Generative Engine Optimization (GEO): How to Win in AI Search
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is quickly becoming one of the most important new topics in search. As large language models (LLMs) change how users discover brands and make decisions, GEO helps ensure your content and brand show up in...

Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is quickly becoming one of the most important new topics in search.
As large language models (LLMs) change how users discover brands and make decisions, GEO helps ensure your content and brand show up in AI-generated answers — not just in traditional search results.
But GEO is just one part of a bigger shift.
We’re entering the era of Search Everywhere (in fact, we’re already in it).
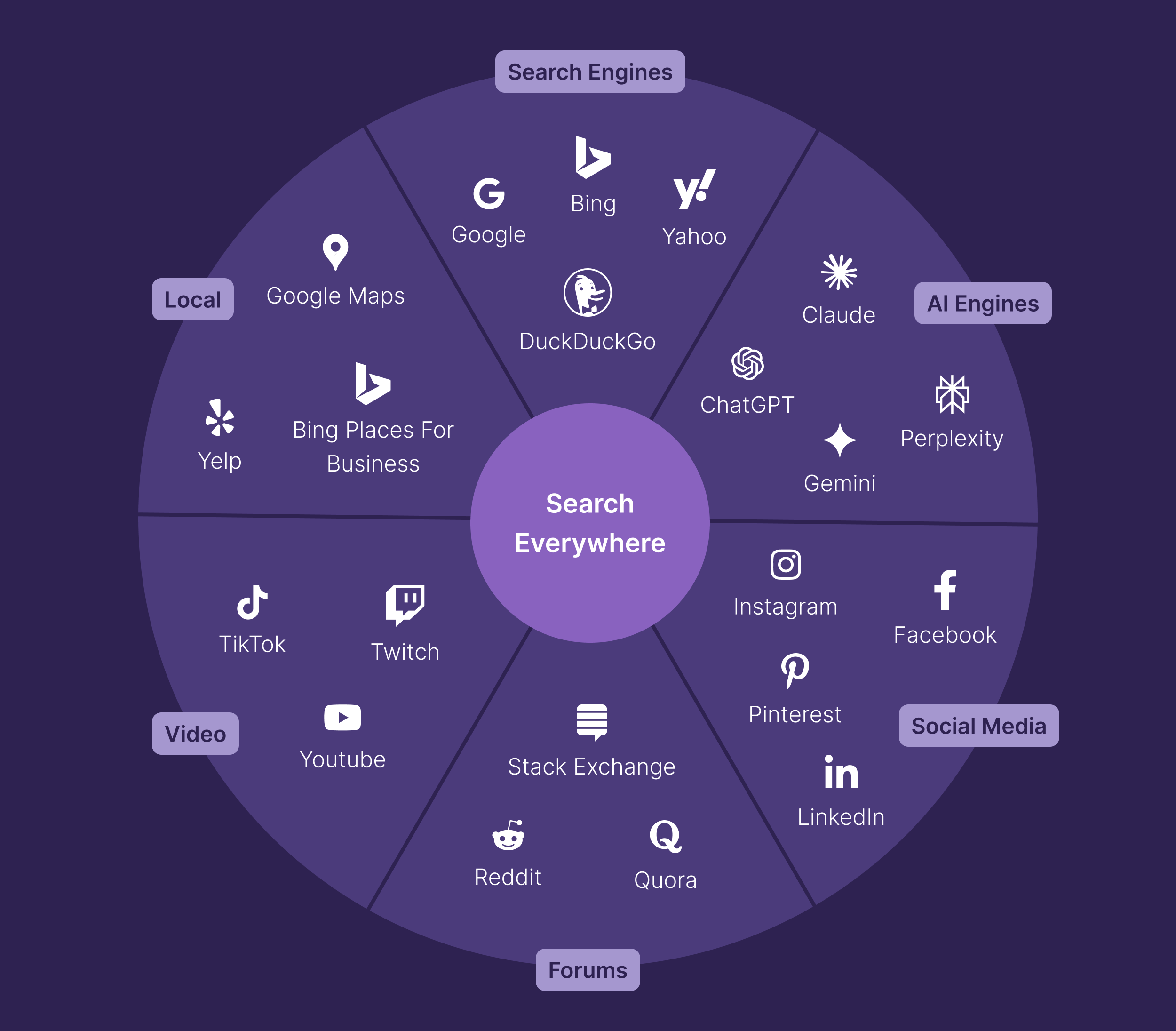
Discovery is no longer confined to Google search results pages.
It’s happening everywhere users seek trusted information and recommendations.
And new data shows just how fast this shift is accelerating.
New research from Semrush predicts that LLM traffic will overtake traditional Google search by the end of 2027.
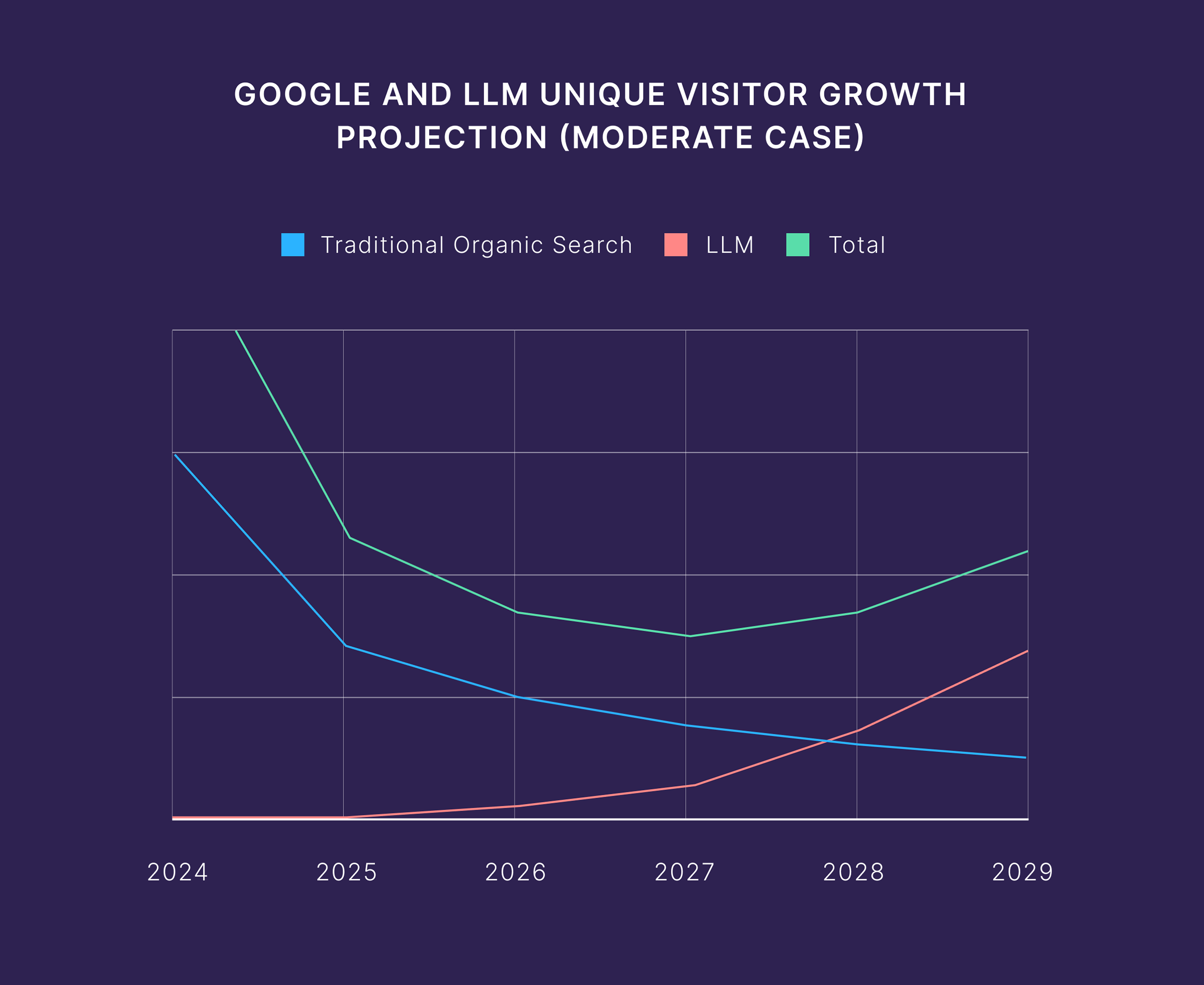
And our own data suggests that’s likely to be true.
In just the past three months, we’ve seen an 800% year-over-year increase in referrals from LLMs.
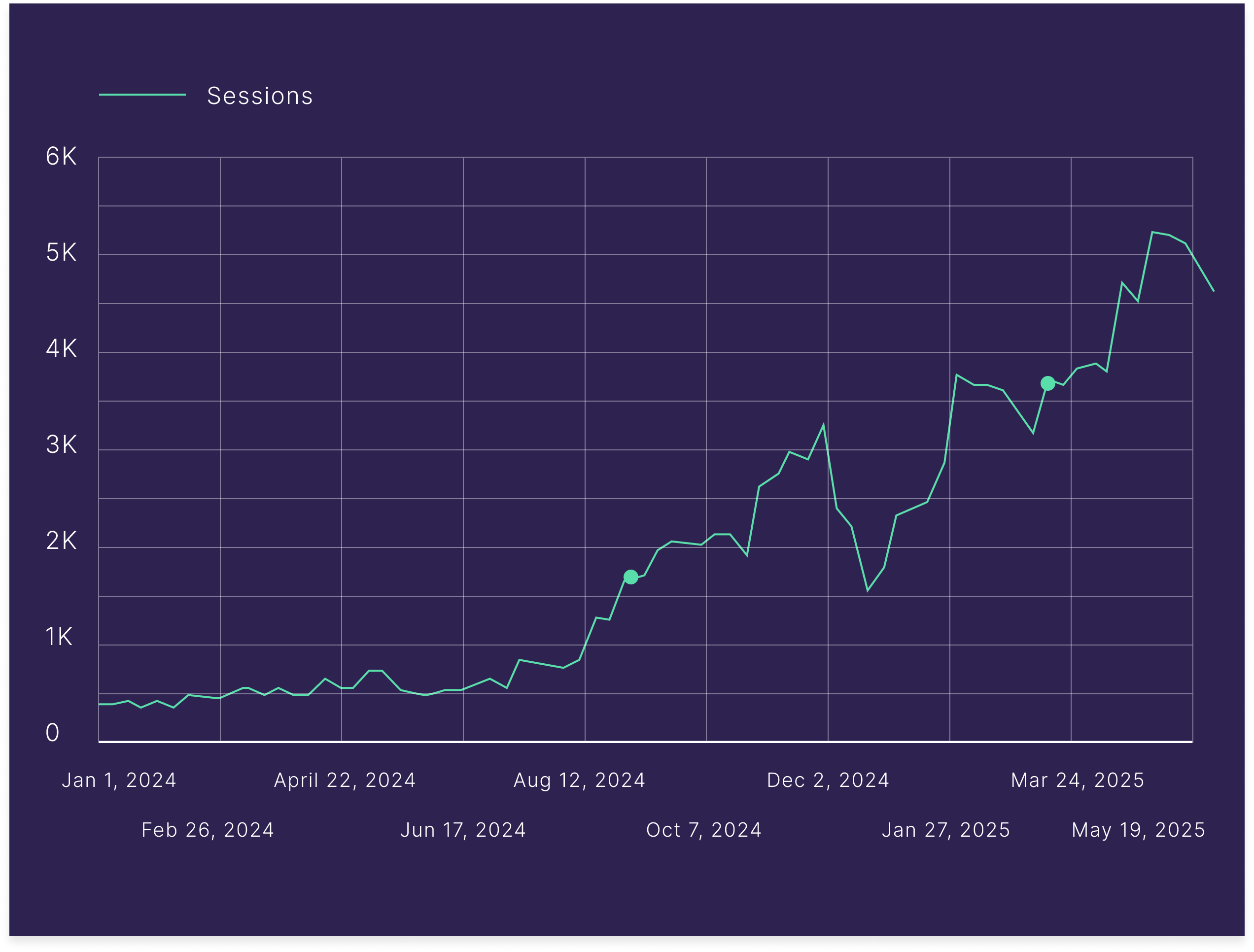
We’re seeing tens of millions of additional impressions in Google Search Console as AI Overviews reshape how Google displays answers.
If your brand isn’t adapting, you could soon be invisible online.
In this guide, I’ll explain:
What GEO is and how it’s different from SEO Why you shouldn’t throw away everything you’ve already learned The top techniques that will help you optimize your content for generative engines (and drive results for your business in the process)What Is GEO and Why Does It Matter?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the practice of creating and optimizing content so that it appears in AI-generated answers on platforms like Google AI Overviews and AI Mode, ChatGPT, and Perplexity.
But GEO goes beyond content optimization. It’s a holistic approach that includes:
Publishing content in the right places where AI tools are most likely to discover it Earning positive brand mentions across the web, even without direct links Ensuring technical accessibility so AI crawlers can easily access and understand your contentInstead of focusing only on traditional rankings, you’re making sure your brand becomes part of what AI tools say when users ask questions.
