First Input Delay: How to Boost Your FID Score
Are you finding it hard to retain your visitors despite having a foolproof website with high-quality content? FID issues may be the culprit. FID is the measure of the time it takes for a browser to respond to the...

Are you finding it hard to retain your visitors despite having a foolproof website with high-quality content? FID issues may be the culprit.
FID is the measure of the time it takes for a browser to respond to the first interaction made by the user while the site is still loading.
Let me tell you everything about FID, why it occurs, how you can measure your site’s FID and how to optimize it.
What is FID?
First input delay (FID) is a metric that denotes the time between the user’s first interaction with the website and the browser’s response to it. First Input Delay is also known as Input Latency. It is one of the three core web vitals.
The other two are:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)Coming back to FID, the user interaction can be anything from clicking a link to tapping a call-to-action button on a web page. However, actions that don’t trigger the browser’s response, such as zooming and scrolling, aren’t part of this metric.
Why Does FID Matter?
Google leverages its Core Web Vitals to measure how well your site is optimized. Well-optimized sites open doors to a smooth user experience and that’s exactly what the search engine and users look forward to.
Being one of the three Core Web Vitals, FID helps Google understand how interactive your site is. And, of course, Google doesn’t want users to wait longer to start interacting with a site.
A minimal FID time tells the search engine that the users don’t have to wait longer to interact with a site.
Can FID be manipulated? No.
FID is a metric that relies completely on real user input and can’t be stimulated using a lab test. So, it’s surprising that Google counts on it, right?
In fact, Core Web Vitals act as a ranking signal that influences how the search engine ranks your site in search results.
What’s a Good FID Score?
As I mentioned earlier, a minimal FID time signals Google that the users don’t have to wait longer to interact with your site.
But how do you know what’s minimal? Let me break it down.
FID scores are usually calculated in milliseconds. The lower the FID time of your site, the better the user experience.
Here’s what Google says about FID scores.

If the FID time of your page is less than or equal to 100 milliseconds, it is likely to be ready to process user interactions instantly. To Google, it’s a sign of a good user experience.
On the other hand, if the page takes anywhere from 100 to 300 milliseconds, it needs improvement. Furthermore, if the FID time surpasses 300 milliseconds, it’s a sign that your site is showcasing a poor performance in terms of FID and needs immediate attention.
Also, from Google,
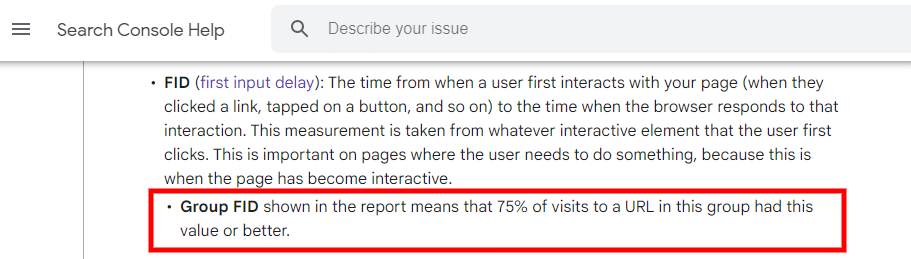
That means if FID is less than 100ms for at least 75% of visits, Google will consider it a good page loading experience.
How to Measure FID?
Now that you know what the recommended FID time is, you need to make sure your website meets it in order to offer a good user experience.
But how do you do that?
The first step to optimizing your FID is knowing the current FID score of your website.
Every site is unique and so are its optimization needs. That said, measuring the FID score of your website helps you know where your site stands in terms of Input Latency.
Upon finding that, you will be able to figure out the kind of effort you have to put into meeting the FID standards set by Google.
For example, let’s take two sites, A and B. Suppose the FID times of A is 200 milliseconds and B is 350 milliseconds.
That means site B has more to do with Input Latency optimization than Site A.
The less the score, the more effort is required. That’s the point.
So, how do you measure FID? I suggest 3 ways.
PageSpeed Insights Tool Google Search Console (Core Web Vitals Report) Chrome User Experience ReportHere’s what I got when I checked the FID score of a page from the Stan Ventures website

