Sam Altman explains why he's helping to take nuclear microreactor company Oklo public via SPAC
Micro nuclear reactor company Oklo announced Tuesday it will go public via merger with a SPAC that was co-founded by Sam Altman, the Chairman of Oklo's board.
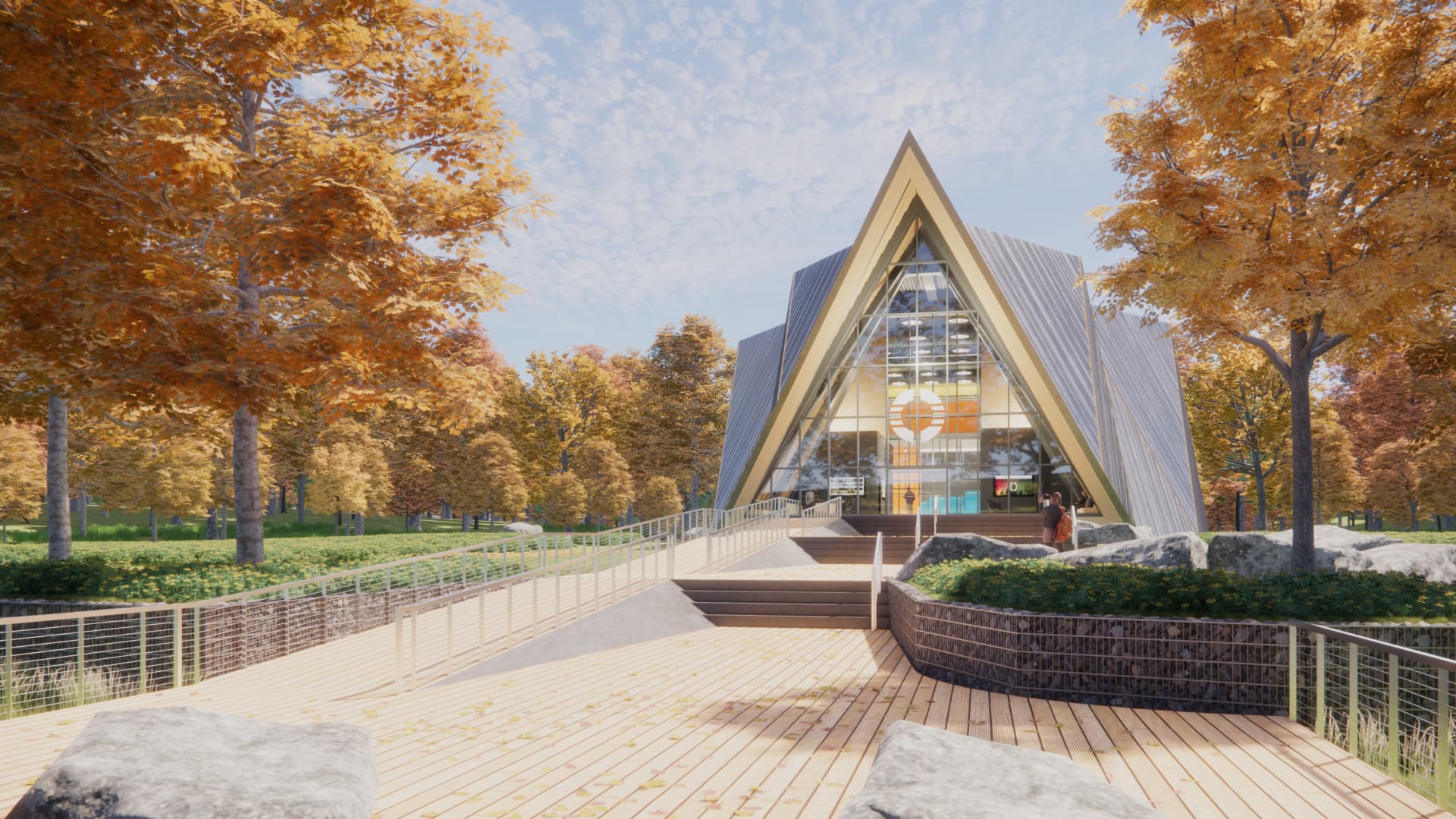

An artist rendition of the Oklo Aurora microreactor.
Image credit: Gensler
Oklo, an advanced nuclear fission microreactor startup, announced on Tuesday that it is going public via merger with AltC Acquistion Corp., a special purpose acquisition company co-founded by OpenAI CEO Sam Altman, who is also the chairman of Oklo's board.
The SPAC will close by early 2024, Oklo co-founder Jake DeWitte told CNBC in a video interview on Friday, and will raise as much as $500 million for the company.
The capital that Oklo raises by going public will go towards ramping up its supply chain and procurement processes and building a pilot scale production facility for its reactor, which it calls Aurora.
Altman best known for his work with artificial intelligence after Microsoft invested billions of dollars in OpenAI and the company's ChatGPT chatbot caught the public's imagination late last year. But Altman's philosophical vision for a better future is dependent on two technologies developing in in parallel: AI and energy.
"My whole view of the world is the future can be radically better and the two things that we really need for that are to lower the cost of energy and lower the cost of intelligence. And if we get those, we'll be quite surprised about how different and how much better the future is," Altman told CNBC in a phone conversation on Friday.