These tools “generate” responses to queries in conversational language. While they can include links, the goal is to give the searcher what they need within the response.
So in GEO, your content needs to shape the conversation, not just try to win a click.
Why GEO Matters Now
Traditional Google search still dominates.
It’ll likely continue to drive most of your traffic in the near term.
But the way people discover information is changing — fast.
Success used to mean ranking at the top of the SERP.
Looking forward, there may not even be a “top spot.”
Instead, you need to become the top recommendation — the solution AI tools choose to recommend in their answers.
The data tells the story:
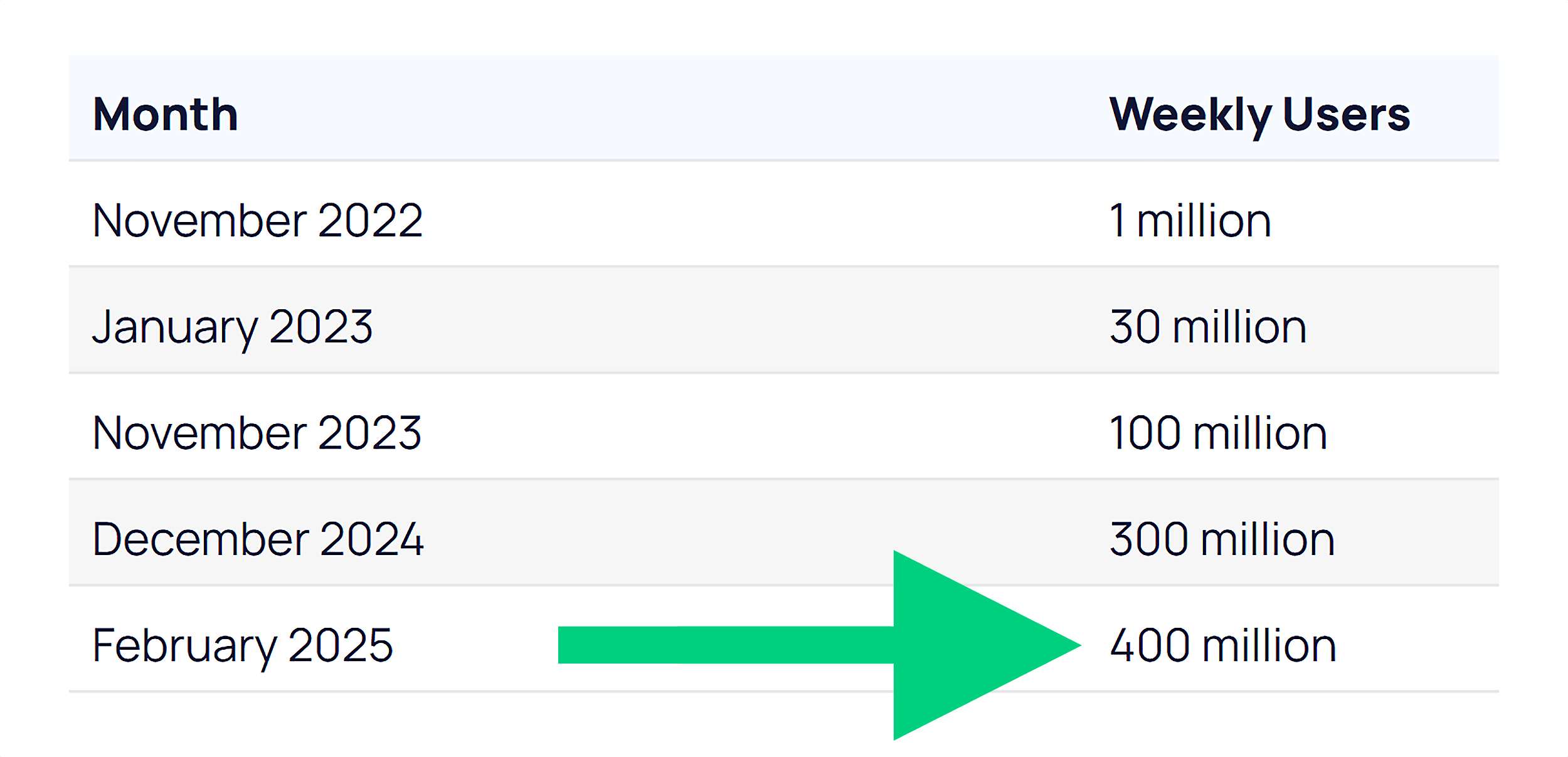
ChatGPT reached 100 million users faster than any app in history. And as of February 2025, it now has more than 400 million weekly users.
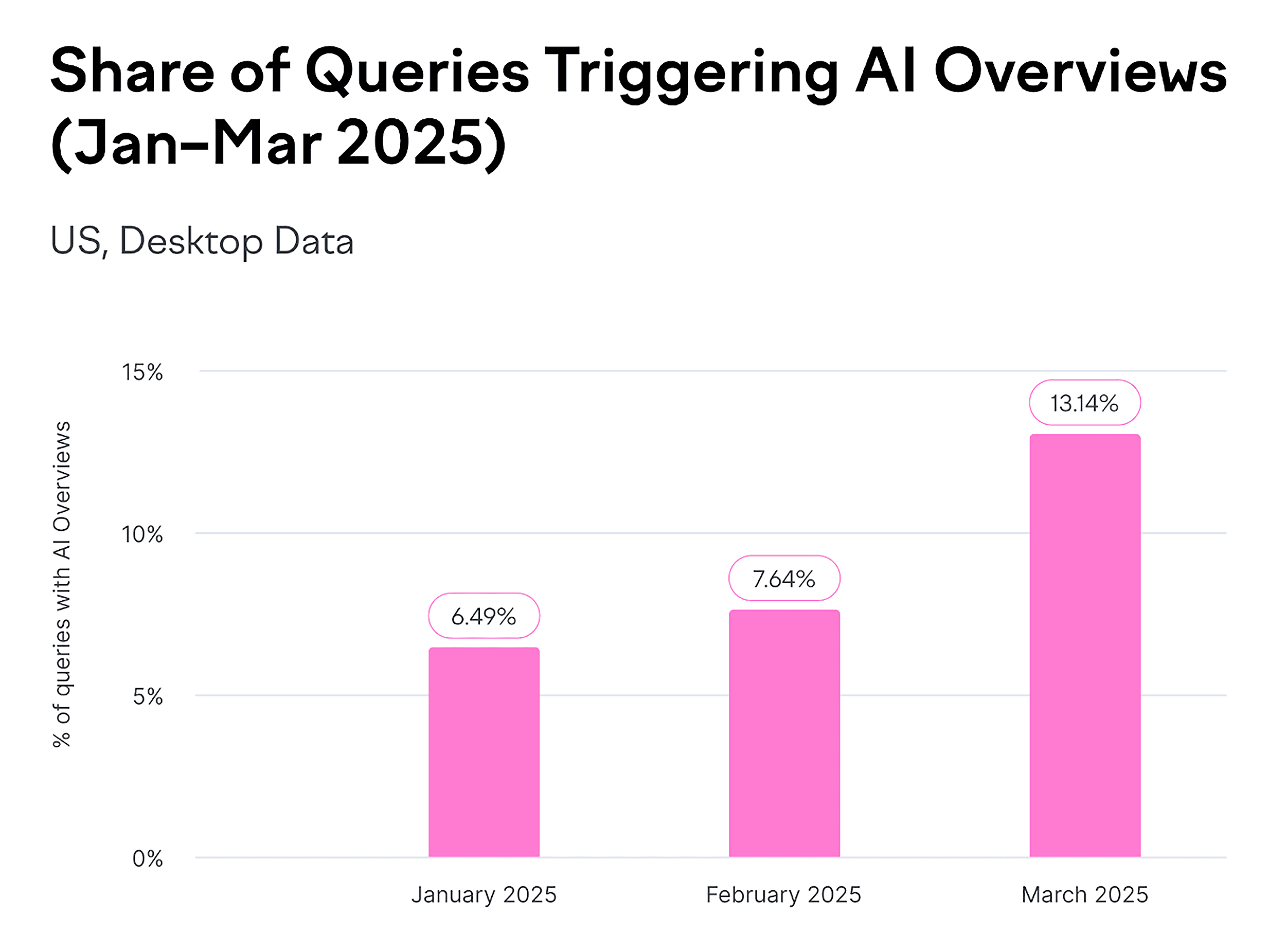
Google’s AI Overviews now appear on billions of searches every month — at least 13% of all SERPs.
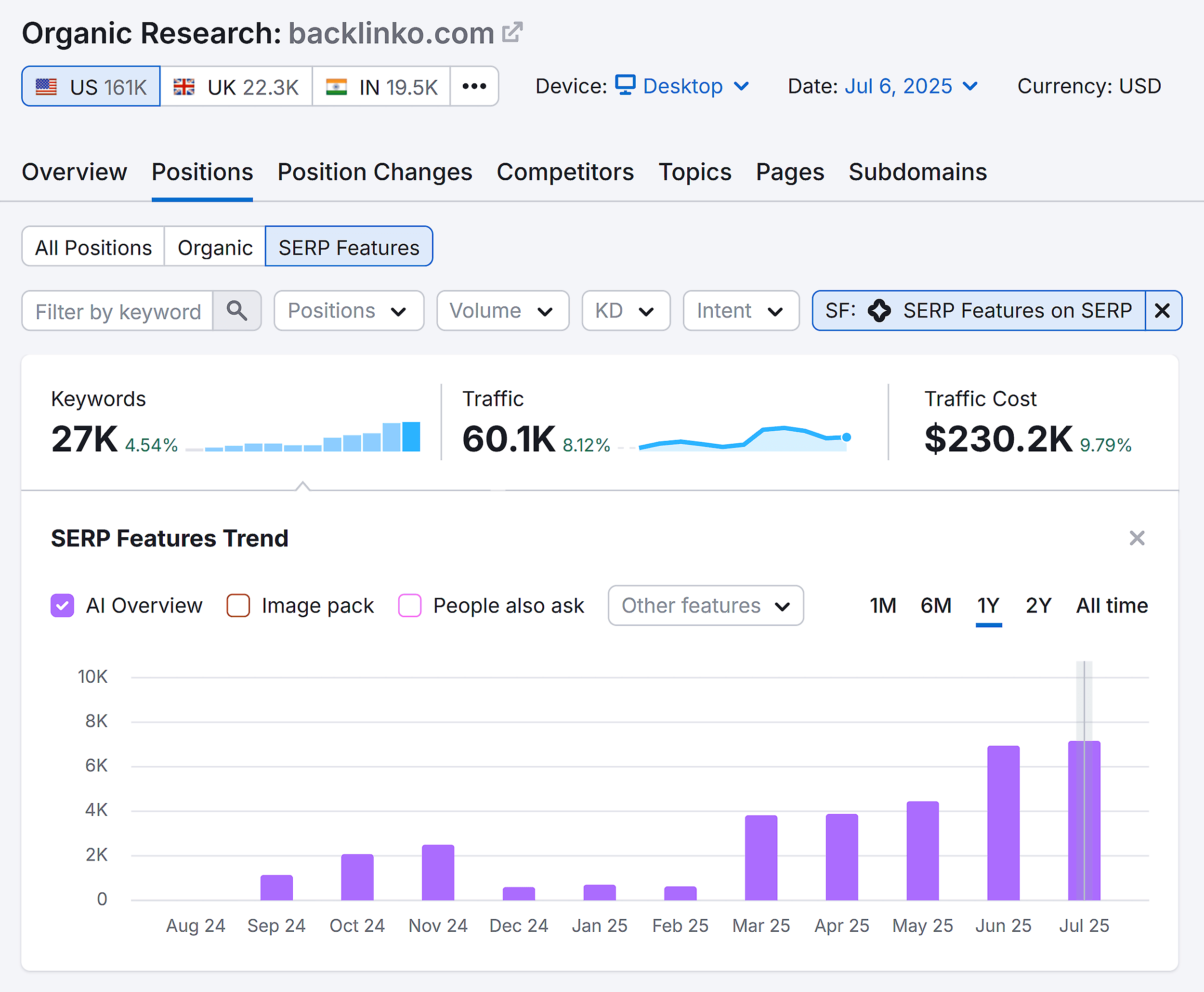
And they appear for more than half of the keywords we track at Backlinko:
Generative engines are influencing YOUR audience too. So it makes sense to start optimizing for them now.
How GEO and SEO Work Together
Before we go any further, let’s get one thing straight:
You might look at this guide and think,
“Isn’t this just SEO with a different name?”
And honestly?
In many ways, it is. But there’s a reason everyone’s talking about it.
