FDA says Eli Lilly's weight loss drug Zepbound is no longer in shortage
The decision that will eventually bar compounding pharmacies from making unbranded versions of the injection.

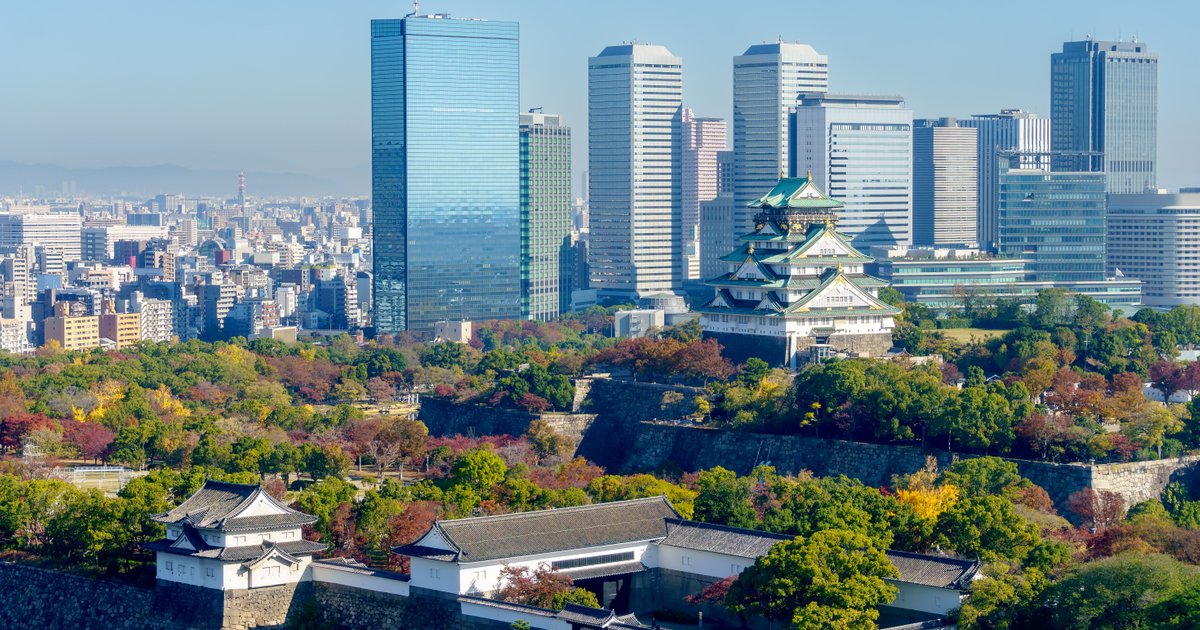
An injection pen of Zepbound, Eli Lilly’s weight loss drug, is displayed in New York City on Dec. 11, 2023.
Brendan McDermid | Reuters
The Food and Drug Administration on Thursday said the active ingredient in Eli Lilly's weight loss drug Zepbound is no longer in shortage, a decision that will eventually bar compounding pharmacies from making unbranded versions of the injection.
The agency's decision, based on a comprehensive analysis, marks the end of a period where certain pharmacies could compound, distribute or dispense the active ingredient in the drug, tirzepatide, without facing repercussions for violations related to the treatment's shortage status.
The FDA said it will provide a 60- to 90-day transition period where it will not take action against pharmacies for making compounded tirzepatide, which will give patients time to switch to the branded version.
It's the latest in a high-stakes dispute between compounding pharmacies and the FDA over a shortage of tirzepatide, the active ingredient in both Zepbound and Eli Lilly's diabetes treatment Mounjaro. Eli Lilly has invested billions to expand its manufacturing capacity for tirzepatide as it struggles to keep pace with unprecedented demand.
A trade organization representing compounding pharmacies — the Outsourcing Facilities Association — sued the FDA on Oct. 8 over the agency's decision to remove tirzepatide from its official drug shortages list just days earlier. The group alleges the FDA acted without proper notice, ignoring evidence that a shortage of tirzepatide still exists. It also argued that the FDA's action was a coup for Eli Lilly that came at the expense of patients.
Following the suit, the FDA said it would reevaluate removing tirzepatide from the shortages list. That allowed compounding pharmacies to continue making copycats while the agency reviewed its decision.
Compounded medications are custom-made alternatives to branded drugs designed to meet a specific patient's needs. When a brand-name medication is in shortage, compounding pharmacies can prepare copies of the drug if they meet certain requirements under federal law.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration does not review the safety and efficacy of compounded products, and the agency has urged consumers to take the approved, branded GLP-1 medications when they are available.
However, the FDA does inspect some outsourcing facilities that compound drugs, according to its website.
Patients have turned to compounded versions of tirzepatide amid intermittent U.S. shortages of the branded drugs, which carry hefty price tags of $1,000 per month before insurance and other rebates. Many health plans don't cover tirzepatide for weight loss, making compounded versions a more affordable alternative.
The active ingredient in Wegovy and Ozempic, semaglutide, has been in intermittent shortages over the past two years. But the FDA earlier this month said all doses of those drugs are now available.
The agency has yet to announce whether it is removing semaglutide from its shortage list — a decision that would likely affect even more compounding pharmacies since it is more widely used than tirzepatide.
Wegovy, Ozempic, Zepbound and Mounjaro are under patent protection in the U.S. and abroad, and Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly do not supply the active ingredients in their drugs to outside groups. The companies say that raises questions about what some manufacturers are selling and marketing to consumers.
Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly have both stepped in to address illicit versions of their treatments, suing weight loss clinics, medical spas and compounding pharmacies across the U.S. over the past year. The FDA last month also said it had received reports of patients overdosing on compounded semaglutide due to dosing errors such as patients self-administering incorrect amounts of a treatment.

 Konoly
Konoly