'I don't see a way for us to get there without nuclear'
The two prongs of the future Altman envisions are connected: If the use of artificial intelligence scales up in the way Altman sees, it will demand "a lot, lot" of energy, he told CNBC.
Altman met the co-founders of Oklo back in 2013 and recruited them to join Y Combinator, the Silicon Valley start-up shop where Altman was president of from 2014 to 2019. Caroline Cochran and Jacob DeWitte, the co-founders of Oklo, joined Y Combinator in 2014 and Altman went on to lead Oklo's Series A in 2015, at which point he also became Chairman of the Board.
"I'm all-in on energy. I think there's urgent demand for tons and tons of cheap, safe, clean energy at scale," Altman told CNBC.
Altman has long promoted the idea that access to energy is a significant determining factor to improving quality of life around the globe.
"The alternative to not having enough energy is that crazy de-growth stuff people talk about. We really don't want that," Altman told CNBC, referring to the philosophy that restricting production, consumption and energy use is a way to conserve natural resources. "I think it's insane and pretty immoral when people start calling for that."
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman addresses a speech during a meeting, at the Station F in Paris on May 26, 2023. Altman, the boss of OpenAI, the firm behind the massively popular ChatGPT bot, said on May 26, 2023, in Paris that his firm's technology would not destroy the job market as he sought to calm fears about the march of artificial intelligence (AI).
Joel Saget | Afp | Getty Images
In particular, Altman believes nuclear energy as necessary to meet demand while moving away from burning fossil fuels, which cause global warming. "I don't see a way for us to get there without nuclear. I mean, maybe we could get there just with solar and storage," Altman told CNBC. "But from my vantage point, I feel like this is the most likely and the best way to get there."
Altman is betting on slightly different nuclear projects.
Oklo is working to commercialize nuclear fission, which is the reaction that powers all of existing nuclear power plants, but using much smaller reactors. He's also invested $375 million into Helion, which is one of a burgeoning industry of startups working to prove out and commercialize nuclear fusion, which is the way the sun generates energy and creates no long-lived nuclear waste, but has never been replicated and scaled on earth.
Altman says fusion, if it can be commercialized as Helion envisions, and Oklo, with its smaller, cheaper nuclear reactors, can co-exist. The need for clean, cheap energy "is so vast" that having multiple source of reliable, clean nuclear energy is a good thing, Altman says. Also, because Oklo reactors are going to be much smaller than Helion power plants, they will likely serve different kinds of customers.
Fundamentally, "the world is just so energy limited, and it's such an energy deficit, we need all of it," Altman told CNBC.
Deployment plans and hurdles
Oklo was founded in 2013 with the vision to re-imagine commercial nuclear energy. Conventional nuclear reactors are expensive construction projects that take a long time. The Vogtle plant in Georgia are the latest of this kind of conventional nuclear reactor to be constructed in the U.S., and its budget and schedule overruns have become infamous.
Oklo plans to make much smaller nuclear reactors that can operate with fresh or recycled fuel for as long as a decade before they need to be refueled. Oklo power reactors will produce consistent levels of energy, as opposed to the intermittent sources of power generated by wind and solar, and Oklo is positioning itself to be a source of power for data centers, utilities, defense facilities, remote communities, factories, and industrial sites.
"Oklo has extremely strong customer interest. There's no lack of desire or need for this," Altman told CNBC.
Also, Oklo plans to operate the reactors itself and sell the power to customers, making it easier for customers to use nuclear energy without having to take on the responsibility of operating a nuclear reactor.
Oklo is still in the relatively early stages. In May, Oklo signed an agreement with the Southern Ohio Diversification Initiative to deploy two commercial plants in Southern Ohio, and it's aiming to have them online by 2030.
Oklo also has received approvals from the U.S. Department of Energy to build a plant at the Idaho National Laboratory by 2027. For that reactor, Oklo has already gotten approval from INL to use some of its spent nuclear fuel. The company has also begun the process of applying for necessary approvals to construct a fuel-recycling facility so that Oklo can put what would otherwise be considered "used" fuel into its advanced reactor design.
An artist rendering of the Oklo Aurora reactor.
Artist rendering by Gensler, image courtesy Oklo.
But Oklo has also faced some setbacks: In Jan. 2022, The Nuclear Regulatory Commission, which is the nation's top nuclear regulatory agency, denied its first application to build and operate its advanced nuclear reactor. The NRC cited information gaps in the application, but Oklo is confident that it will be able to resolve the issue.
"We've made a lot of progress with the NRC dating back to 2016," DeWitte told CNBC. "In many ways, a lot of the licensing details around this are focused more on what I call structural and kind of procedural elements."
If Oklo does make it past the regulatory process, it has the potential to make nuclear energy much more affordable than it is now, which is part of what makes Altman interested.
"One of the things that I'm so excited about the Oklo design is that I think the economics can be very, very different," Altman said.
Some of that is the reactor's smaller size, but some of it is how the Oklo reactors have been designed.
"We made intentional design decisions to build on demonstrated technology that also uses parts, major parts and components that are used in other industries," DeWitte told CNBC. "So that means we get to buy into an already established, effectively economy of scale production supply chain."


 AbJimroe
AbJimroe