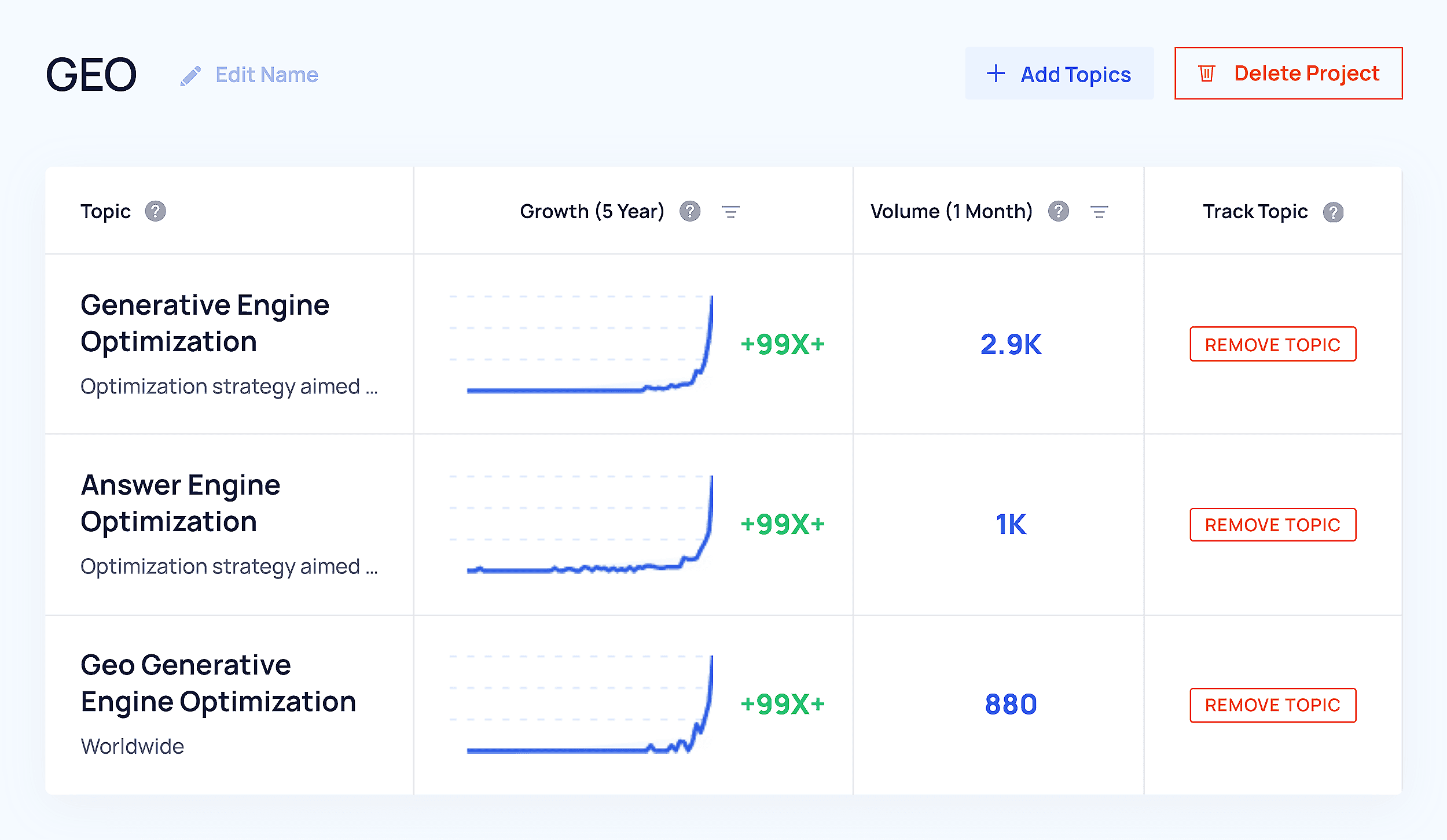
Terms like GEO, AEO (Answer Engine Optimization), and AIO (AI Optimization) have exploded in interest — because they reflect a real shift.
And with all the acronyms flying around, it can be tough to know who to listen to.
We’re not saying GEO replaces SEO.
But it does help reframe your strategy for how discovery works now — across AI tools, social platforms, and new surfaces beyond traditional search.
From Traditional SEO to Search Everywhere
| SEO = Google Search | SEO = multi-surface visibility (Search, AI/LLMs, social) |
| Success = ranking for keywords | Success = being found across Search + Chat |
| SEO is a siloed function | SEO is cross-functional + connected to product, brand, PR, and social |
| Keyword-first content planning | Intent and entity-driven topic planning with semantic structure |
| Backlinks to pass PageRank | Traditional backlinks plus more focus on brand mentions and co-citations |
| Traffic as a core KPI | Visibility, influence, and conversions across touchpoints as core KPIs |
| Technical SEO as the foundation | Technical SEO as the foundation (with additional focus on JavaScript compatibility) |
That means there’s good news:
If you’ve invested in good SEO, you’re already a lot of the way there.
GEO builds on the foundation of great SEO:
Creating high-quality content for your specific audience Making it easy for search engines to access and understand Earning credible mentions across the webThese same elements help AI engines decide which brands to reference.
But here’s the difference:
AI engines don’t work exactly like Google.
That means some of your tactics (and what you track) need to evolve.
So let’s walk through how to do that.
7-Step GEO Action Plan
We’re still in the early days of understanding exactly how AI engines pull and prioritize content.
But one thing is clear:
You need to adapt or reprioritize some traditional SEO tactics for Generative Engine Optimization.
The first three steps below cover overarching best practices for GEO.
Steps 4-7 cover optimizing content for generative engines specifically (and how to track your results).
Step 1. Nail the Basics of SEO
As I said earlier, good GEO is also generally good SEO. But not everything you do as part of your wider SEO strategy is as important for generative engine optimization.
I won’t go through all the fundamentals of SEO here. We do that in our guide to the SEO basics.
Let’s focus on what really matters for generative engines.
Make Your Site Easy to Read (for Bots)
Crawlable and indexable: If AI tools can’t access your pages, you won’t show up in answers Fast and mobile-friendly: Slow, clunky sites hurt UX — and your chances of getting cited Secure (HTTPS): This is now table stakes, and it builds trust with users and AI systems Server-side rendering: Some AI crawlers still struggle with JavaScript, so use server-side rendering as opposed to client-side rendering where you canShow You’re Worth Trusting (E-E-A-T)
AI wants trustworthy sources. That means showing E-E-A-T:
Experience: Share real results, personal use, or firsthand knowledge Expertise: Stick to topics you truly know — and go deep Authority: Get quoted, guest post, or contribute to well-known sites Trust: Use real author bios, cite sources, and include reviews or testimonialsStep 2. Build Mentions and Co-Citations
AI systems don’t just look at backlinks to understand your authority. They pay attention to every mention of your brand across the web, even when those mentions don’t include a clickable link.

Backlinks are still important. But this changes how you should think about building your wider online presence.