As you can see, our First Input Delay score was 6 milliseconds and appeared in green, signaling a good score. As for the other two Core Web Vitals, Our CLS score looked healthy. while LCP needed a bit of improvement with 2.7 seconds (just 0.2 seconds behind the mark).
Causes of FID
To fix an issue, you have to know what triggers it. This is applicable to FID as well. Here’s a look at the causes of FID.
Heavy Upfront JavaScript Payloads
It may take a long time for the browser to process large JavaScript bundles. As it has to wait for the page to all referenced JavaScript, the page response time will be affected.
As a result, the user has to wait for a long time to interact with the web page. So, that’s an FID issue that needs to be fixed to achieve a good score.
Long Running JavaScript
A long-running task on JavaScript may run on the main thread even after referenced JavaScript is loaded.
This activity is likely to block the user input until such time the task finishes and the browser is free to take the user input.
Long running JavaScript is often a result of coding mistakes or poorly optimized codes.
Unused JavaScript
Including unnecessary JavaScript that won’t be used is another cause of FID issues.
The browser will also process the Unused JavaScript and will take more time to load the page. This, in turn, will fuel first input delays.
How to Optimize FID
Now that you know what happens behind the scenes regarding FID, let me tell you how you can optimize your site for an improved FID score.
Decrease JavaScript Execution Time
Reducing the amount of JavaScript that runs on a web page helps decrease the time the browser will spend executing the JavaScript.
This way, the browser will be quickly available to handle user interactions and respond to them. Eliminating unused JavaScript, for example, is a good way to reduce JavaScript execution time and ultimately boost your FID score.
You can also remove unused polyfills if any. Not sure what polyfills are? They are codes that you use for your site to work properly on older browsers.
Make sure you remove only the unused ones. If not, your page may not work properly on browsers that are widely used. That will make it a bumpy ride for your website visitors and have a negative impact on user experience.
Break Up Long JavaScript Tasks
As I mentioned in the previous section, a long JavaScript task may run on the main thread and make your page unresponsive to user interaction. So, break the long-running tasks into smaller chunks.
But how do you determine a task is actually long running?
Any JavaScript task that occupies the main thread for more than 50 milliseconds is a long task. Breaking such tasks into asynchronous ones ensures that they don’t run at the same time. That’s a good way to reduce user input delays.
Reduce the Impact of Third-Party Code
Including third-party codes and tags may keep the network busy and make your page unresponsive. This will, again, lead to input latency.
Remove unnecessary third-party codes on your page. Third-party tags may provide additional benefits for your business, but are they worth it if they are actually affecting the performance of your site?
If you still think you want them, make sure you feature them below the fold. This way, the third-party tags will still be there on your site without affecting the user’s first interaction with your site because they appear only when the user scrolls down on your page.
Run Long Tasks Off the Main Thread
As we discussed above, breaking long JavaScript tasks can help reduce first input delays. However, if you prefer not to break a long-running task and improve your FID score simultaneously, here’s an alternative:
Using the Web Workers API, you can run long JavaScript tasks on a separate thread in the background.
By doing so, you can keep long tasks away from the main thread and still have them running on a separate one without affecting the user’s interaction with your site.
Use Reliable WordPress Themes and Plugins
If you’re running a WordPress site, ignoring this tip will lead you to pay a huge price. Hang on.
BEWARE: Random themes and plugins can have a negative impact on your FID score.
That said, make sure you use only high-quality, trusted WordPress plugins and themes for your site. Also, ensure that you weed out unused, unsafe plugins and themes from your WordPress backend.
Lazy Load Your Images
Enabling lazy loading of images, especially the ones below the fold, allows you to free up some bandwidth and allocate the same for code transferring.
This will reduce the time the browser takes to execute codes and make the page available for user interaction without longer waiting times.
That will fetch your page a better FID score.
Final Thoughts
First Input Delay may look like a small metric, but it may drive visitors away from your site and affect your Google ranking if you don’t pay proper attention to it.
As FID derives from real user input, manipulating it for better rankings is NOT a possibility.
Leverage the above practices to optimize Input Latency effectively and boost your chances of ranking higher on Google.
Author
Ananyaa Venkat
Ananyaa has been penning down industry-specific content for 6+ years. With blogging as her special interest, she loves exploring multiple verticals to keep track of dynamic market trends.

 UsenB
UsenB 
































