The Natural Order of Virtual Spaces
This article will review the phenomenon of the natural order of virtual spaces. Specifically, we’ll address repeating patterns of technical building blocks that, when pieced together (like pieces from a puzzle), enable us to work, play and stay healthy...

This article will review the phenomenon of the natural order of virtual spaces. Specifically, we’ll address repeating patterns of technical building blocks that, when pieced together (like pieces from a puzzle), enable us to work, play and stay healthy remotely — and ultimately make the virtual experience as good as in-person.
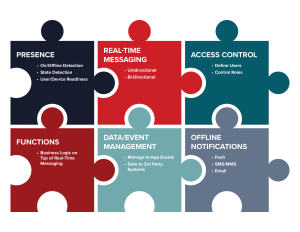
Here the 6 key building blocks are summarized (below).
According to the Merriam-Webster Dictionary, the natural order is “the orderly system comprising the physical universe and functioning according to natural as distinguished from human or supernatural laws.” But in the world of software development, there’s a surprising natural order to how real-time interactions in virtual spaces are built, and we’re not just referring to AR/VR and the metaverse.
The natural order of virtual spaces – similar to what you’d find in the physical universe — repeats itself across business worlds, from the consumer (e.g., gaming, rideshare, food delivery, telemedicine, marketplaces, etc.) to enterprise (e.g., contact center, business collaboration, asset & fleet tracking, network ops, etc.).
Going back to 1962 and the advent of virtual space technology, distinct patterns of technical ‘building blocks’ have evolved that today form the foundation of how we interact digitally (human-to-human, human-to-AI, and device-to-device). All stemmed from the needs of software developers as they attempted to build real-time interactive experiences while looking to simplify complexity, accelerate time to market, and satisfy complex business requirements at scale.
Proof of Natural Order by Industry
For proof, let’s examine some of the ways that our key building blocks are used across industries. We’ll start with 5 different examples.
Gaming Shared Mobility Live Streaming Asset & Fleet Tracking Health/TelemedicineGaming
Beginning with the first virtual space for 2D gaming (Pong) and more recently with games like PUBG Mobile, Magic: The Gathering, Coin Master, War Dragons, and Pokémon GO, game developers have been forced to invent new ways to deliver scalable real-time gameplay paired with features that motivate user engagement.
In approach, our 6 key building blocks have become essential. Presence is used for detecting who’s online, game lobbies, and active player counts. Real-Time Messaging for player movements, game state, social interactions, gamification, and in-game auctions.
Access Control for permissions and security. Functions for player matching, game logic, user/content moderation, and triggering bot actions. Data/Event Management for managing backend data events, and Offline Notifications for activating dormant users.
Shared Mobility
With a nod to e-hailing apps like Uber, Lyft, DiDi, Grab, and Ola, this category of apps has transformed our world in just over a decade. To get there, software teams have faced immense challenges, and our 6 key building blocks once again proved their merits.
Presence is used for driver availability and detecting who’s online. Real-Time Messaging for dispatch, time-critical alerts, location tracking, chat, and orchestrating IP-based support calls. Access Control for permissions and security. Data/Event Management for managing backend data events, and Offline Notifications for activating dormant users.
Live Streaming
Thanks to the explosive growth of OTT (cue leading companies like Disney+ Hotstar, DAZN, Amagi, 17LIVE, Veeps, Twitch, etc.) plus affordable access to both high-speed cellular data and smartphones in emerging markets like India, Indonesia, and Nigeria — the global live streaming industry is projected to reach $543 billion by 2030 (per Market Research Future).
Once again, using our 6 key building blocks has proven to be essential. Presence is used for lobby counts, detecting who’s online, and enforcing subscription-based business models. Real-Time Messaging for emotes, live scores/stats/updates/odds, social interactions, gamification, and commerce features (inventory, pricing, bids, order/delivery tracking).
Access Control for permissions and security. Data/Event Management for managing backend data events, and Offline Notifications for activating dormant users.
Asset & Fleet Tracking
The ability to know the exact whereabouts and performance state of vehicles, trailers, equipment, and other industrial assets is no small task. The same goes with actioning time-critical preventative maintenance tasks, particularly at scale and across fragmented devices.
In fact, asset and fleet tracking companies (for example: UPS, FedEx, Waste Management, AT&T, etc.) have also faced immense challenges making it all work. And yet again, our 6 key building blocks have proven to be essential.
Presence is used for asset/fleet availability, state/readiness, and detecting who’s online. Real-Time Messaging for dispatch, time-critical alerts, location tracking, chat, and orchestrating service calls. Access Control for permissions and security. Data/Event Management for managing backend data events, and Offline Notifications for activating dormant users/devices.
Health/Telemedicine
Accelerated by the pandemic, plus an ever-growing population of seniors and a shortage of caregivers, telemedicine has become the new norm. Once again (to no surprise!), our 6 key building blocks have proven to be essential. Presence is used for patient lobbies (to optimize caregiver time), detecting who’s online, and location detection.
Real-Time Messaging is used for compliant chat, time-critical alerts/reminders, streaming of sensor data, orchestrating voice/audio calls, virtual whiteboards, and highlighting in shared images/docs. Access Control for permissions and security. Data/Event Management for managing backend data events, and Offline Notifications for activating dormant users.
Conclusion
There is indeed a natural order of virtual spaces that forms the foundation of how we interact digitally. This phenomenon has evolved over the last 60 years. It is rooted in repeating patterns of 6 key technical building blocks that, when combined, help software developers to bring transformative virtual space innovation to market.
From this humble writer’s point of view, the evolution of virtual space technology will continue for many years to come. Still, the key building blocks (as used by software developers) will remain the same, albeit they will become easier to use through improved developer education, tools, frameworks, and standards.
Featured Image Credit: Photo by Ann H; Pexels; Thank you!
![]()
Jonas Gray
Jonas is VP of Business & Corporate Development at PubNub, a leading developer platform for delivering real-time capabilities in Mobile, Web, and IoT apps. Previously, he served as SVP, Global Business Development and Brand Partnerships at UberMedia (part of Idealab).

 Koichiko
Koichiko