Audit Your Current Mentions
Start by auditing where you’re currently mentioned. Search for your brand name, product names, and key team members across Google, social media, and industry forums.
Take note of what people are saying and where those conversations are happening.
You’ll probably find mentions you didn’t know existed. Some will be positive, others neutral, and a few might need your attention.
Also run your brand name and related terms through the AI tools themselves.
Does Google’s AI Mode cite your brand as a source for relevant terms? Does ChatGPT know who your team members are? What kind of sentiment do the answers have when you just plainly ask the tools about your brand?
For a more in-depth sentiment analysis, use Semrush’s AI Toolkit.
It’ll let you track your LLM visibility (a by-product of good GEO) in top tools compared to your rivals:
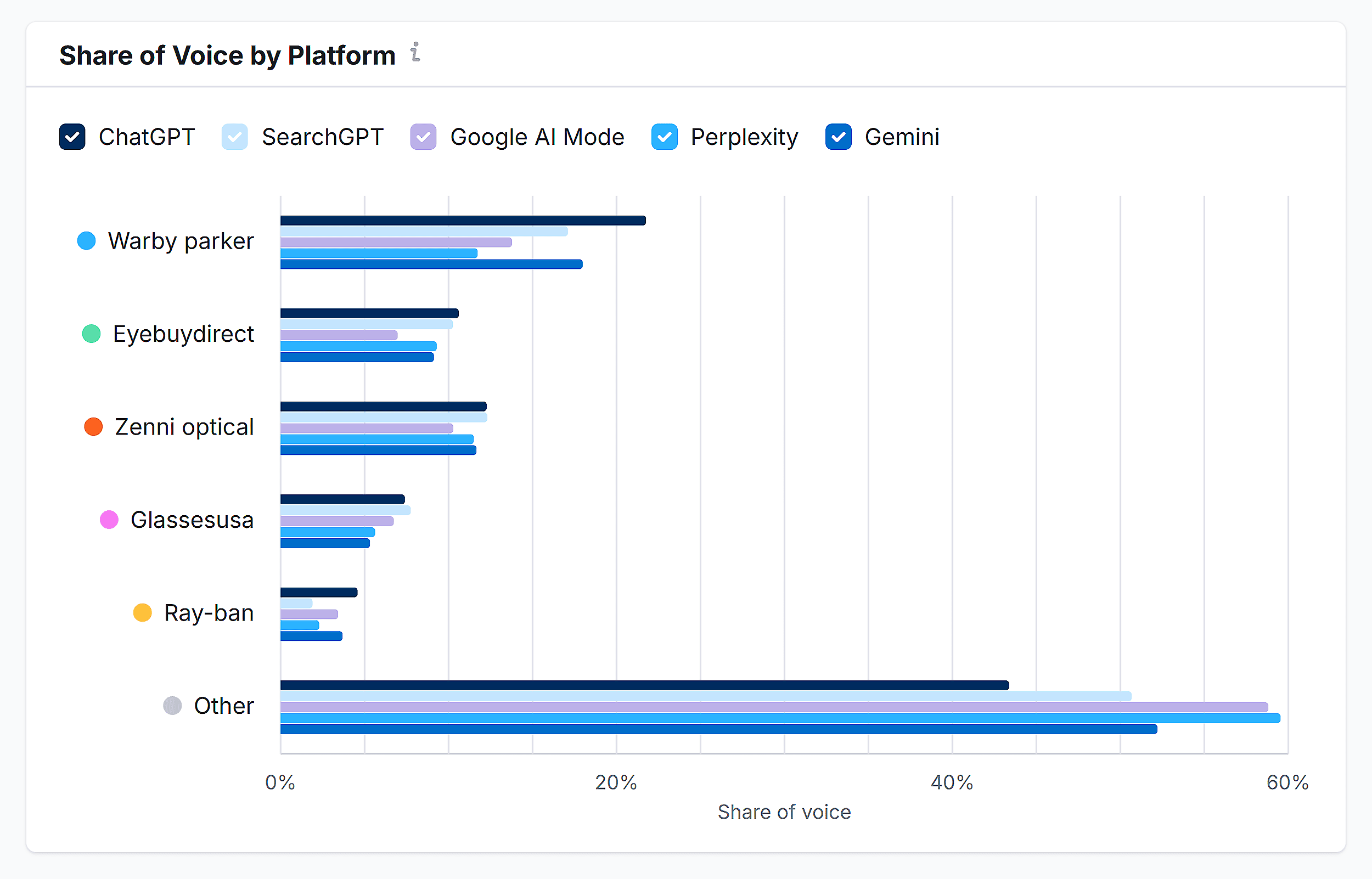
The tool compares your brand to your rivals in terms of AI visibility, market share, and sentiment:
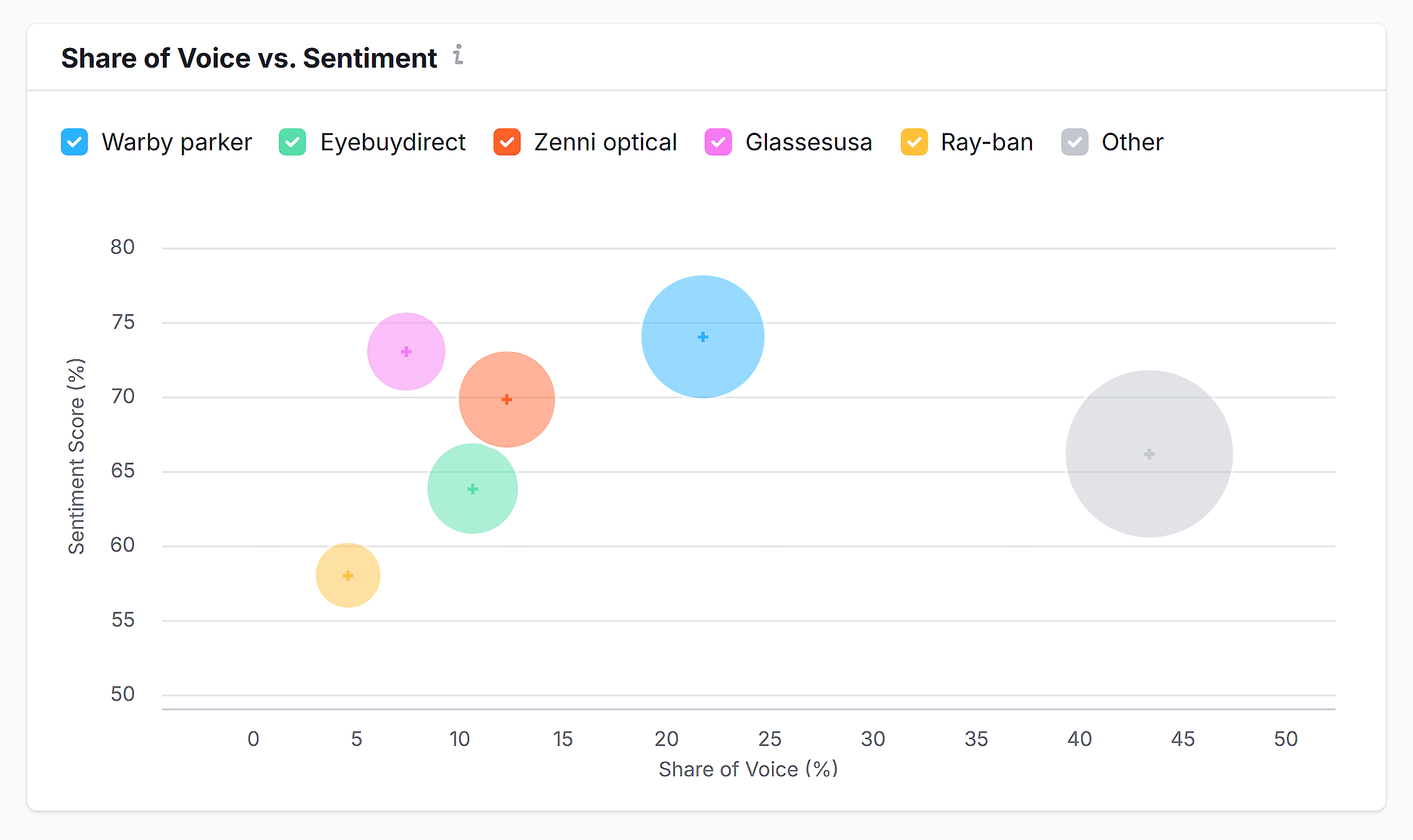
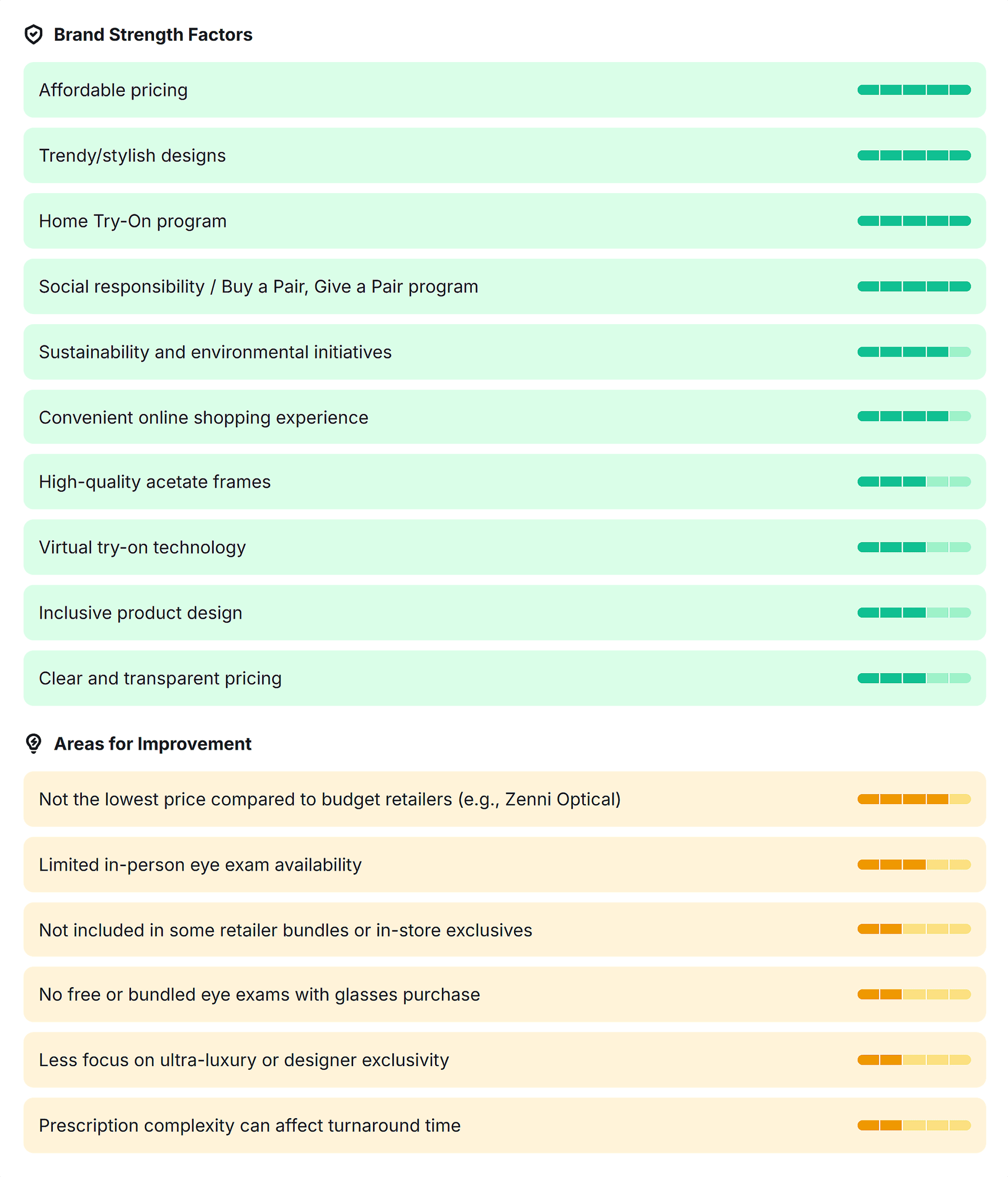
And it’ll show you where your brand strengths are and where you can improve:
Keep Building Quality Backlinks
Just because mentions are more important than before with GEO, it doesn’t mean you should abandon traditional link building. Backlinks still matter for SEO, and they often lead to the kind of authoritative mentions that AI systems value.
But expand your focus beyond just getting links.
Aim to Build Co-Citations and Co-Occurences
There are a few different definitions out there of co-citation and co-occurence.
I’ll be honest: the definitions don’t matter as much as the implications. I’ve seen one source define co-citations as the exact thing another source calls co-occurence. So for this section, I’m just going to talk about what these are and why they matter, without getting bogged down in definitions.
The first important way to think of co-citations/co-occurences is simply the mention of one thing alongside another.
In the case of GEO, we’re usually talking about your brand or website being mentioned alongside a different website or topic/concept on another website.
For example, if your brand is Monday.com, you’ll pick up co-citations involving:
Your competitors (ClickUp, Asana etc.) Key terms or categories associated with your business (like “project management software”) Specific concepts or questions related to what you do (e.g., “kanban boards” and “how to automate workflows”)In Monday’s case, there are hundreds of pages out there that mention it alongside ClickUp and Asana in the context of “project management tools”:
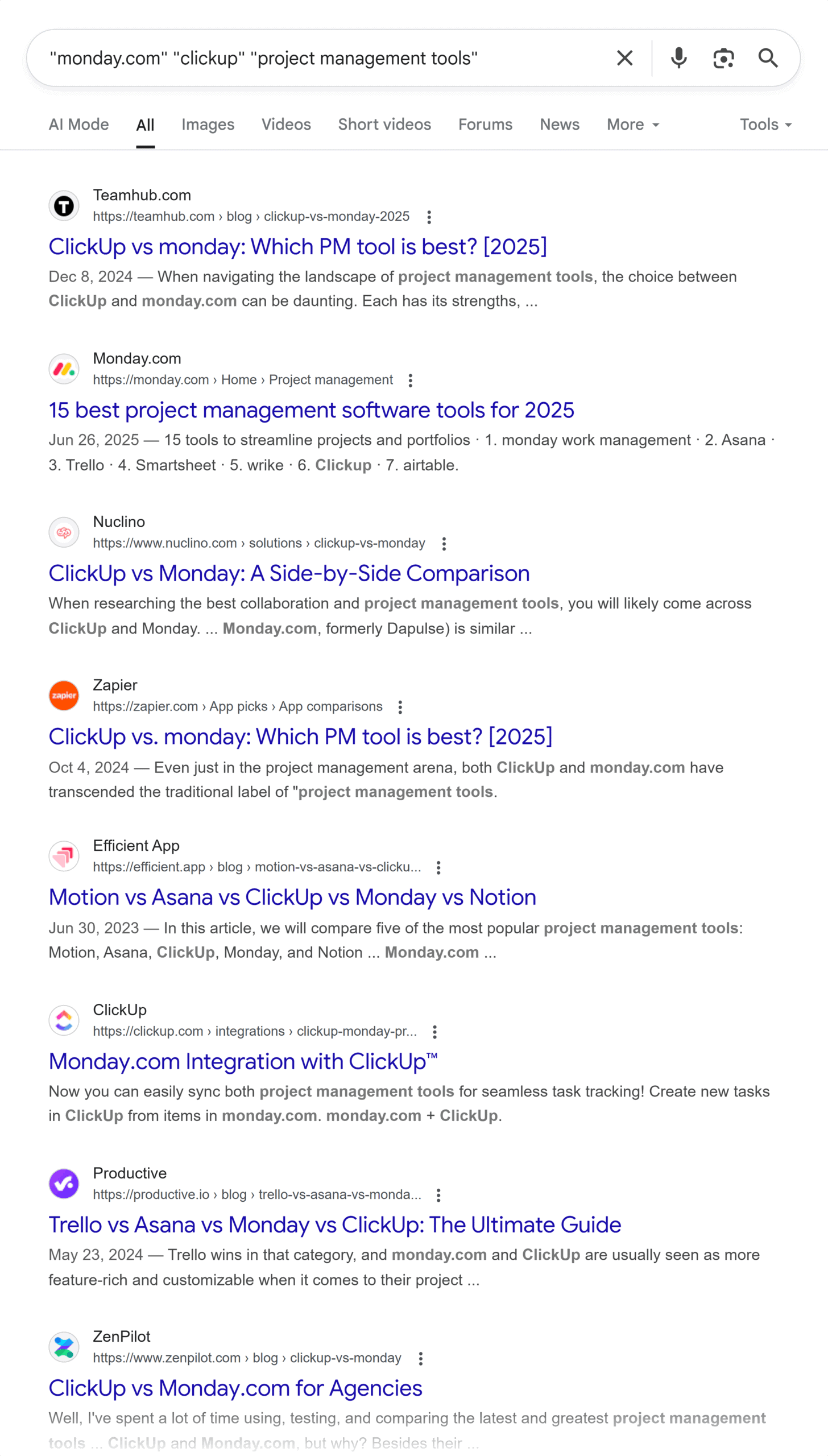
This suggests to Google and other generative AI tools that Monday and ClickUp are both related to the term “project management tools” and are both popular providers of this kind of software.
The other common way to think about co-citations is mentions of your brand across different, often unrelated websites. For example, Monday being mentioned on Forbes and Zapier would be a co-citation involving them.
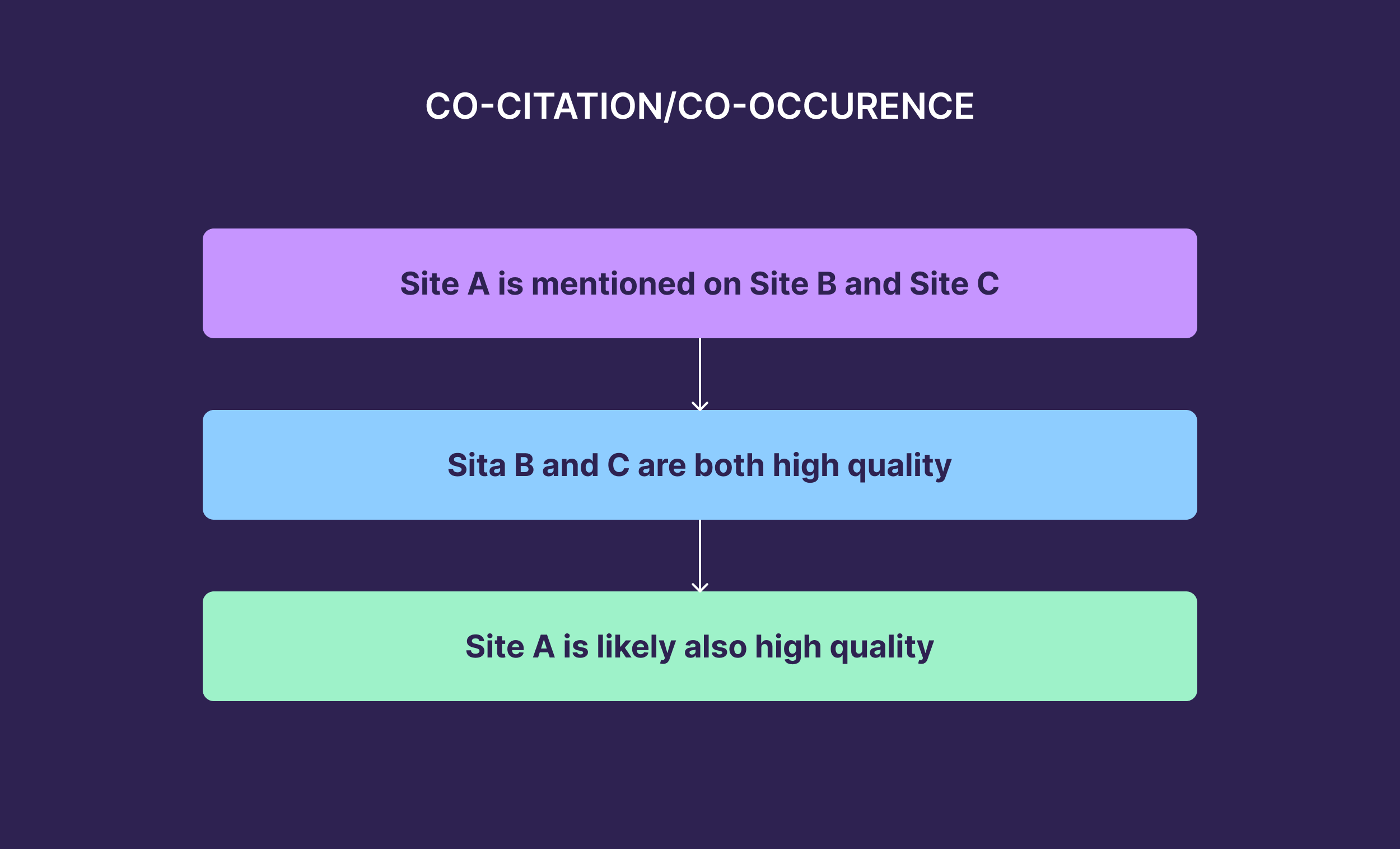
To sum it up:
If two (or more) brands/websites are often mentioned alongside each other, AI tools will assume they are related (i.e., they’re competitors) If a brand is often mentioned in the context of a particular topic, concept, or industry, AI tools will assume the brand is related to those things (i.e., what you offer) If lots of different websites mention a particular brand, the AI tools will assume that brand is worth talking about (i.e., probably trustworthy)Obviously, there’s a lot more to it, but this is a fairly basic overview of what’s going on.
