What is Deep Learning? Here's Everything Marketers Need to Know
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been in the spotlight lately as many companies and brands like Zara and H&M incorporate AI into their business models. As a marketer, you may wonder if this is cause for concern. Is AI going...

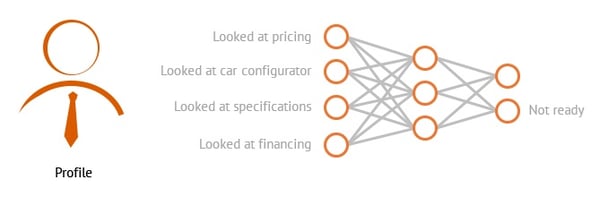
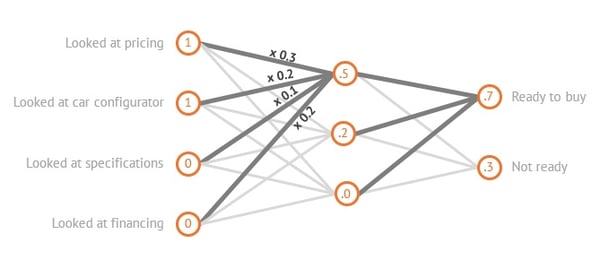
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been in the spotlight lately as many companies and brands like Zara and H&M incorporate AI into their business models. As a marketer, you may wonder if this is cause for concern. Is AI going to take over our jobs? In reality, AI can actually make marketing easier and more efficient for marketers via deep learning technology. But what is deep learning? How does it work? And how can it be applied to marketing and sales in your company? Here is everything marketers need to know about deep learning and the helpful role it can play in the marketing industry. What is deep learning in artificial intelligence? Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning Example of Deep Learning in Marketing and Advertising Training of the Neural Network How Marketers Can Use Deep Learning Embracing Deep Learning in Marketing Deep learning is a subset of machine learning and is a discipline within AI that uses algorithms mimicking the human brain. Deep learning algorithms use neural networks to learn a specific task. Neural networks consist of interconnected neurons that process data in both the human brain and computers. Similar to how humans learn from experience, the deep learning algorithm performs a task repeatedly, making adjustments each time to improve the outcome. "Deep learning" refers to the neural networks' vast (deep) layers that enable learning. Deep learning is a type of machine learning. Machine learning means computers learn from data using algorithms to think and act without being programmed — in other words, without human intervention. As mentioned earlier, deep learning is about computers learning to think using structures modeled after the human brain. Machine learning also involves less computing power, while deep learning requires less ongoing human intervention. Let’s say we are an online car dealership, and we want to use real-time bidding (RTB) to buy ad space for our product on other websites for retargeting purposes. RTB is an automated process that takes place in a short time frame of under 100 milliseconds. When a user visits a website, an advertiser is alerted, and a series of actions determine whether or not that advertiser bids for an ad display. In RTB, we use software to decide if we want to bid for a particular ad — the software will decide by predicting how likely the website visitor is to buy one of our products. We call that "buying propensity." In this instance, we'll use deep learning to make this prediction. That means our RTB software will use a neural network to predict the buying propensity. The neural network inside our RTB software consists of neurons and the connections between them. The neural network in the above image has only a handful of neurons. In this scenario, we want to find out if a certain website visitor is likely to buy a car and if we should pay for an ad to target the visitor. The result will depend on the interests and actions of the website visitor. To predict the buying propensity, we first choose several “features” that are key to defining this person’s digital behavior. Those features will consist of which of the following four web pages were visited: Those features will influence the output of our neural network and our conclusion. That output can have one of two values: For each input, we use “0” or “1”. “1” means the user has visited the webpage. The neurons in the middle will add the values of their connected neurons using weights — meaning they define the importance of each visited webpage. This process continues from left to right until we reach the “output” neurons —“ready to buy” or “not ready,” as per our earlier list. The higher the value of the output, the higher the probability that this output is the correct one —or the more accurately the network predicts the user’s behavior. In this example, a website visitor looked at the Pricing and Car Configurator pages, but skipped Specifications and Financing. Using the numerical system above, we get a “score” of 0.7, which means that there is a 70% chance this user is “ready to buy” our product. So, if we look at our original formula, that score indicates the conclusion that we should buy the RTB ad placement. Training a neural network means feeding the network the