As the editor-in-chief of the Journal of the American Dietetic Association put it, “What could be more nutrient-dense than a vegetarian diet?” Choosing a healthy diet may be easier than eating more than 37,000 daily calories, which is like putting 50 sticks of butter in your morning coffee.
We aren’t just talking about not reaching your daily allowances either. Children have gotten scurvy on ketogenic diets, and some have even died from selenium deficiency, which can cause sudden cardiac death. The vitamin and mineral deficiencies can be solved with supplements, but what about the paucity of prebiotics, the dozens of types of fiber, and resistant starches found concentrated in whole grains and beans that you’d miss out on?
Not surprisingly, constipation is very common on keto diets. As I’ve reviewed before, starving our microbial self of prebiotics can have a whole array of negative consequences. Ketogenic diets have been shown to “reduce the species richness and diversity of intestinal microbiota,” our gut flora. Microbiome changes can be detected within 24 hours of switching to a high-fat, low-fiber diet. A lack of fiber starves our good gut bacteria. We used to think that dietary fat itself was nearly all absorbed in the small intestine, but based on studies using radioactive tracers, we now know that about 7 percent of the saturated fat in a fat-rich meal can make it down to the colon. This may result in “detrimental changes” in our gut microbiome, as well as weight gain, increased leaky gut, and pro-inflammatory changes. For example, there may be a drop in beneficial Bifidobacteria and a decrease in overall short-chain fatty acid production, both of which would be expected to increase the risk of gastrointestinal disorders.
Striking at the heart of the matter, what might all of that saturated fat be doing to our heart? If you look at low-carbohydrate diets and all-cause mortality, those who eat lower-carb diets suffer “a significantly higher risk of all-cause mortality,” meaning they live, on average, significantly shorter lives. However, from a heart-disease perspective, it matters if it’s animal fat or plant fat. Based on the famous Harvard cohorts, eating more of an animal-based, low-carb diet was associated with higher death rates from cardiovascular disease and a 50 percent higher risk of dying from a heart attack or stroke, but no such association was found for lower-carb diets based on plant sources.
And it wasn’t just Harvard. Other researchers have also found that “low-carbohydrate dietary patterns favoring animal-derived protein and fat sources, from sources such as lamb, beef, pork, and chicken, were associated with higher mortality, whereas those that favored plant-derived protein and fat intake, from sources such as vegetables, nuts, peanut butter, and whole-grain bread, were associated with lower mortality…”
Cholesterol production in the body is directly correlated to body weight, as you can see in the graph below and at 3:50 in my video.
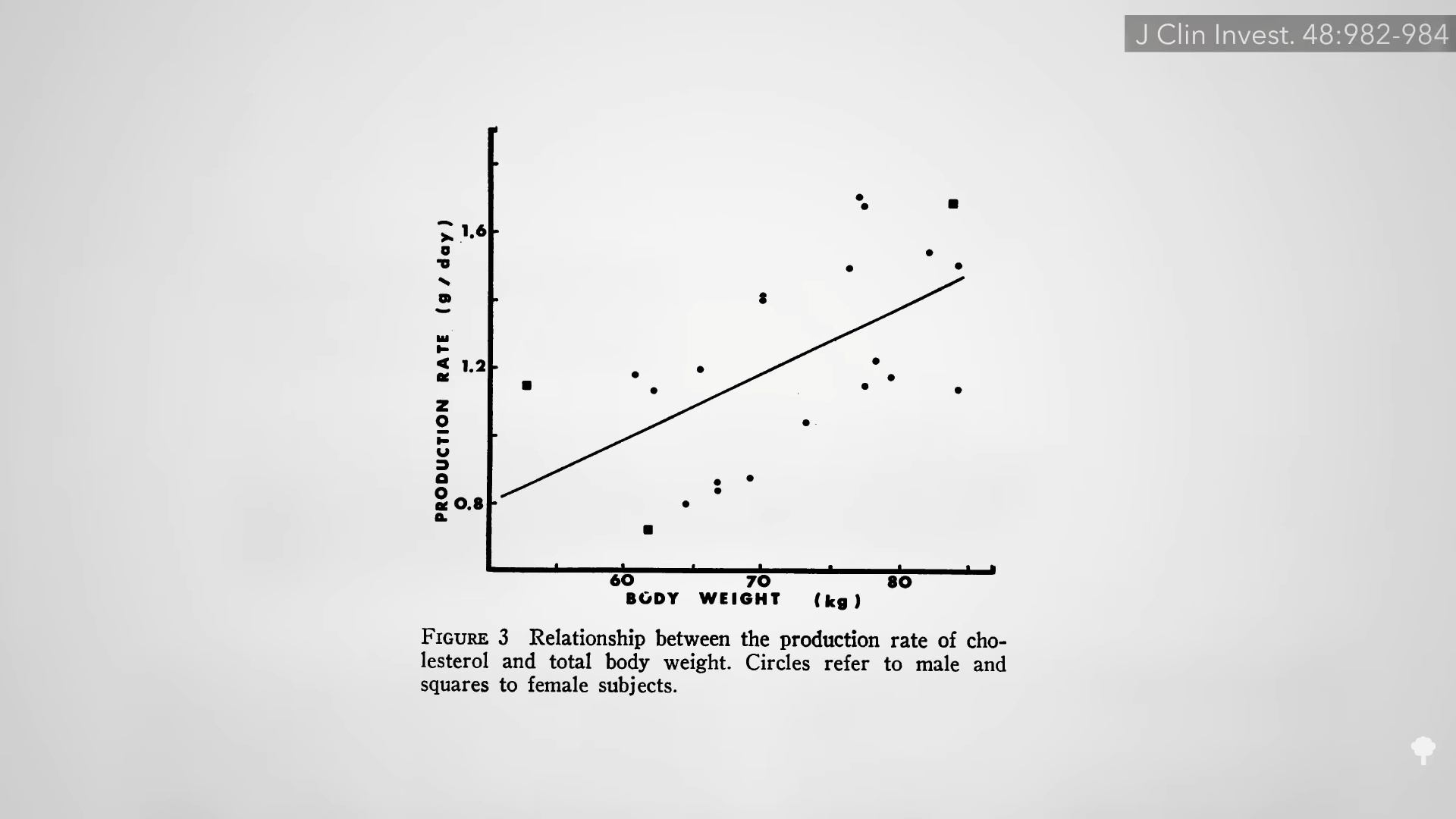
Every pound of weight loss by nearly any means is associated with about a one-point drop in cholesterol levels in the blood. But if we put people on very-low-carb ketogenic diets, the beneficial effect on LDL bad cholesterol is blunted or even completely neutralized. Counterbalancing changes in LDL or HDL (what we used to think of as good cholesterol) are not considered sufficient to offset this risk. You don’t have to wait until cholesterol builds up in your arteries to have adverse effects either; within three hours of eating a meal high in saturated fat, you can see a significant impairment of artery function. Even with a dozen pounds of weight loss, artery function worsens on a ketogenic diet instead of getting better, which appears to be the case with low-carb diets in general.
For more on keto diets, check out my video series here.
And, to learn more about your microbiome, see the related videos below.

 Tfoso
Tfoso 

























.jpg&h=630&w=1200&q=100&v=154b70b92d&c=1)