How to Put This into Action
To build citations, co-citations, and co-occurences:
Look for opportunities to get mentioned alongside your competitors. When publications write comparison articles or industry roundups, you want your name in that list. These co-citations help AI systems understand where you fit in your market. Participate in industry surveys and research studies. When analysts publish reports about your sector, being included gives you credibility (and any backlinks are a bonus). Get involved in relevant online communities. Answer questions on Reddit, contribute to LinkedIn discussions, and join industry-specific forums. These interactions create mentions in places where AI systems often look for authentic, community-driven insights.
The goal is to become a recognized voice in your space. The more often your brand appears in relevant contexts across the web, the more likely AI systems are to include you in their responses.
Step 3. Go Multi-Platform
Going beyond Google is something top SEOs have been telling us to do for a long time. But AI has made this an absolute must.
Platforms like Reddit, YouTube, and other user-generated content sites appear frequently in AI outputs.
So, a strong brand presence on these platforms could help you show up more often.
The benefits here are (at least) three-fold:
Being active on multiple platforms lets you reach your audience where they are. This helps you boost engagement, brand awareness, and, of course, drive more conversions. AI tools don’t just look at Google search results. They pull from forums, social media, YouTube, and lots of other places beyond traditional SERPs. Being active on multiple platforms means you’re less exposed to one particular algorithm or audience. Diversification is just good practice for a business.Brian Dean did an excellent job of this when he was running Backlinko. That’s why you’ll see his videos appear in Google SERPs for ultra-competitive keywords like “how to do SEO”:
We’re taking our own advice here. In fact, it’s a big part of why we launched the Backlinko YouTube channel:
Here’s some quick-fire guidance for putting this into practice:
People go to YouTube to learn how to do things, research products, and find solutions to their problems. This makes product reviews, tool comparisons, and in-depth tutorials great candidates for YouTube content. Podcast content and transcripts are beginning to surface in AI results (especially in Gemini). Building a presence here is a great opportunity to grab some AI visibility. TikTok and Instagram Reels reach younger audiences who increasingly use these apps for search. Short-form videos that answer common questions in your industry can drive discovery, and AI tools can also cite these in their responses to user questions. AI tools LOVE to cite Reddit as a source of user-generated answers (especially Google’s AI Overviews and AI Mode). To grow your presence on the platform, find subreddits where your target audience hangs out and share genuinely helpful advice when people ask questions related to your expertise. Don’t promote your business directly — focus on being useful first. LinkedIn works similarly to Reddit for B2B topics. Publish thoughtful posts and engage in relevant discussions to help establish your voice in professional circles. These interactions can then get picked up by AI systems looking for expert perspectives.Step 4. Find Out What AI Platforms Are Citing for Your Niche
What’s a powerful way to understand both what to create and what topics to target?
To simply learn what AI tools are likely to include in their responses to questions that are relevant to your business.
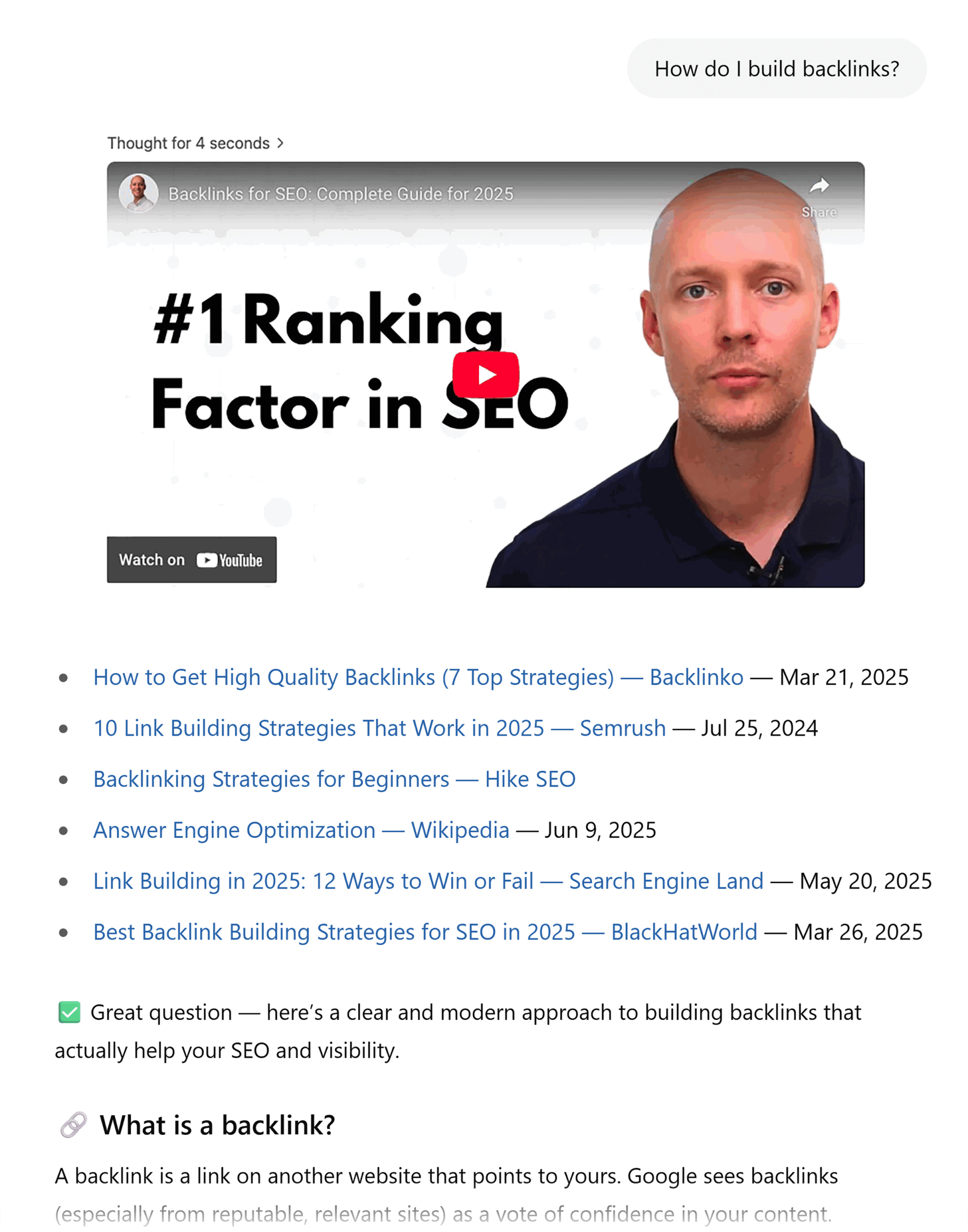
Start by directly testing whether/how your content appears in AI tools right now. Go to ChatGPT, Claude, or Perplexity and ask questions that your content should answer.
In the example below, Backlinko is mentioned (great), but there’s also a YouTube video front and center. And forums are appearing too. These are places we might want to consider creating content or engaging with conversations.
As you do this for your brand, pay attention to the sources they cite:
Are they commonly mentioning your competitors? What platforms do they tend to cite? (Reddit, YouTube etc.) What’s the sentiment of mentions of both your brand and your competitors?As you do this, try different variations of the same question.
For example, you could ask “What’s the best email marketing software?”

Then try “Which email marketing tool should I use for my small business?”

Notice how the answers change and which sources get mentioned consistently.
In the example above, the first prompt mentioned MailerLite, which was absent in the list for small businesses. But the second prompt pushed Mailchimp to the top and mentioned three new options (Constant Contact, Brevo, and ActiveCampaign).
If you were MailerLite and trying to reach small businesses, you’d want to understand why you’re not being cited for that particular prompt.
You can automate this process with tools like Profound or Peec AI. These platforms run prompts at scale, helping you understand how and where your brand appears. But they can be pricey.
That’s why I recommend you spend some time running these prompts manually at first.
By the way:
This isn’t just important for “big brands” or those selling products. You can (and should) do this if you run a blog, local business website, or even a personal portfolio.
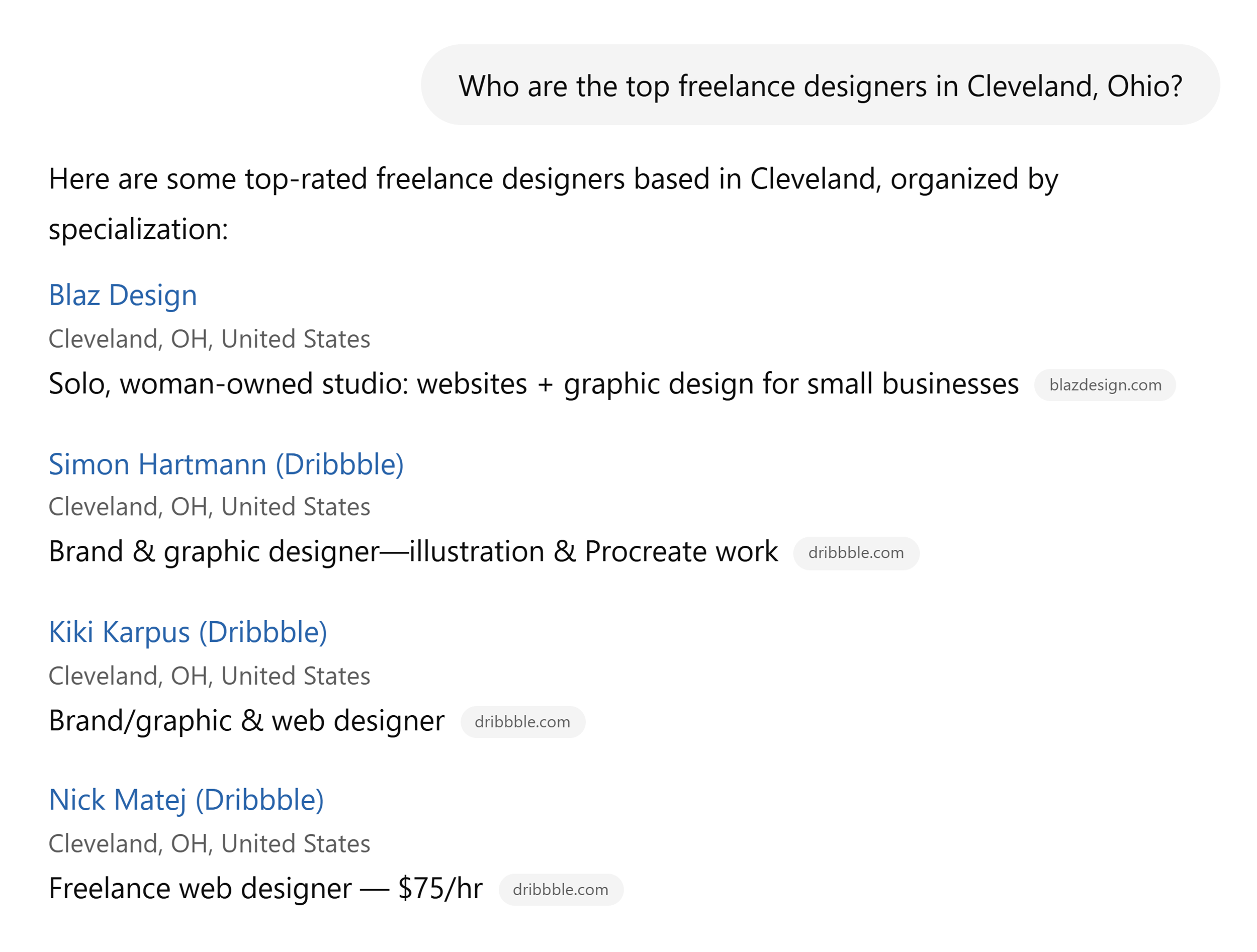
For example, consultants and freelancers will find these tools often cite marketplaces like Upwork and Dribbble. If you don’t have a profile on there, you’ll likely struggle to get much AI visibility.