data it needs to generate outcomes. The challenge is to develop the correct “weight” factors for all the connections inside the neural network, which is why it needs to undergo training. In our car dealership example, we would feed the neural network data from multiple website visitors. The data would include visitor features such as which web pages users have visited. The data would also include indicators of their eventual purchase decisions from us, which are labeled as "yes" or "no." The neural network processes all these data, adjusting the weights of each neuron until the neural network makes appropriate calculations for each person within the training data. Once that step is complete, the weights are fixed, and the neural network can more accurately predict new website visitors' outcomes. "Machine learning can be used for efficiency or optimization gains," says Jim Lecinski, co-author of The AI Marketing Canvas: A Five Stage Roadmap to Implementing Artificial Intelligence in Marketing, in an interview with Kellogg Insight. "So, for example, any rote reporting could be automated and done more efficiently. Then those full-time employees could be repurposed and reapplied to other strategic growth projects," he said. But more importantly, Lecinski says AI and deep learning has the ability to drive growth. "More and more, CEOs, boards, and marketing departments are viewing marketing as being the chief growth engine charged with making informed-by-data predictions or projections to find the optimal combination of the right product at the right price, promoted in the right way via the right channels to the right people," he said. Lecinski explained, "Big data plus machine learning can, in many cases, make those predictions and drive growth better than humans without data or humans merely assisted by data." Here are a few ways marketers can use deep learning to foster growth. Deep learning models are able to find patterns in data that make them excellent for advanced segmentation. This allows marketers to easily and quickly identify the target audience for a campaign while machines use past behaviors to predict potential leads. Machines can also use neural networks and data to identify which customers are on the verge of leaving — allowing marketers to act quickly. Ultimately, AI takes the guesswork out of segmentation, allowing marketers to focus their efforts elsewhere. Our HubSpot AI, for example, makes segmentation easier via our automatic email data capture feature. The feature allows users to automatically capture important contact information like names, job titles, phone numbers, and addresses from leads and prospects. The feature makes segmentation, routing, and reporting quick and easy for marketers. A recent study by McKinsey shows that 71% of consumers expect companies to deliver personalized interactions, and 76% get frustrated when it doesn't happen. While personalization is crucial to the customer experience, it's difficult to execute when there is so much information to analyze. However, deep learning can be used to develop personalization engines that can help marketers streamline the process of delivering hyper-personalized content. Examples of hyper-personalized materials include websites that display content that varies depending on who's browsing or push notifications for customers who leave without making a purchase. Hyper-personalization can also extend to communication features such as live chats, and deep learning can make gathering information from these live chats a breeze. Our live chat name recognition AI, for instance, can gather valuable contact information (like names) and update it in the HubSpot CRM without having to integrate anything. Deep learning also helps marketers predict what customers will do next by tracking how they move through your website and how often they make a purchase. In doing so, AI can tell companies which products and services are demand and should be the focus of upcoming campaigns. Though deep learning and AI may sound intimidating, it's actually another tool marketers can leverage to streamline processes and promote growth for their company. Marketers can integrate deep learning and AI into many aspects of digital marketing and sales automation. So, don't fear the machine — embrace it!
What is deep learning in artificial intelligence?
Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning
Example of Deep Learning in Marketing and Advertising
Training of the Neural Network
How Marketers Can Use Deep Learning
Segmentation
Hyper-personalization
Predicting consumer behavior
Embracing Deep Learning in Marketing

 Troov
Troov 

