And if you’re a local business owner, you’ll often find specific service and location pages appear in AI responses:
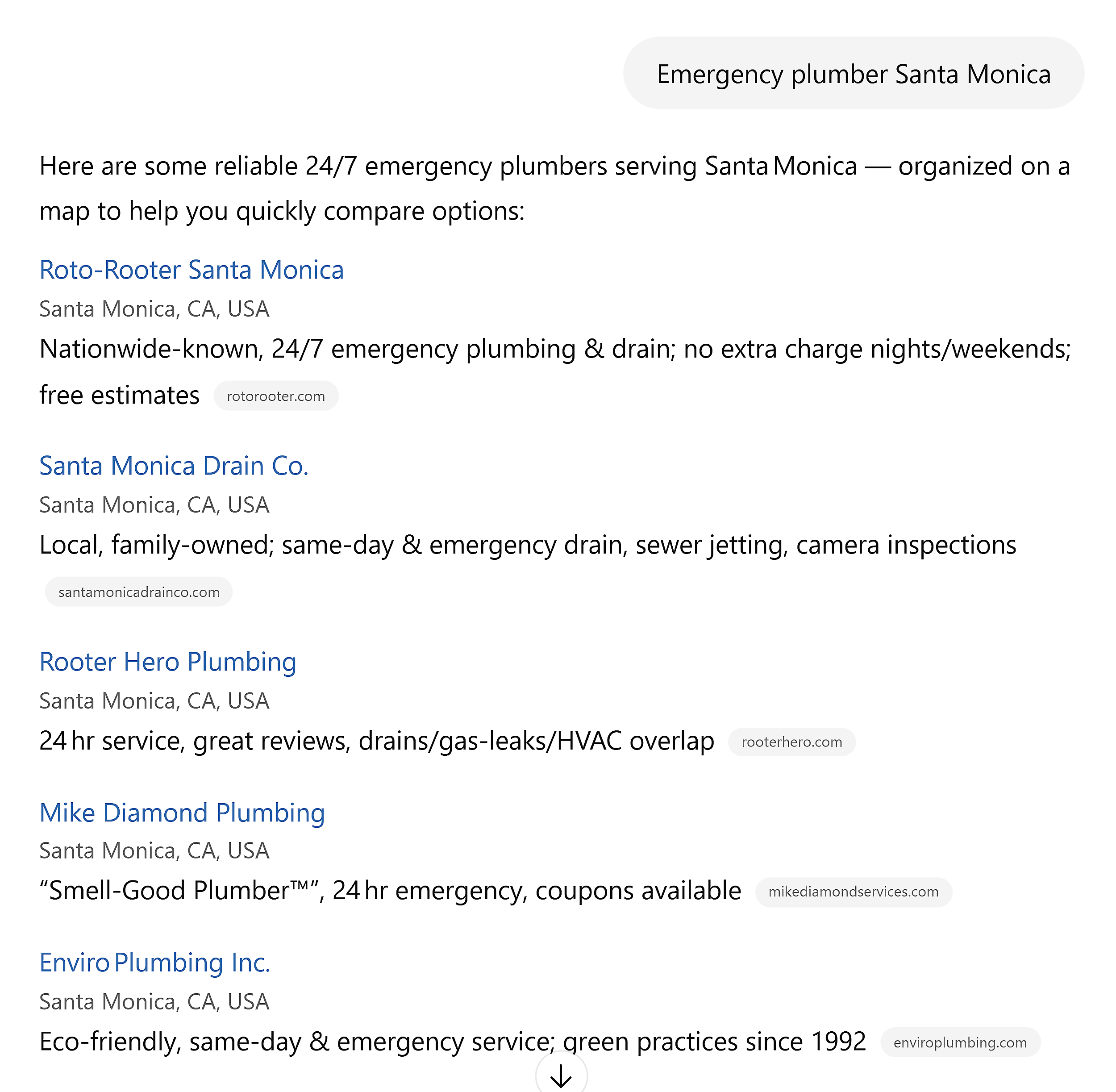
This is useful for understanding the types of content you should be focusing on for GEO. Now it’s time to decide what topics to focus on in your content.
Step 5. Answer Your Audience’s Questions
The way people search with AI tools is fundamentally different from how we use traditional Google search. This changes how you should plan your content.
Traditional SEO taught you to target specific keywords. You’d create a page optimized for “healthy meal prep ideas” and try to rank for that phrase.
But what happens when people are instead searching for “what to cook for dinner when I’m trying to lose weight”?
The answer might involve healthy meal prep as a solution, but it’s a completely different prompt (not a search) that gets to that answer (not a SERP).
When you run these queries through Google’s AI Mode, you see two totally different sets of sources and content types.
For the “healthy meal prep ideas” query (which is a perfectly valid and searchable term), the focus is listicles, single recipes, and YouTube videos. And the format is categories (bowls, wraps, and sandwiches etc.) with specific recipes:
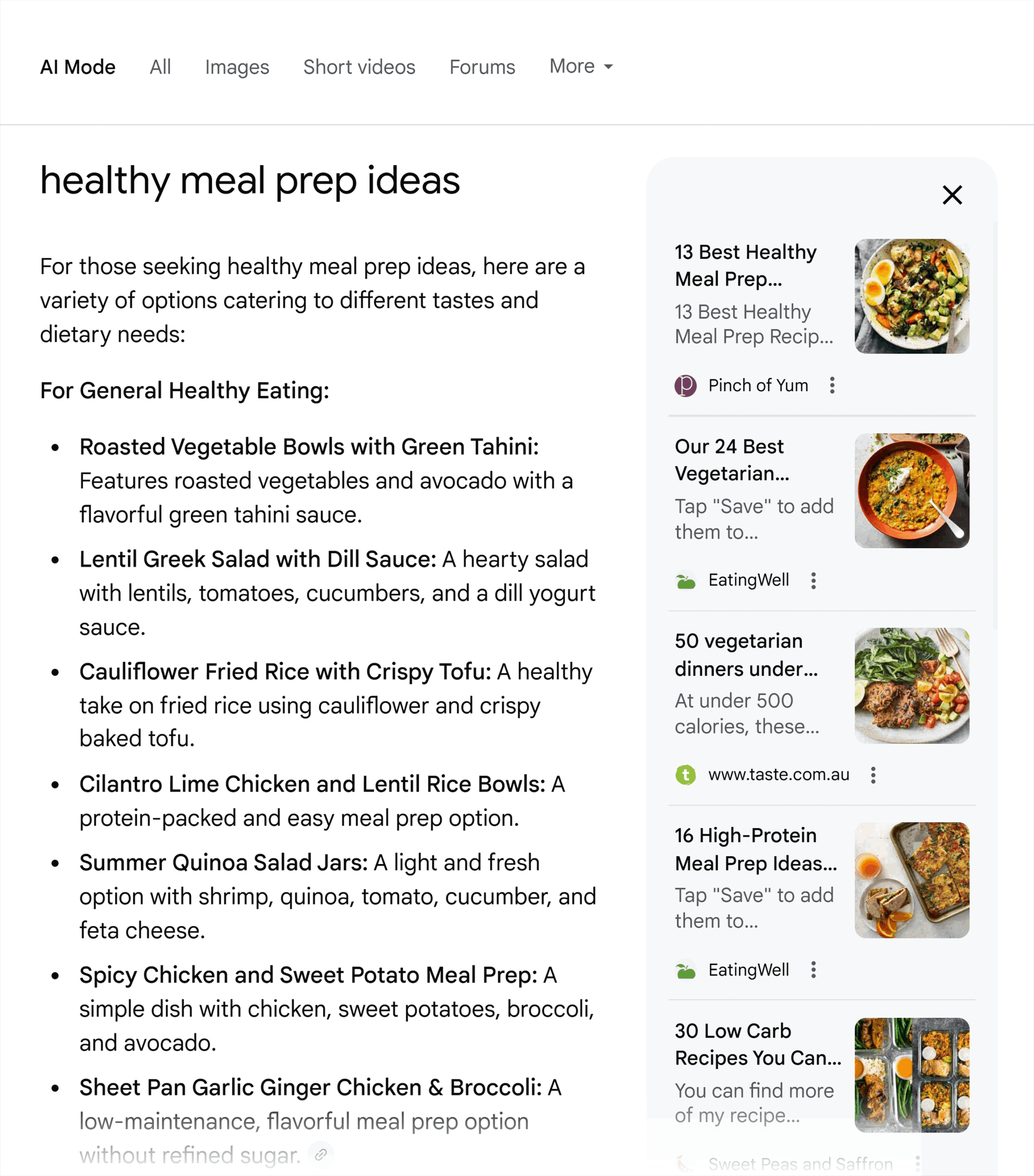
But for “what to cook for dinner when I’m trying to lose weight,” the sources are primarily lists, forum results, or articles specifically around weight loss.
In this case, the format of the answer is largely broad tips for cooking healthily and then some general cooking styles or meal types, rather than specific recipes:
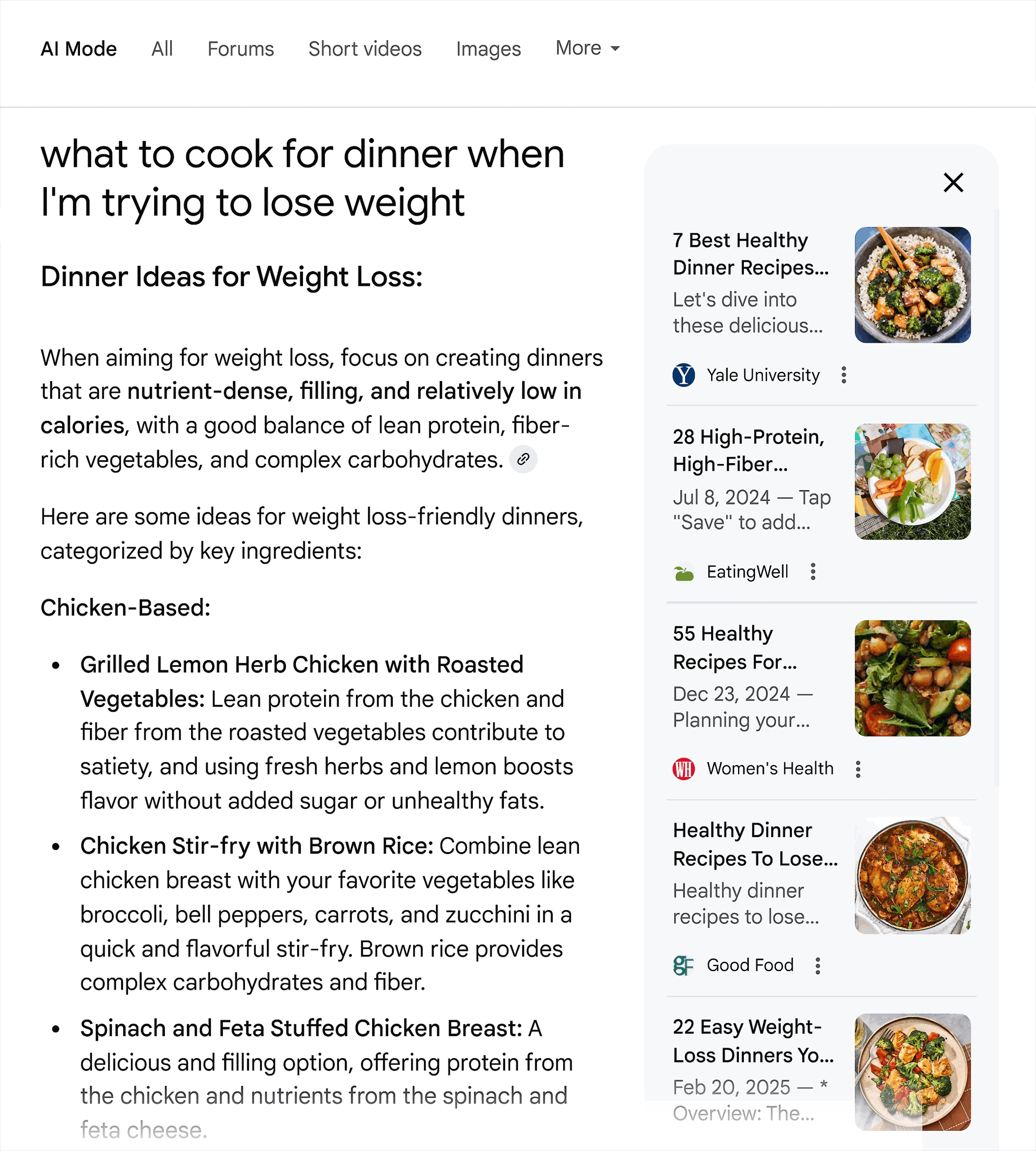
As more users realize they can use conversational language to make their searches, longer queries will become more common. This makes this kind of intent analysis critical.
These longer, more specific queries represent huge opportunities. Most companies aren’t creating content that answers these detailed questions.
The more specific the question, the more likely you are to show up when AI systems look for authoritative answers. You want to own the long-tail queries that relate directly to your product or expertise.
But:
You obviously can’t reasonably expect to create content for every single long-tail query out there. So how do you approach this in an efficient way?
How to Choose the Questions to Answer
Start by listening to the actual questions your customers ask.
Check your customer support tickets, sales calls, and user feedback. These real questions from real people often make the best content topics — because they’re the same kinds of questions people will ask these AI tools.
Don’t have any customers? No problem.
Use community platforms to find these conversational queries. Reddit, Quora, and industry forums are goldmines for discovering how people actually talk about problems in your space.
Step 6. Structure Your Content for Generative Engines
AI systems process information differently than humans do. They break content into chunks and analyze how those pieces relate to each other.
Think of it like featured snippets but more granular, and for much more than just direct questions.
This means the way you structure your content directly impacts whether AI systems can understand and cite it effectively.
One Idea per Paragraph
Keep your paragraphs short and focused on one main idea.
When you stuff multiple concepts into a single paragraph, you make it harder for AI systems to extract the specific information they need.
Also avoid burying important information in the middle of long sentences or paragraphs. Front-load your key points so they’re easy to find and extract.
And guess what?
It also makes it easier for your human readers to understand too. So it’s a win-win.
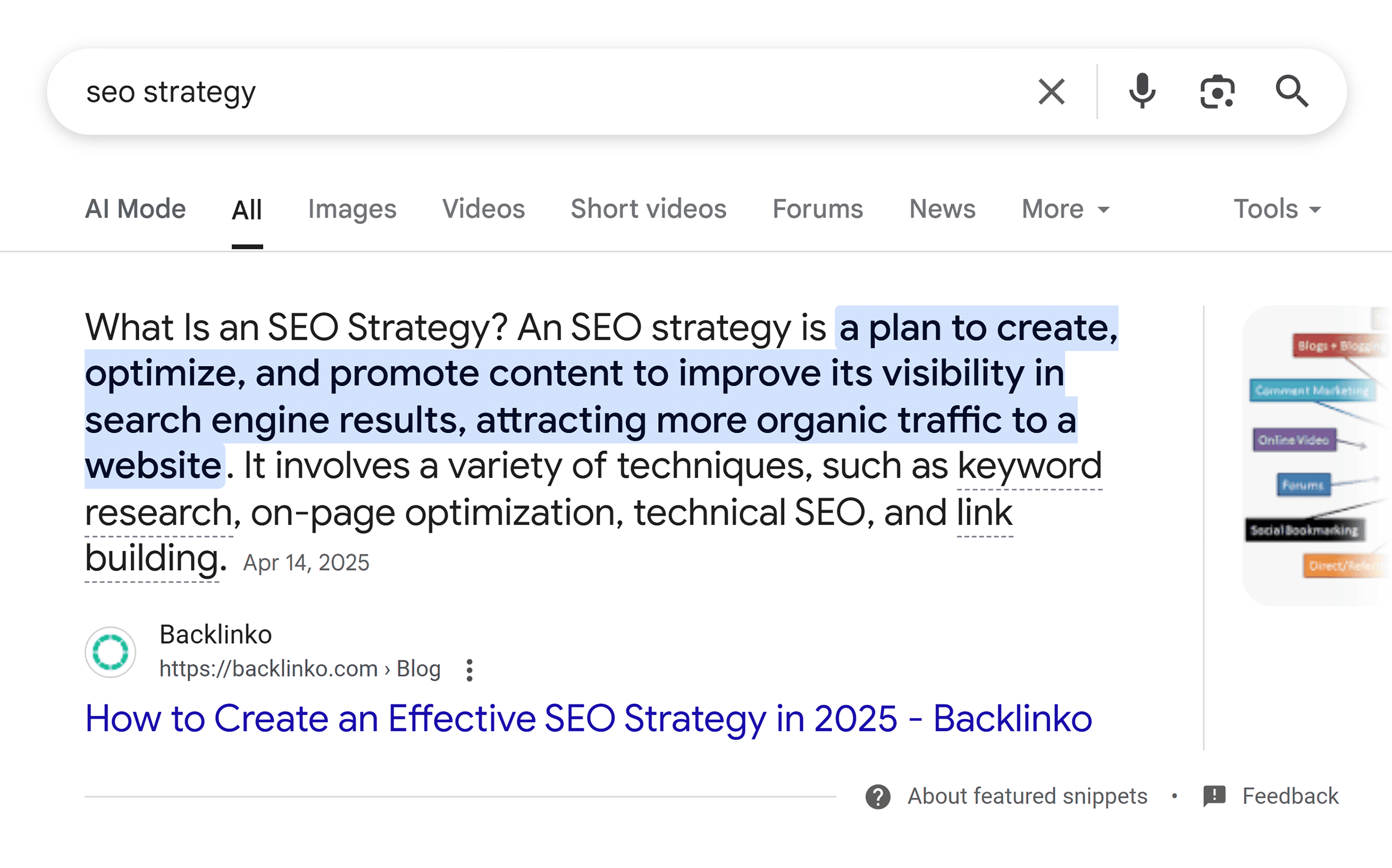
Use Clear Headings
Use clear headings and subheadings to organize your content logically.
Think of these as signposts that help both readers and LLMs navigate your information. And make sure your content immediately under the headings logically ties to the heading itself.
For example, look at the headings in this section. Then read the first sentence under each one.
Notice how they’re all clearly linked?
This is a common technique when trying to rank for featured snippets. You’d have an H2 with some content that immediately answers the question…

…and this would rank for the featured snippet for that query:
This is still a valid strategy for traditional search. But for GEO, you need to have this mindset throughout your content.
Don’t make every H2 be a question (this will quickly end up looking over-optimized). But do make sure the content that follows your (logical) headings is clearly linked to the heading itself.
Break Up Complex Topics into Digestible Sections
If you’re explaining a complex or multi-step process, use numbered steps and clear transitions between each part.
This makes it easier for AI systems to pull out individual steps when someone asks for specific instructions. And it’ll make it much easier for your readers to follow.
Also write clear, concise summaries for complex topics. AI systems often look for these kinds of digestible explanations when they need to quickly convey information to users.
Include Quotes and Clear Statements
Include direct quotes and clear statements that AI systems can easily extract.
Why is this worth your time?
Because pages with quotes or statistics have been shown to have 30-40% higher visibility in AI answers.

So instead of saying “Email marketing could be an effective channel for your business,” write “Email marketing generates an average ROI of $42 for every dollar spent.”
Use Schema Markup
Schema markup gives you another way to structure information for machines. This code helps systems understand what type of content you’re presenting.

For example, FAQ schema tells algorithms that you’re answering common questions. HowTo schema identifies step-by-step instructions.
You don’t need to be a developer to add schema markup. Many content management systems (like WordPress) have plugins that handle this automatically.
Make It Scannable
Use formatting like bold text to highlight important facts or conclusions and make it easier for readers to skim your content. This helps both human readers and AI systems identify the most important information quickly.
This has always been a big focus of content on Backlinko. We use lots of images to convey our most important points and add clarity through visualizations:
And we use clear headings to make our articles easy to follow:
The goal is to make your content as accessible as possible to both humans and machines. Well-structured content performs better across all types of search and discovery.
And if your content is enjoyable to engage with, it’s probably going to do a better job of converting users into customers as well.
Step 7. Track Your Visibility in LLMs
How often are tools like ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Gemini mentioning your brand?
If you’re not tracking this yet — you should be.
Tracking your visibility in AI-generated responses helps you understand what’s working and where you need to focus your efforts.
But where do you start? And what should you track?
Manual Testing as a Starting Point
Start with manual testing. This is the simplest way to see how you’re performing right now.
Ask the same questions across different AI platforms, like ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, and Google (both AI Mode and AI Overviews). Take screenshots of the responses and note which sources get cited.
Do this regularly, and you’ll start to see patterns in which types of content get mentioned and how your visibility changes over time.
Honestly though: you’re going to struggle to get a lot of meaningful data doing this manually. And it’s not scalable. Plus, so much of what an AI tool outputs to a user depends on the previous context, like:
Past conversations Previous prompts within the same conversation Project or chat settingsThis makes it challenging to get truly accurate data by yourself. This is really more of a “feel” test that, in the absence of dedicated tools, can provide a very rough idea of how generative engines perceive your brand.
Use LLM Tracking Tools
For more comprehensive tracking, dedicated tools can automate this process.
Platforms like Semrush Enterprise AIO help you track your brand’s visibility across AI platforms like ChatGPT, Claude, and Google’s AI Overviews.
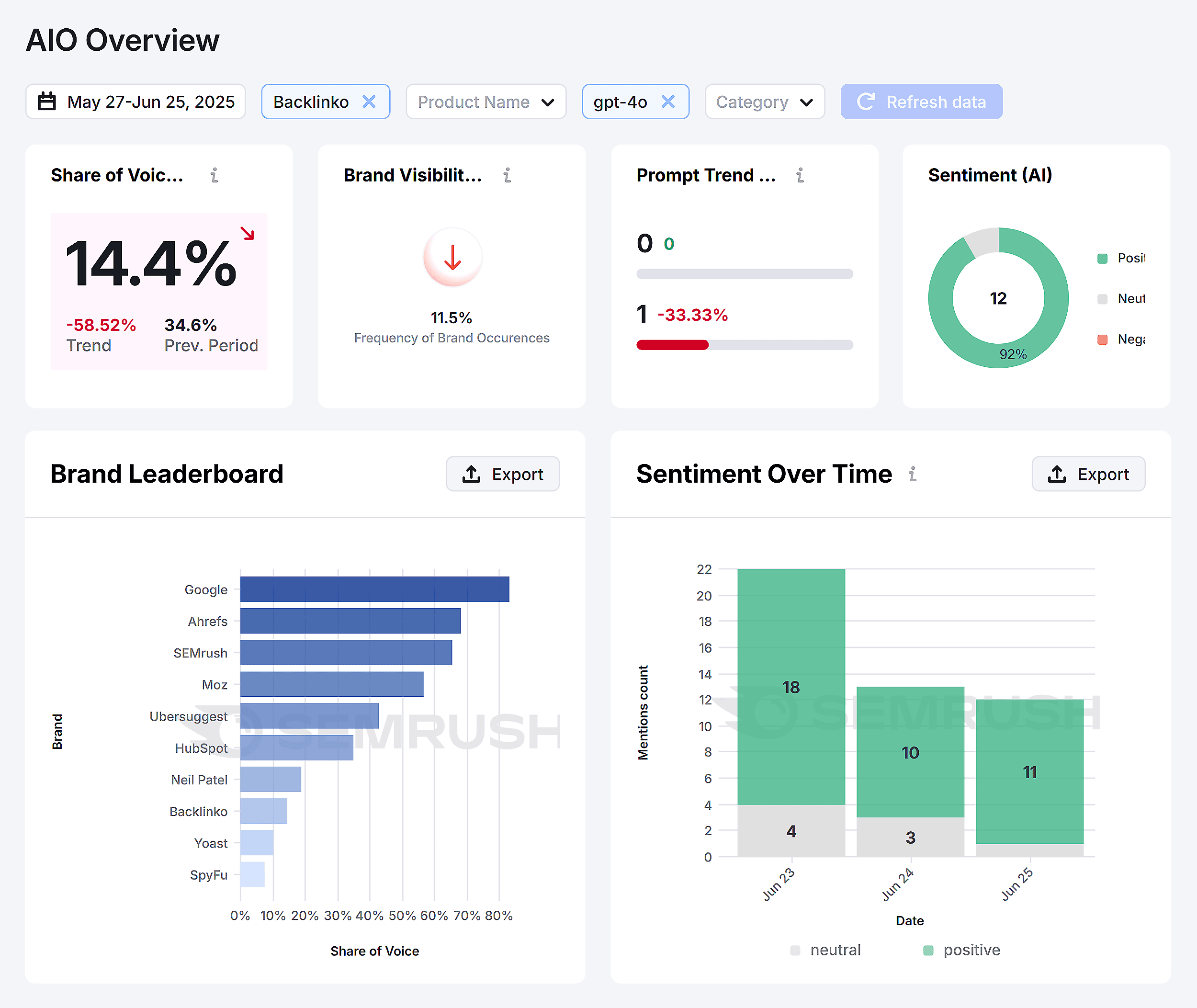
It shows you exactly where you stand against competitors and gives you actionable steps to improve.
Competitive Rankings is my favorite feature. Instead of guessing why competitors might rank better in AI responses, you get actual data showing mention frequency and context.
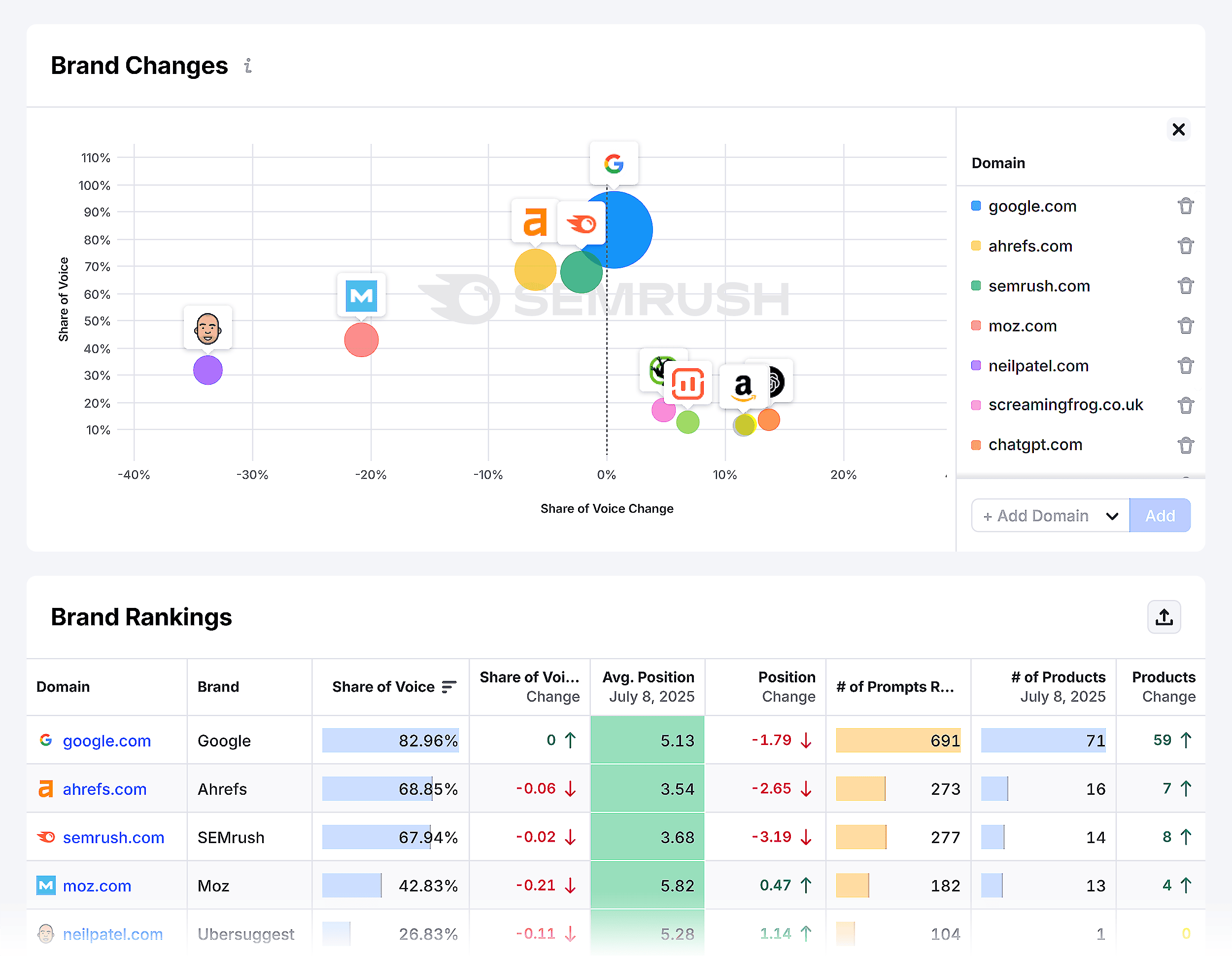
Another option is Ziptie.dev. It’s not the most polished tool yet, but they’re doing some really interesting work — especially around surfacing unlinked mentions across AI outputs.
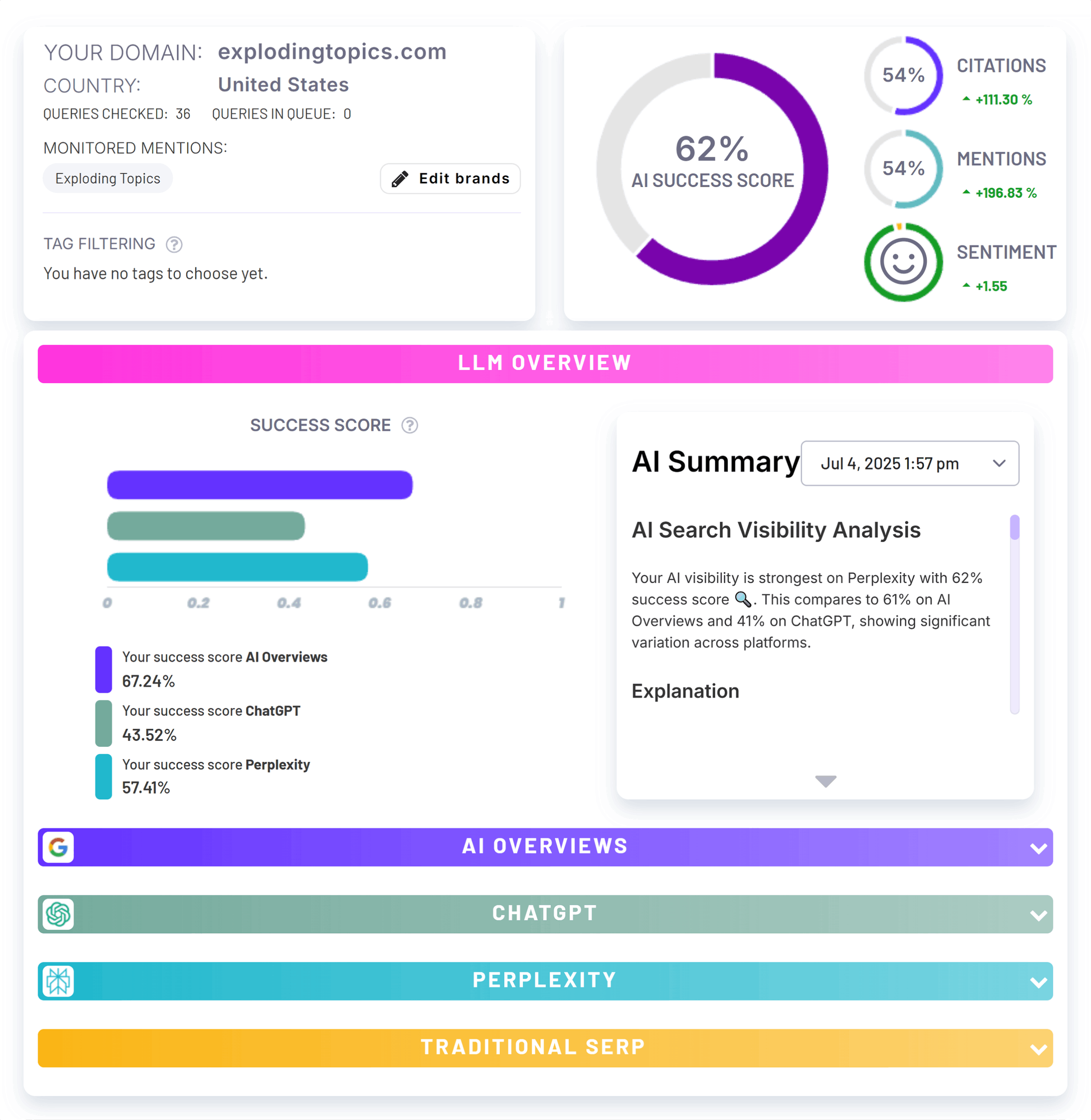
If you already have Semrush, then the Organic Research report within the SEO Toolkit does provide some tracking for Google AI Overviews specifically.
You can track which keywords you (or your competitors) rank for that have an AI Overview on the SERP. If you don’t currently appear in the overview, that’s a keyword worth targeting.
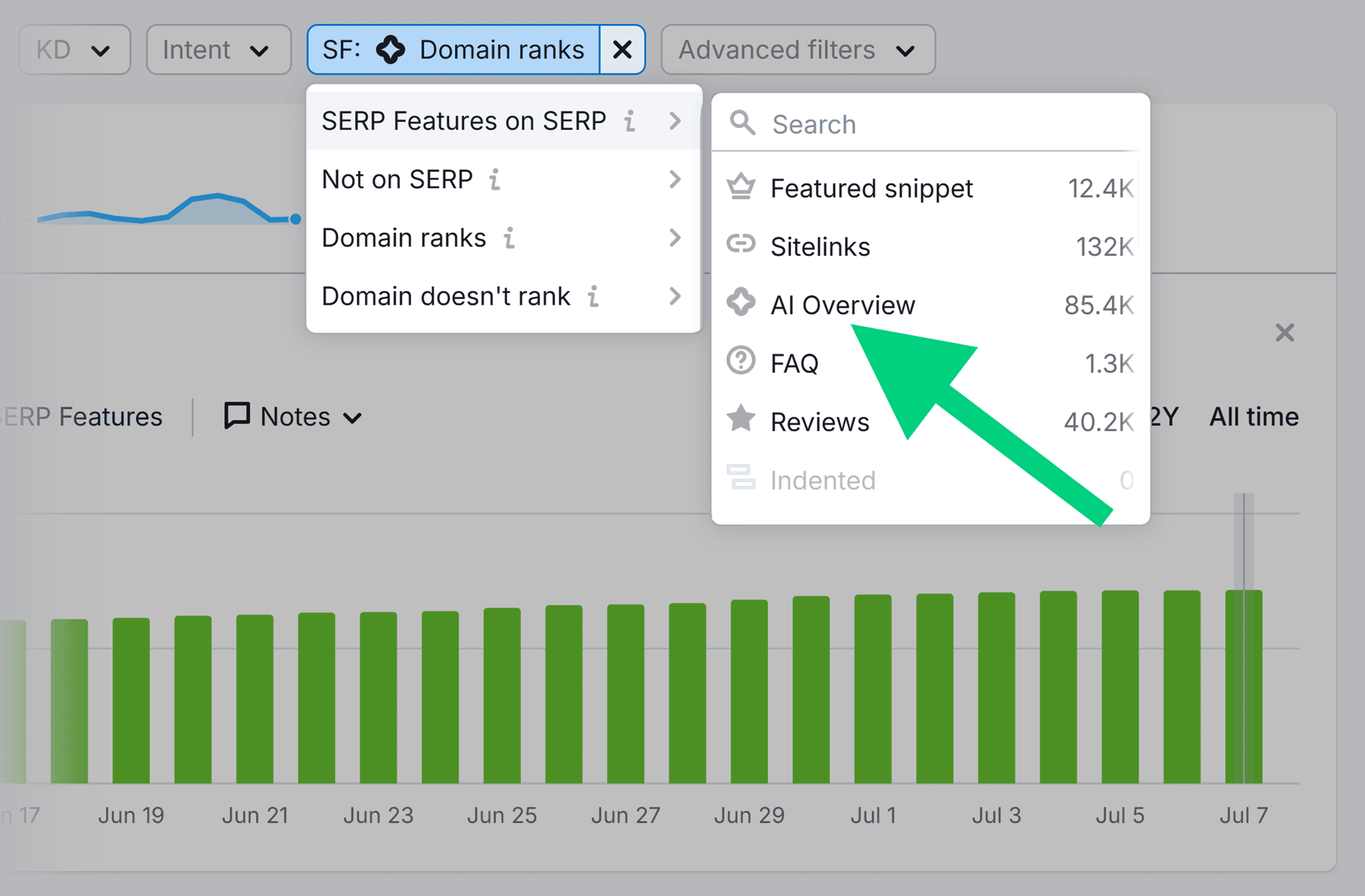
Tracking the keywords you do rank for in these AIOs over time can help you gauge the performance of your GEO strategy.
Why Talk to Your Boss (or Clients) About GEO?
You’ve seen the steps. Now you need a story.
GEO isn’t just a tactical shift — it’s a way to explain what’s changing in search without resorting to hype.
GEO helps you frame those changes clearly:
Traditional SEO still works Your past investments are still paying off But the bar is higher now Visibility means more than rankings Your brand needs to be mentioned, cited, and trusted across every channelGEO gives you the framework to explain what’s changing and how to stay ahead of it.
You Need to Start Now to Stay Visible
This space is evolving fast. New capabilities are rolling out monthly.
The key is to start tracking now so that you can benchmark where you are and spot new opportunities as AI search matures.
Grow your presence by adding a GEO approach on top of your SEO efforts:
Continue optimizing for strong rankings and authority (AI still leans on this) But now, prioritize content and signals that AI engines are more likely to reference directlyWant to learn more about where the world of search is heading? Check out our video with Backlinko’s founder Brian Dean. We dive into how search habits are changing and how you can build a resilient, multi-channel brand.
Backlinko is owned by Semrush. We’re still obsessed with bringing you world-class SEO insights, backed by hands-on experience. Unless otherwise noted, this content was written by either an employee or paid contractor of Semrush Inc.

 Aliver
Aliver